
Introduction
Nodejs is JavaScript cross-platform runtime environment. When it comes to building a simple HTTP server for a project, building with nodejs, is simpler and lighter. This is because you don’t get to introduce external modules, built-in node modules.
This is a typical example of a node application:
const http = require('http')
const port = process.env.PORT
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.statusCode = 200
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html')
res.end('<h1>Hello, World!</h1>')
})
server.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server running at port ${port}`)
})In the code snippet above, we included Nodejs http module, which was used to create the HTTP server.
Yet, building a project requires more than setting up an HTTP server. You’ll have to handle routing, errors, parsing data, security, file uploads, and so much more. That’s where frameworks come in. Frameworks handle all these cases and more.
The most popular framework for building nodejs web applications is Express. Express offers really great syntax for routing HTTP requests, MVC like architecture, and it allows you easily setup middleware to respond to HTTP requests.
Let’s take a look at what our previous application might look like with Express.js:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello World')
});
app.get('/test', (req, res) => {
res.send('this is a different page')
})
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server running at http://localhost:3000/');
});In this code snippet, things get simpler. We got to specifically define the http method and path we wanted in our app. If you head to http://localhost:3000/test you should get the message this is a different page. Yet another elegant feature, is that we do not have to set the content-type because Expressjs, res.send automatically assigns the Content-Length HTTP response header field.
However, Express isn’t exactly the perfect web framework. It still gives us the same method of using the http module. The fact that we are still required to pass req and res even when almost all the time, we don’t need everything in res.
The req object contains information about the request we are receiving while the res object represents the HTTP response that the express app sends when it gets an HTTP request. But, we want to perform less asynchronous work in our code, and only want the result from the controller functions as a reply.
Handling this with async/await or promises is an option, but Express wasn’t built to work that way. This means you’d have to introduce middleware to handle that behavior.
Nevertheless, they are frameworks that have request and reply in their handler functions. One of them is Fastify.
Fastify is a powerful web framework inspired by Express, it handles issues with Express and even more.
Introducing Fastify
Fastify is not just another framework, it is one of the fastest web frameworks out there. What makes Fastify a great choice for me is the fact that it is:
- Open-sourced
- Developer friendly
- It’s highly performant
- It comes with a logger too
Let’s explore fastify by building a simple REST CRUD API.
Pre-requisites
- Node.js installed (minimum v12 or above)
- JavaScript
- Visual Studio Code (or your preferred code editor)
- MongoDB (include MongoDB Compass too)
- Postman
What we would be building
In this article, we would be building a REST API where you can create, view, edit, and delete books from a book store. We will be using our local MongoDB to store and retrieve our books.
Dependencies
Let’s go through all the dependencies we will be using:
fastify: Well yes, we need fastify. Fastify is a web framework highly focused on providing the best developer experience with the least overhead and a robust plugin architecture.boom: Boom will help us in handling HTTP errors properly.mongoose: It provides a straight-forward, schema-based solution to model our application data.nodemon: we will use nodemon to watch live changes in our application.
Setting up the Fastify Server
Firstly, we have to bootstrap a node project.
Run this command on your terminal:
//bash mkdir fastify-store && cd fastify-store && touch index.js && npm init -y
Here, we have created a index.js file and also initialized the project. A package.json file will be created too.
Now, we can add our dependencies to the project.
Run this command on your terminal to add the dependencies:
npm install boom mongoose fastify nodemon
When that is done, let’s get our server up and running. Add this code snippet to your index.js
//index.js
const fastify = require('fastify')({
logger: true
})
const PORT = 3000
fastify.get('/', async() => {
return {
Test: 'This is working fine'
}
})
const serve = async () => {
try {
await fastify.listen(PORT)
fastify.log.info(`Server listening to PORT ${fastify.server.address().port}`)
} catch (err) {
fastify.log.error(err)
process.exit(1)
}
}
serve()Let’s go through the working parts of the snippet above
- Firstly, we enabled fastify logger. By default, it is disabled.
- Next, we assigned a port number for our application. However, when deploying to production, it’s recommended you use
process.env.PORT. - Next, we created our first route! You notice that our controller function is synchronous. We will see more of that when we write our controller.
- Finally, we start the server on port 3000.
Save and then run this command on your terminal to start the server.
npx nodemon index
I recommend you use this method when working with nodemon. Most times, you might encounter issues running the nodemon command (most especially Windows users). What npx does is, it goes through your node_modules and checks for the package (in this case; nodemon) and executes it. Thus the name Node Package Execute.
When you run the command, your terminal should look like this:
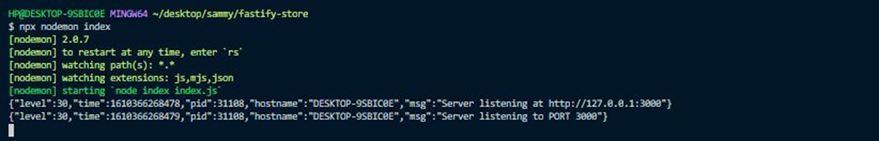
Have you noticed our logger in action? Awesome.
Navigate to http://127.0.0.1:3000 on your browser and you will get something like this.
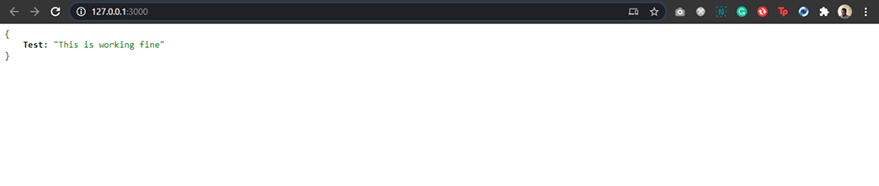
P.S: I use JSONView on chrome for formatting JSON data. You can download it from the chrome web store.
Setting up MongoDB
Let’s now set up a Mongo database. We will be using the CLI.
Launch the CLI by navigating to MongoDB > Server > 4.4 > bin > mongo.exe
You should get something like this:
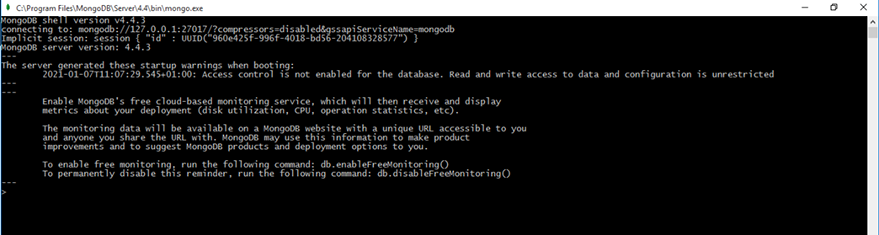
To create a new database, run this command:
use fastify-store
To show the list of databases created, run this command:
show dbs

Our new database isn’t displayed in the list because we don’t have any data in it at the moment.
To do this, run this command:
db.user.insert({title:"The book for new humans", genre: "Self Help"})

Check the database list again.
show dbs

Awesome!
Now when our mongo URI will be: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/fastify-store
Let’s connect our app to the database already.
Add this code snippet to index.js
const mongoose = require('mongoose')
//setup DB
const mongoUrl ="mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/fastify-store"
try {
mongoose.connect(mongoUrl, {
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true
})
console.log("Database connected sucessfully")
} catch (error) {
console.log(error)
}Here, we make a connection to MongoDB using mongoose.connect. Compared to the MongoDB Node driver , mongoose abstracts the complexities in this step, waiting for the connection to be established before sending data.
Note: To avoid warnings on your dev server, include useNewUrlParser and useUnifiedTopology alongside with your mongoUrl.
Now when you save, your server should restart and you get something like this:
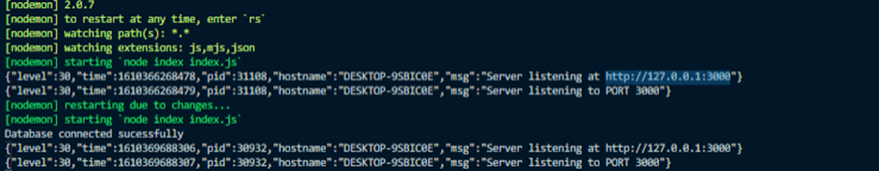
The Database connected successfully the message means we are good to move on.
Creating the Book Model
A Model is a class that helps us interact with MongoDB. An instance of a model is a document.
Run this command to create a models directory and Book.js in it.
mkdir models && touch Book.js
Now, let’s create a mongoose model.
//models/Book.js
const mongoose = require('mongoose')
const bookSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
title:{
type: String,
required: true
},
description:{
type: String,
required: true
},
genre: {
type: String,
required: true
},
author: {
type: String,
},
price: {
type: Number,
required: true
},
completed:{
type: Boolean,
required: true
}
});
module.exports = mongoose.model('BOOK', bookSchema)Mongoose converts our bookSchema into a document in the Mongo database. We then defined the structure of the document and assigned types too.
Creating Routes and Controllers
Let’s now configure the endpoints of our app.
These are the routes
method:GET, url: /api/books– returns a list of all the books in the storemethod: GET, url: /api/book/:id– returns a single book by idmethod:POST, url:/api/book– add and saves a new book to the storemethod:PUT, url: /api/book/:id– updates a single book by idmethod:DELETE, url: /api/book/:id– deletes a single book by id
Run this command from your root directory to create a routes folder with the bookRoutes.js file in it.
mkdir routes && cd routes && touch bookRoutes.js
Add this code snippet:
//routes/bookRoutes.js
const bookController = require('../controller/bookController');
const routes = [
{
method: 'GET',
url: '/api/books',
handler: bookController.getAllBooks
},
{
method: 'GET',
url: '/api/book/:id',
handler: bookController.getSingleBook
},
{
method: 'POST',
url: '/api/book',
handler: bookController.addNewBook
},
{
method: 'PUT',
url: '/api/book/:id',
handler: bookController.updateBook
},
{
method: 'DELETE',
url: '/api/book/:id',
handler: bookController.deleteBook
}
]
module.exports = routesLine 1 of our code, tries to import a controller. Controllers are simply route methods or handler functions. We will be creating this file shortly. We assign the routes method from our controller to the handler property.
Now let’s create this controller.
Run this command from your root directory to create a controllers folder and bookController.js file.
mkdir controllers && cd controllers && touch bookController.js
Now add the following lines of code:
//controllers/bookController.js
const boom = require('boom')
const Book = require('../models/Book');
// get all books
exports.getAllBooks = async (req, reply) => {
try {
let books = await Book.find()
return reply.code(200)
.send(
{
Message: "Success",
data: books
}
)
} catch (err) {
throw boom.boomify(err)
}
}
//get a single book by id
exports.getSingleBook = async (req, reply) => {
try {
const id = req.params.id
let book = await Book.findById(id)
return reply.code(200)
.send({ Message: "Success", data: book}, )
} catch (err) {
throw boom.boomify(err)
}
}
//add a new book
exports.addNewBook = async (req, reply) => {
try {
let book = new Book(req.body);
let newBook = await book.save()
return reply.code(200)
.send({ Message: "New Book added successfully", data: newBook})
}
catch (err) {
throw boom.boomify(err)
}
}
//edit a book
exports.updateBook = async (req, reply) => {
try {
const id = req.params.id
let updatedBook = await Book.findByIdAndUpdate(id, req.body, {
new: true
})
return reply.code(200)
.send({ Message: "Book updated successfully", data: updatedBook}),
} catch (err) {
throw boom.boomify(err)
}
}
//delete a book
exports.deleteBook = async (req, reply) => {
try {
const id = req.params.id
let deletedBook = await Book.findByIdAndDelete(id);
return reply.code(200)
.send({ Message: `${deletedBook.title} has been deleted successfully`, data: id})
} catch (err) {
throw boom.boomify(err)
}
}Let’s go through the working parts of this code snippet:
Firstly, we introduced boom for error handling. By default, boom.boomify sets the status code to 500 but you can always override it like this boom.boomify(err, { statusCode: 400 });.
Next, we imported our mongoose model. In Mongoose, our model is the subclasses of the mongoose.model('BOOK', bookSchema) class. We then used the model to make queries to our DB.
Next, the fastify server provides us with a handler function async (req, reply) that the server will bound to when it is called. In our case, we have broken the binding of this because we used arrow functions.
Finally, we used the fastify Reply object. reply.code() sets the status code (if it wasn’t set, by default, the status code will be 200). reply.send() sends payload just sends a payload to the user.
You’re doing great so far!!
Now, we have to do one last thing. We have to include the routes in our server.
Modify you’re index.js with the following lines of code:
//index.js
...
const routes = require("./routes/bookRoutes")
...
routes.forEach((route, index) => {
fastify.route(route)
})
...If you don’t have any errors, congratulations!! You just successfully built a CRUD API using Fastify.
Testing with Postman
Postman is a very powerful API client tool for sending REST requests. Postman does more than sending requests to REST API endpoints but for the purpose of this article, we will only be dealing with that aspect.
Let’s create add a book to the store. This is a POST request
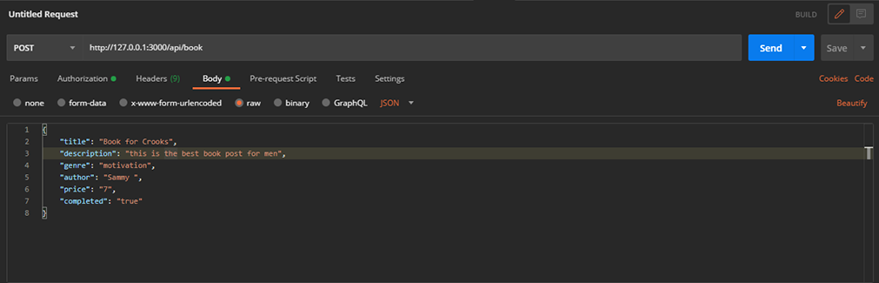
Creating a BookThe results:
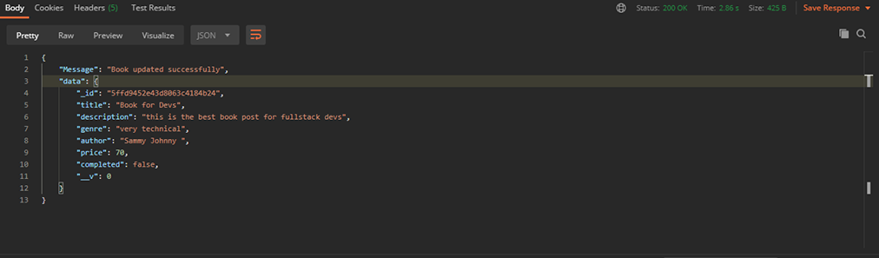
You should add up to 5 books.
Let’s retrieve all books from the store. This is a GET request.

{
"Message": "Success",
"data": [
{
"_id": "5ffd9452e43d8063c4184b24",
"title": "Book for Crooks",
"description": "this is the best book post for men",
"genre": "motivation",
"author": "Sammy ",
"price": 7,
"completed": true,
"__v": 0
},
{
"_id": "5ffd9609e43d8063c4184b25",
"title": "Book for Devs",
"description": "this is the best book post for devs",
"genre": "technical",
"author": "Sammy ",
"price": 7,
"completed": true,
"__v": 0
}
]
}Let’s retrieve a single book by :id. This is a GET request

The result:
{
"Message": "Success",
"data": {
"_id": "5ffd9452e43d8063c4184b24",
"title": "Book for Crooks",
"description": "this is the best book post for men",
"genre": "motivation",
"author": "Sammy ",
"price": 7,
"completed": true,
"__v": 0
}
}Let’s edit a book by its :id. This is a PUT request.
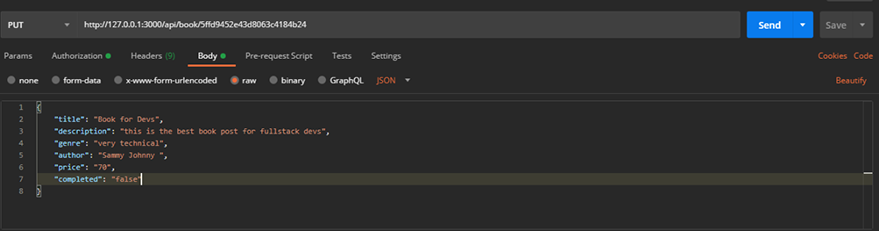
The result:

Finally, let’s delete the book. This is a DELETE request.

The result:
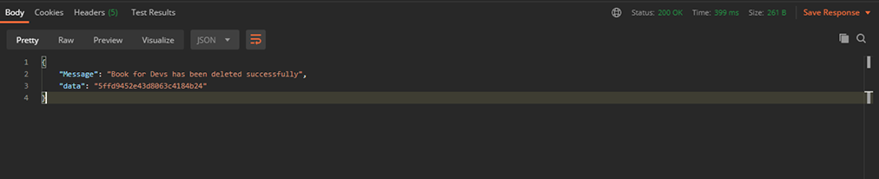
Postman request DELETE resultThe source code for this project is on Github.
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed why fastify could be a better option in your future projects. Fastify enables us to handle server resources more efficiently than express. We also learned how to build a REST API with the framework and in the process, I shared some insights on tools such as mongoose and boom.
If you have any questions or suggestions, please do well to share them in the comments section.

