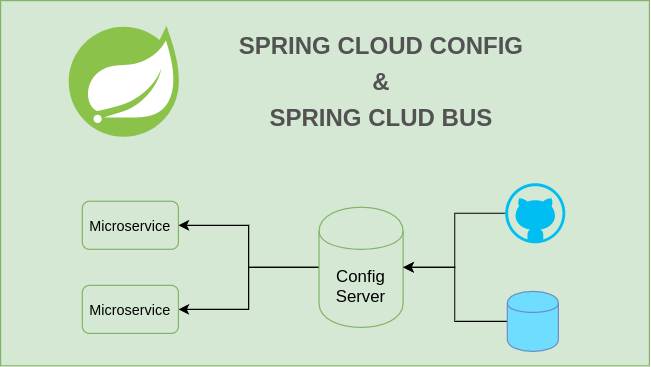
In the previous article, we have looked over the Spring Cloud Config basics and created a sample config client and config server with a git repository as a configuration data store. Thus, we created a central configuration server to manage all the configuration in one place.
In this article, we will focus on how to refresh configurations fetched from the config server.
1. Spring Boot Application Properties
A Spring application holds the properties, which are read from an external property source such as a properties file or a config server, in PropertySource abstractions, and serves these properties to the beans of the Spring Application Context via the Environment interface.
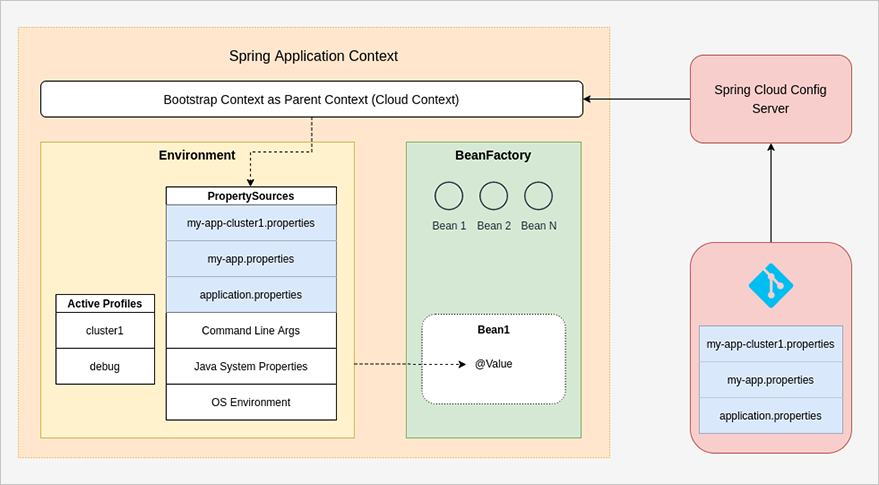
As you see in the diagram above when the Spring Boot Config Client application starts up, it fetches the remote property sources from the config server in precedence we looked over in the previous article and put them higher on the property source list. Higher in this list means higher in precedence. Actually there are more property sources than in the diagram but to be shown here, the ones coming from the bootstrap context generally have priority over the ones from local property files.
Just after this refreshment of property sources, the next step is wiring these properties to the Spring beans and this happens when the beans are instantiated. This can happen via @Value or @ConfigurationProperties annotations.
2. Refreshing Properties
When it comes to refreshing the properties in the application context, there are two steps again; reloading the property sources in the Environment and refreshing the attributes of Spring beans.
In the case of using Spring Cloud Config Server; Spring Cloud offers the following methods to refresh the properties in config clients.
- By calling the /actuator/refresh endpoint exposed on the config client via the Spring Actuator.
- By calling the /actuator/bus-refresh endpoint exposed on the config client integrated with Spring Cloud Bus.
- By calling the /monitor endpoint exposed on the config server integrated with Spring Cloud Bus.
3. Calling The /actuator/refresh Endpoint
The first method of property refreshment is calling the /actuator/refresh endpoint. This endpoint is exposed in config clients so a call to this endpoint just refreshes the client to which the request is made.
Let’s look over the following diagram to understand this type of refresh process:
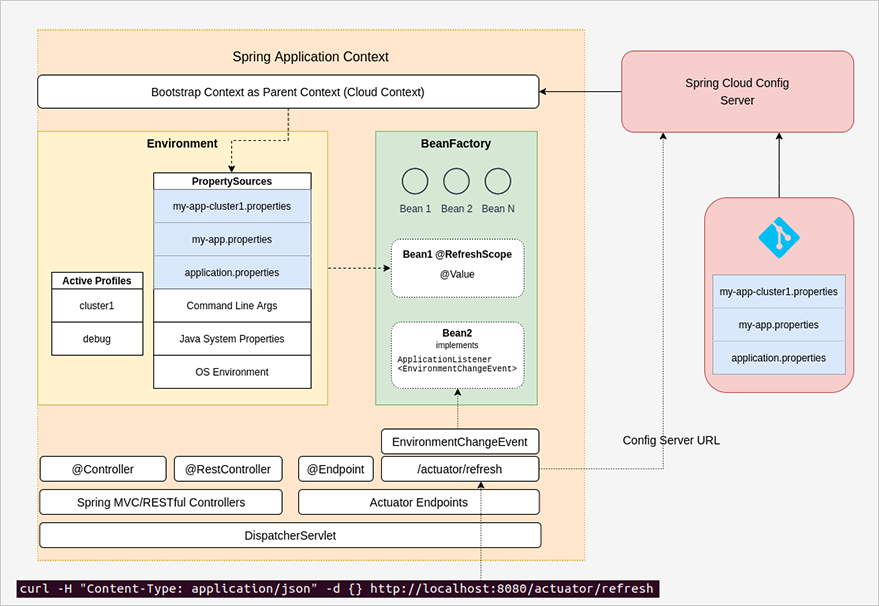
- Think that we have committed a change in a property file in the git repository, say it is my-app.properties and we want to reflect this change to our application.
- So we make a rest call to the /actuator/refresh endpoint exposed by the config client application.
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d {} http://localhost:8080/actuator/refresh - With this call, the RefreshEndpoint in the config client prepares the config server url as mentioned in the previous article, and makes a call to the config server to fetch the most recent version of the properties.
- With the up-to-date properties, the property sources in the Environment are refreshed and the bean attributes are refreshed also if the bean has the annotation @RefreshScope.
- Just after that, an event named EnvironmentChangeEvent is thrown and the listeners of it can handle the effect of this change if it’s needed.
3.1 Adding Actuator Dependencies
In order to expose an actuator endpoint, we add the following dependency to our config client’s pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>3.2 Enabling The Actuator Endpoint
By default, most of the actuator endpoints are disabled. To display which endpoints are enabled, you can call the /actuator endpoint. To enable all the actuator endpoints, including the /actuator/refresh endpoint, we can make the following configuration:
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
We can also just enable the endpoints we need by separating them via commas:
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=refresh, bus-refresh, beans, env
3.3 @RefreshScope
Just after the reloading of property sources by calling the /actuator/refresh endpoint, the attributes bounded with @Value in the beans having the annotation @RefreshScope is refreshed.
The property bindings made with the @ConfigurationProperties annotation do not need @RefreshScope annotation to be refreshed.
And also, property readings directly from the Environment interface does not need this annotation.
@Service
@Getter @Setter
@RefreshScope
public class MyService {
@Value("#{'yes'.equals('${activated:false}')}")
private Boolean activated;
}3.4 EnvironmentChangeEvent
Sometimes, we calculate a bean attribute with the use of a configuration parameter mostly in the post-construction of the bean itself. In this case, besides the refreshment of the attribute annotated with @Value, we also need to execute this initial calculation of the relevant bean attribute. This capability is provided as throwing an event named EnvironmentChangeEvent just at the end of the refresh process. So, the beans listening to this event can recalculate their attributes just like in the following sample:
@Service
@RefreshScope
@Getter @Setter
public class RefreshScopedService {
@Value("${tps}")
Integer tps;
String responseMessage;
@PostConstruct
public void refresh(){
responseMessage = responseMessage = "Service is running with tps: " + tps;
}
}@Service
public class MyRefreshListener implements ApplicationListener<EnvironmentChangeEvent> {
@Autowired RefreshScopedService refreshScopedService;
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(EnvironmentChangeEvent event) {
if(event.getKeys().contains("tps")) {
refreshScopedService.refresh();
}
}
}Calling the refresh endpoint is simple and to the point when the requirement is refreshing the configuration properties in a single config client. However, we generally have numerous instances of several services, and calling the refresh endpoint for each of them manually can be cumbersome work.
So, one solution to this problem is that; we can write bash scripts for each service and call the script of the relevant service when a configuration change happens.
But, there is also an alternative more advanced solution to this problem, provided with another project under Spring Cloud.
4. Refreshing The Configuration Properties Over Spring Cloud Bus
Spring Cloud Bus enables broadcasting the state changes among the services over a message broker like Kafka or RabbitMQ.
So in our scenario, each config client reading from the same config server can communicate over a message broker and refresh themselves in case of configuration changes. That means we do not need to make a refresh request for each config client application instead, we just broadcast a message to the services over Spring Cloud Bus to refresh themselves.
Let’s look over the following diagram:
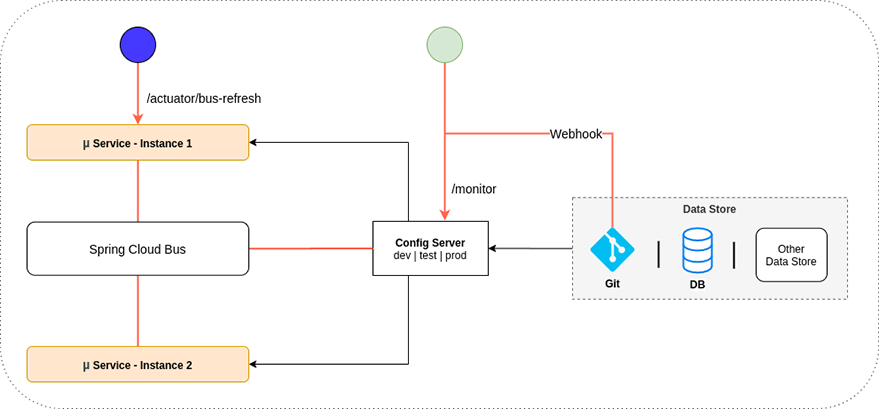
The refresh process can be triggered by calling the actuator endpoint /actuator/bus-refresh exposed on a config client instance or, by calling the /monitor endpoint exposed on the config server.
In each case, a state change message is broadcasted to the services over the message broker configured via Spring Cloud Bus and then each service makes a request to the config server with the config server url to refresh themselves.
The /monitor endpoint is designed for git cloud solutions, like Github, to make push notifications using git webhooks. However, one can manually trigger a refresh event by making a POST request to this endpoint.
4.1 Configuring the Spring Cloud Config Server
We want to send a refresh message over a message broker by calling the /monitor endpoint, so we add the Spring Cloud Bus dependency; in our case, we will use Kafka as a message broker so the relevant dependency to be added is:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>To be able to expose the /monitor endpoint over the config server, we need to add the following dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-monitor</artifactId>
</dependency>And lastly, we need to enable Spring Cloud Bus and configure Kafka settings in the bootstrap.properties:
spring.cloud.bus.enabled = true spring.cloud.bus.id=my-config-server spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.zkNodes=localhost:2181 spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.brokers=localhost:9092
That’s all to wire the config server to a message broker to enable the refresh process over Spring Cloud Bus.
What we have done here is that:
- We have made our config server able to broadcast state changes messages over Kafka.
- We enabled the endpoint /monitor over the config server which broadcasts a refresh state message over the message broker to all the config client services.
And now, let’s configure the client-side.
4.2 Configuring the Spring Cloud Config Client
We want to make our services also communicate over a message broker for listening and broadcasting refresh events. So here too, we need to add the Spring Cloud Bus dependency to the config client’s pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>And Kafka settings are also nearly the same.
spring.cloud.bus.enabled = true spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.zkNodes=localhost:2181 spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.brokers=localhost:9092
And now, our config clients are ready to be refreshed with an incoming refresh message over Spring Cloud Bus.
4.3 Refresh By Calling The /actuator/bus-refresh Endpoint
We have just configured our config server and config client applications to be able to communicate via Spring Cloud Bus integration and refresh themselves with the special endpoints. One of them is bus-refresh provided by Spring Cloud as a Spring actuator endpoint.
We have already configured it to be exposed. When a configuration property changes, then we just call this endpoint on any one of the config clients.
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/actuator/bus-refresh
Then the followings happen:
- The config client makes a request to the config server with the config server URL and refreshes itself.
- The config client broadcasts a refresh event to the other services over the message broker.
- The services received the refresh event also make a request to the config server to fetch the up-to-date configuration data.
Note that, you do not need to call the /actuator/bus-refresh endpoint for every client unlike as in /actuator/refresh endpoint.
4.4 Refresh By Calling The /monitor Endpoint
Another endpoint to refresh the configuration data via Spring Cloud Bus is /monitor endpoint. Here are some notes about this endpoint:
- It’s exposed on the config server by the module spring-cloud-config-monitor.
- It’s mainly designed for triggering with git webhooks and supports the git cloud solutions like Github and Bitbucket.
- You can also call this endpoint to trigger a refresh event.
And it’s time to try, let’s run the sample codes and see what happens.
4.5 Running the code
- Clone the sample code from my Github repository:
https://github.com/erolhira/spring-cloud-config - To be able to run the sample code, you first need to install Kafka and start it up.
- Start config server:
erol@ehira:~/.../case3_config-server-bus$ ./mvnw spring-boot:run
- Test the config server by typing the following config server URL in your browser.
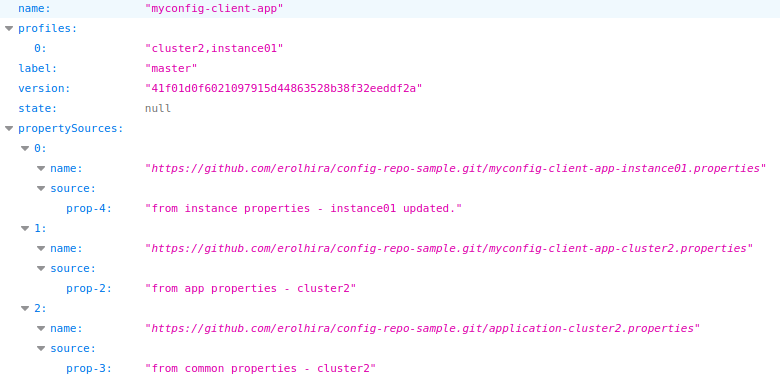
http://localhost:8888/myconfig-client-app/cluster2,instance01/master
You will see the properties fetched from a sample config repository in my Github since we declare it in the bootstrap.properties:
You should create your own repository or fork from mine to be able to change properties.
spring.cloud.config.server.git.uri = https://github.com/erolhira/config-repo-sample.git
Config Server Test - Start a config client instance:
erol@ehira:~/.../case3_config-client-bus$ ./mvnw spring-boot:run
- Test the config client by typing the following URL in your browser:
http://localhost:8080/config
You will see the configuration properties fetched from the config server according to the profiles and application name in the bootstrap.properties file.
Config Client Test - Now start a second config client instance with a different port:
erol@ehira:~/.../case3_config-client-bus$ ./mvnw spring-boot:run -Dspring-boot.run.arguments="--server.port=8081"
- Update the value of prop-3 in myconfig-client-app.properties and commit.
- When you test the config client as in #6, you will not see the change you have just made.
- To reflect the changes on to the clients, we will send them a refresh event by calling the /monitor endpoint over the config server.
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8888/monitor' --header 'X-Github-Event: push' --header 'Content-Type: application/json' --data-raw '{"commits": [{"modified": ["myconfig-client-app.properties"] }]}' - This call to the config server makes the config server throw a refresh event over the message broker. The message sent over Kafka is here:
{ "type":"RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent", "timestamp":1585513056017, "originService":"my-config-server", "destinationService":"myconfig-client-app-instance01:**", "id":"a5ede7cd-9c33-450a-938d-b414e9271c46" } - Clients read this message and send an ack message back to the config server over the message broker again. Here is the ack message:
{ "type":"AckRemoteApplicationEvent", "timestamp":1585513056471, "originService":"myconfig-client-app-instance01", "destinationService":"**", "id":"fcd5737d-1685-433e-a669-dc5ab2bc9540", "ackId":"a5ede7cd-9c33-450a-938d-b414e9271c46", "ackDestinationService":"myconfig-client-app-instance01:**", "event":"org.springframework.cloud.bus.event.RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent" } - Later on, the client makes a call to the config server with the config server url to refresh its configuration.
- As you see on #11, the type of the event sent by the config server is RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent. On the time the config client received this event, the refresh process is not started yet. So if the client listens to this event and reads a configuration property; that will be the old value of the property. So unlike the EnvironmentChangeEvent, we can do some pre-process by listening to the RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent just before the refreshment of our configuration data. You can also see this use case in the sample code.
- Here, we have called the /monitor endpoint manually, but in real-life scenarios, you probably want to call it from your git cloud solution by defining a git webhook after push events in your config repository. Or it may be more suitable to call the /actuator/bus-refresh over any config client. It’s up to your case.
5. Sample Code
You can see the sample code for this article on my Github page:
https://github.com/erolhira/spring-cloud-config
6. References
https://docs.spring.io/spring-cloud-config/docs/2.2.5.RELEASE/reference/html/
https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/spring-cloud-bus/2.2.2.RELEASE/reference/html/
https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/Hoxton.RELEASE/reference/html/spring-cloud-hoxton-configprops.html