
Apache Kafka is an Open-source asynchronous publish-subscribe messaging system that can help you build any of the offline task handling system, streaming service or any other data pipeline service.
My first interaction with such a system was back in Google Summer of Code – 2017 when I used celery for handling the long-running asynchronous tasks.
In this article, you’ll learn about the following things
1. Basic Introduction to Kafka
2. Basic terms and their definitions used in Kafka
3. Architecture of Kafka
4. Zookeeper
5. How to create a producer and consumer using JavaScript that can interact with Kafka broker.
History of Kafka
Kafka was originally built at LinkedIn and was later open-sourced and donated to Apache Software Foundation. It is basically written in Scala. It is being used by all the top companies out there like Twitter, Airbnb and many more.
Other tools in the same domain at that time were giving high latency for the event data being passed and consumed by the services. The folks at LinkedIn wanted to build a tool that can replace the already existing non-scalable version of the data processing pipelines and create something that handles high scales.

source: https://redmonk.com/fryan/2016/05/23/kafka-summit-the-four-comma-club/
Introduction to Kafka
According to the official documentation of Kafka, it is a distributed streaming platform and is similar to an enterprise messaging system.
What is a simple messaging system?
A simple messaging system consists of 3 main parts.
- Producer
A producer/ publisher is the part of the system which produces the messages. A message can be anything. Mostly there is a limit to the size of the message that a producer can produce and with the broker.
For SQS the upper limit of the size if 256 KB.
- Broker
A Broker is an interface/ intermediate are the receivers of the messages. They store the messages for some time and pass it on to the consumers for further usage. In most of the brokers, there is a limit on till when you can store the message on a broker.
For SQS the limit is 15 minutes whereas in Kafka the messages can stay for a longer time which can be configured according to the requirement.
- Consumer
The consumer is the part of the application which consumes the messages passed on by the broker. The consumer can handle the messages accordingly.
This simple setup can be used to handle log shipping to S3 or sending notifications to the customers.
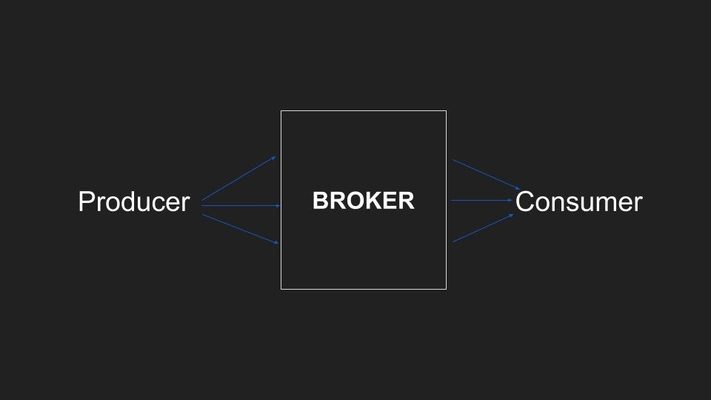
This simple setup seems to solve small problems when the number of messages being consumed daily is somewhere below a few thousand. But once your application starts growing you will start facing the latency issues in the setup. The messages will be consumed at a slower rate leading to more messages in the queue at any given time.
As the number of producers increases, this kind of combination is hard to maintain and your broker becomes the bottleneck for your solutions to provide real-time solutions to your customers.
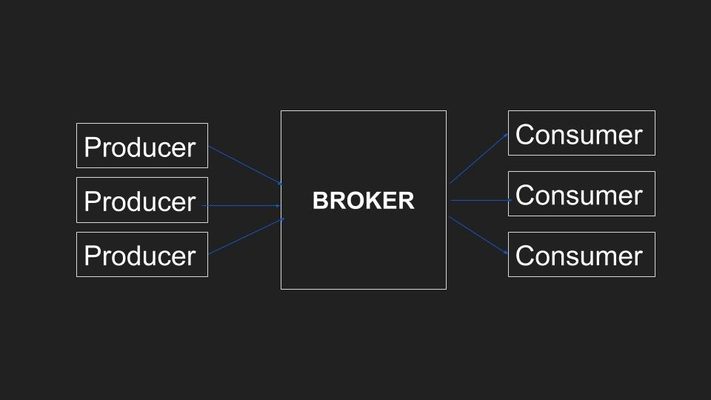
The basic Kafka features help us to solve all the problems that the other queue systems had at that time.
The main feature of Kafka are:
- It allows the saving of the messages in a fault-tolerant way by using a Log mechanism storing messages in with a timestamp.
- It is distributed so if one of the nodes fails, your messages are still safe at some other node.
- It processes messages as they occur by using the timestamp which is saved along with the message.
- It provides both the features of the queue and producer-consumer architecture i.e. You can send the messages to a group of consumers in which case only one of the consumers will get the message or you can send it over to all the consumers.
Architecture of Kafka
Kafka provides 4 core APIs which you can use to carry any operations related to Kafka.
- Producer API
- Consumer API
- Stream API
- Connector API
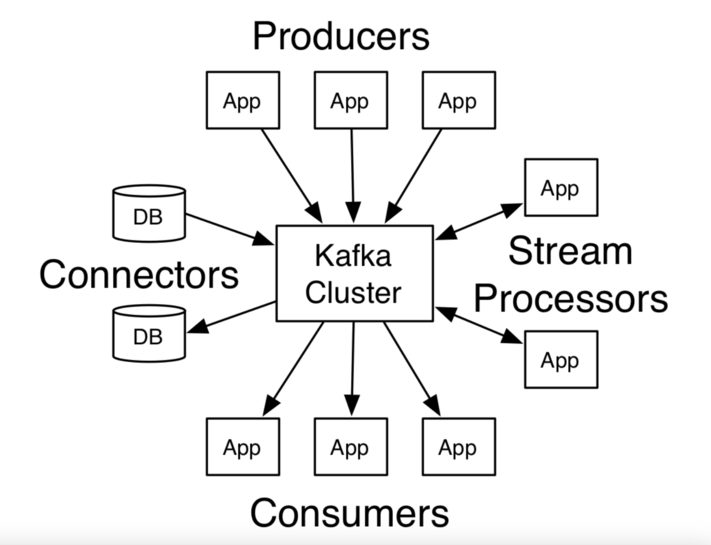
source: https://kafka.apache.org/intro
Topic
A topic is a unique name given to the Kafka data stream so that we can easily identify it.
For example, All the user click data is given a separate topic name so that the consumers who want to subscribe to the given topic can subscribe to the stream easily.
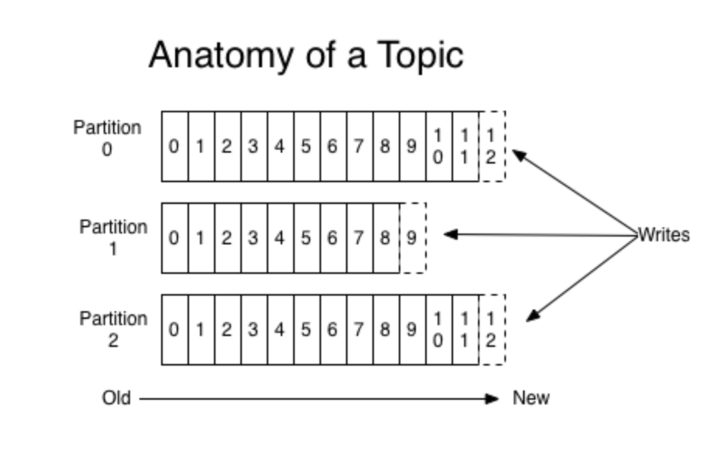
source: https://kafka.apache.org/intro
Kafka stores the messages as a partitioned log which saves offset for any given message on the partition log. This offset is unique across the whole partitioned log.
The performance of the Kafka is never deteriorated with the size of data being present on the Kafka this is because the only pointer that the application has to keep is the which record is being read and in case of Kafka, this is handled by the consumer.
Comparing to others O(log N), read and write are done in constant time O(1) if you know the record ID.
Reading and writing are independent of one another and writing to one log don’t lock it for reading or some other purposes.
Since the messages are not removed from the Kafka after they are consumed. They are only removed when a given time is reached which is again configurable. Due to this reason, the consumer can read the messages in whatever way they want to.
Clustered architecture
Since Kafka is a distributed system, there are a number of instances each executing a separate instance of Kafka broker. So at any given instance a group of Kafka brokers will be receiving the messages from producers and a number of broker instances will be sending the messages to Kafka producers.
Due to the same reason, every Kafka topic has a few partitions. A given Kafka topic can be running on multiple machines and they can have multiple partitions.
For uniquely identifying any message on the Kafka cluster, you need to know 3 things,
- Topic Name of the message.
- Partition number of the message on a Topic.
- Offset value of the message on that partition.
So, each topic has a few partitions and each partition has a few messages stored with unique offsets.
On the destination side as well we can have a few consumers running to handle the consumption of messages. We have to tell the Consumer Group on which partitions they should be taking data from.
To stop a message being read by two consumers, each partition is at max tied to one consumer.
Zookeeper
Apache ZooKeeper is an effort to develop and maintain an open-source server which enables highly reliable distributed coordination.
Zookeeper is distributed, centralized and robust coordination service which helps the Kafka nodes to coordinate between themselves. Zookeeper just helps you manage a large number of hosts with reliability.
Zookeeper helps you with all the management tasks that you can think for while running any distributed system.
It can help you with the availability, naming configuration management, acquiring and managing locks in the system, master-slave management and many more.
When a producer wants to send a message to the broker, it sends a message to the broker asking for the metadata of the broker, this metadata will contain the information related to the leader broker.
The metadata information is passed on to Kafka using the connected Zookeeper, which keeps the full metadata information related to the whole cluster. Once the producer knows the related information, it writes the message to the leader broker instance.
How to install and use Kafka
The installation part of Kafka is pretty straight forward. Go to the Kafka quickstart page and download the code.
If you are on MAC, you can directly do,
brew install kafka
and then start Kafka services
brew services start kafka
For starting a dev environment, you will have to start the zookeeper.
zookeeper-server-start /usr/local/etc/kafka/zookeeper.properties
Now you will have to start the Kafka server.
kafka-server-start /usr/local/etc/kafka/server.properties
Now you will have to start the Kafka topic named test on 9092 port.
kafka-topics --create --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic test
You can list down all the Kafka topics running.
kafka-topics --list --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
This should show the newly created topic.
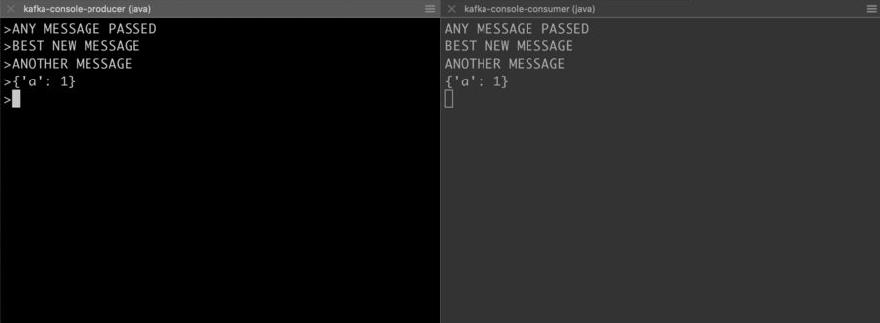
Now create a consumer subscribing to the test topic in a separate shell.
kafka-console-consumer --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic test --from-beginning
Log in to the producer console using the following command.
kafka-console-producer --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic test
Now pass in any message from the producer console and you will be able to see the message being delivered to the consumer on the other side.
The next step is to create separate producers and consumers according to your needs in which the client-side you want to choose for yourself.
Creating a Kafka producer using JavaScript
Let’s create a simple producer application in JavaScript. Kafka clients are present in all languages, you can choose from any one of them available on the apache website.
Let’s first install the following Kafka client using NPM.
npm i kafka-client
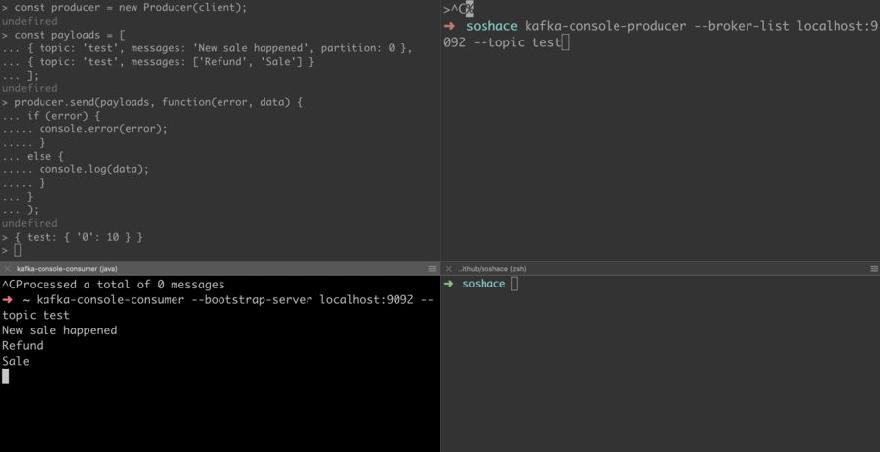
Write the following code in a file using the node shell, while console consumer with test topic is running
const kafka = require('kafka-node');
const Producer = kafka.Producer;
const client = new kafka.KafkaClient();
const producer = new Producer(client);
const payloads = [
{ topic: 'test', messages: 'New sale happened', partition: 0 },
{ topic: 'test', messages: ['Refund', 'Sale'] }
];
producer.send(payloads, function(error, data) {
if (error) {
console.error(error);
} else {
console.log(data);
}
You will see the messages appeared in the consumer console.
Creating a Kafka consumer using JavaScript
Stop the console consumer and create write a consumer using the following code,
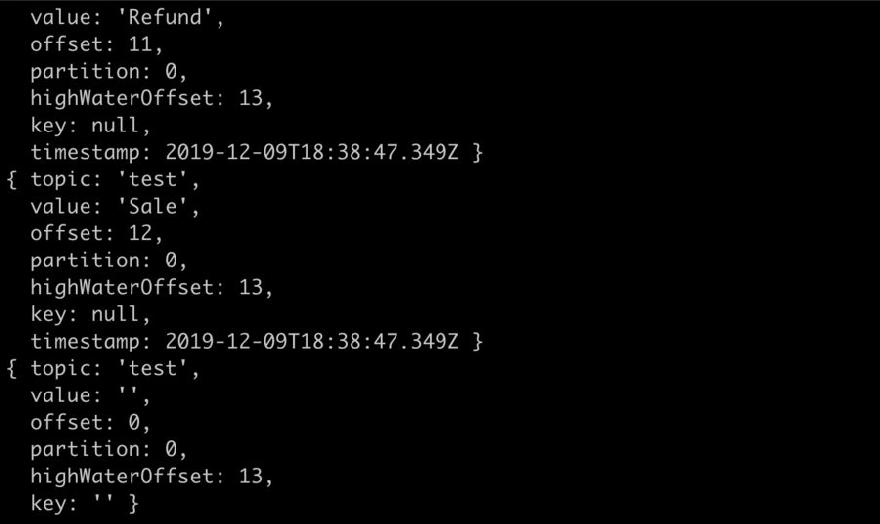
const Consumer = kafka.Consumer;
const consumer = new Consumer(
client,
[
{ topic: 'test', partition: 0 }, { topic: 'test', partition: 1 }
],
{
autoCommit: false
}
);
consumer.on('message', function (message) {
console.log(message);
});
This will show all the messages available consoled out on the node terminal. You might have to tweak it a little to make it favorable for your use.
How does Kafka handle failure
We already have discussed that Kafka is a distributed system and we know that it is highly fault-tolerant. This means that when you use Kafka it sends the data in the broker to many nodes distributed over various systems( Might be in separate geolocations).
So even if some of the nodes fail in the system your data will still be available.
The number of copies made for a single message over the Kafka system (or any other distributed system) is defined using the replication factor. In a Kafka system, we apply this replication factor to a given topic.
This way a Kafka system takes care of the failures and tries to minimize it. So, if your data is very critical, you can set the replication factor to some high number.
Hopefully, you liked the introduction to Kafka, there is a lot more to the distributed world which you might want to explore.
Please follow and share this article on social media.

