Developing applications that are fast and efficient has always been the goal of every developer out there. Most of the job when working towards achieving the goals above gets done by frameworks and libraries like React, Angular, etc. A library like React is fast, and in most cases, you won’t need to apply optimization techniques to make your application faster or more efficient.
But sometimes, there is a chance that the optimization techniques might help your application. The point to remember before diving into some of the optimization techniques is that use these techniques wisely and use them only when you observe a considerable benefit from it. There are many ways by which one can try to optimize the performance. In this article, we are going to discuss three of them.
Using React.PureComponent
Use-case: To avoid re-renders of a component whose state and props have not changed.
What is React.PureComponent?
Generally, for creating components in React, we use the React.Component extension. In the version 15.3 of React, the React team introduced another extension to create a component called React.PureComponent. So what is the difference? The difference lies in the implementation of shouldComponentUpdate( ) method. The shouldComponentUpdate( ) method decides whether a component should be re-rendered whenever state or props of a component is changed. By default, when using the React.Component extension, the shouldComponentUpdate( ) method returns true. When using React.PureComponent extension, the shouldComponentUpdate( ) method does not default to true, instead, it performs checks by comparing props and state of the component.
**Note- React.PureComponent performs shallow comparison of props and states therefore, it is not suitable to use this extension while comparing complex data structures. Example of when to use React.PureComponent:
Consider the following Parent and Child Components:
Parent Component:
class ParentComponent extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {
name: “Vivek”,
birthdate: “01-04-1897”
}
this.changeBirthdate = this.changeBirthdate.bind(this);
}
changeBirthdate(){
this.setState(prevState=>{
return {birthdate: '28-08-1984'}
})
}
render(){
console.log("Parent rendered!");
return(
<div>
<ChildComponent name={this.state.name}/>
<button onClick={this.changeBirthdate}>ChangeBirthday</button>
</div>
)
}
}
Parent component consists of two states, one is stored in the variable name and the other stored in birthdate. The state variable name is passed as props to the child component and we have a button when clicked, changing the birthdate to a new value.
Child Component:
class ChildComponent extends React.Component{
render(){
console.log("Child rendered!");
return(
<div>
<p>Name : {this.props.name}</p>
</div>
)
}
}
The child component just displays the name property which it receives from props. Let’s understand the problem with these components. Remember that we have attached a console.log to the render method of both the components.
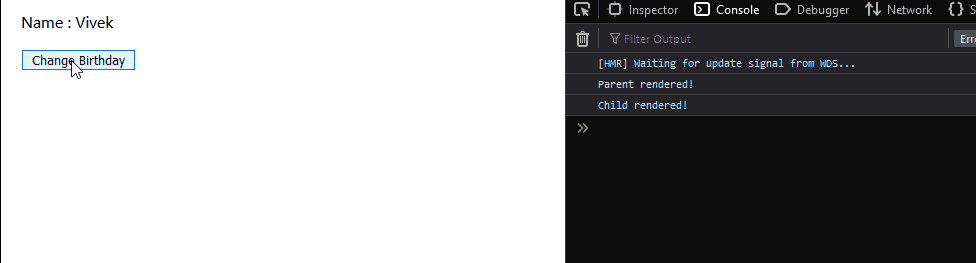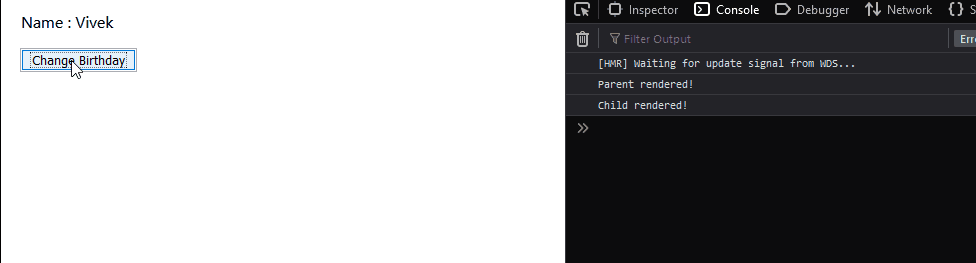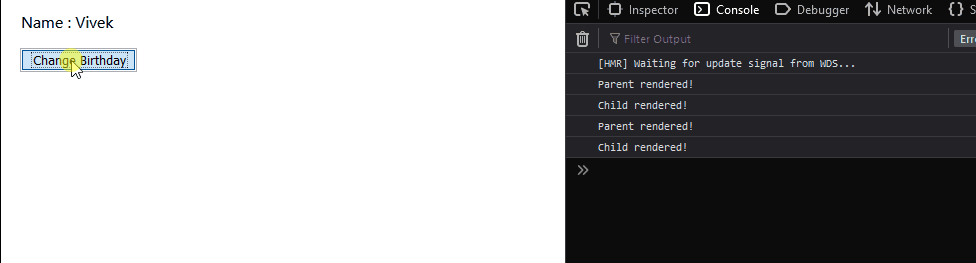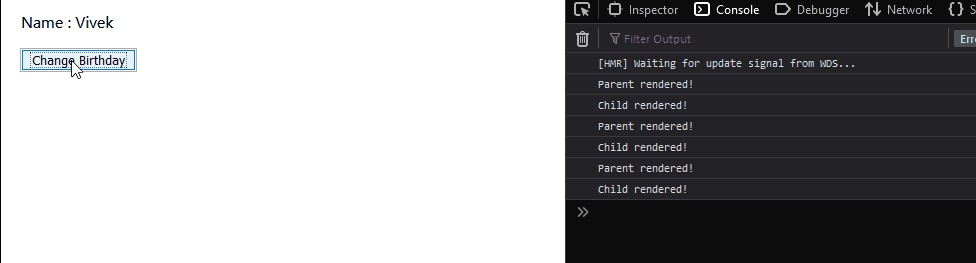
As we can see above, even though we are clicking a method in the parent component, the child component also gets re-rendered. We are not changing the props of the child component and yet it gets re-rendered. Why does this happen? This is the natural behavior of React components, irrespective of any change in the child component’s props or state, it gets re-rendered. Any change in the state or props of the parent component leads to re-renders of all the child components. How can we avoid this? Using React.PureComponent obviously! Redeclare the child component using the React.PureComponent extension:
class ChildComponent extends React.PureComponent
Then, let’s see the output:
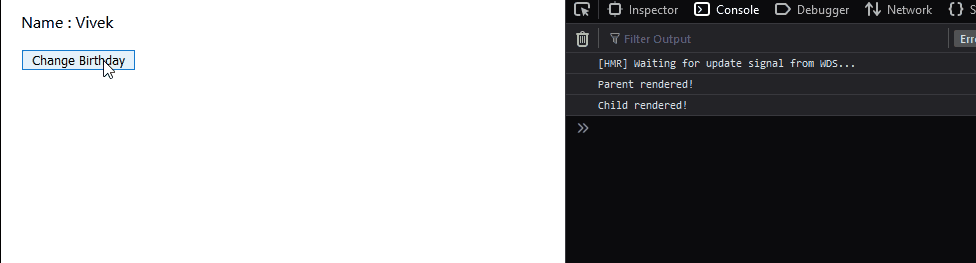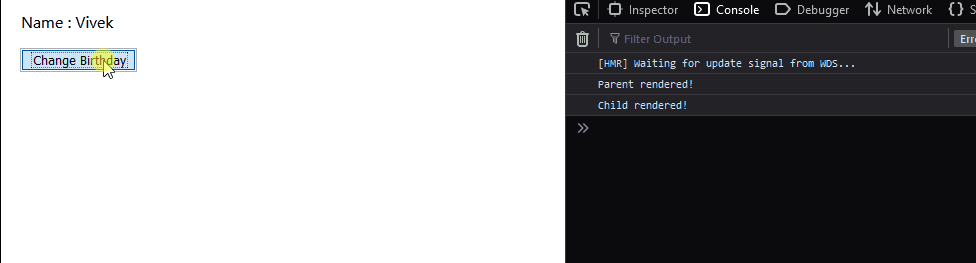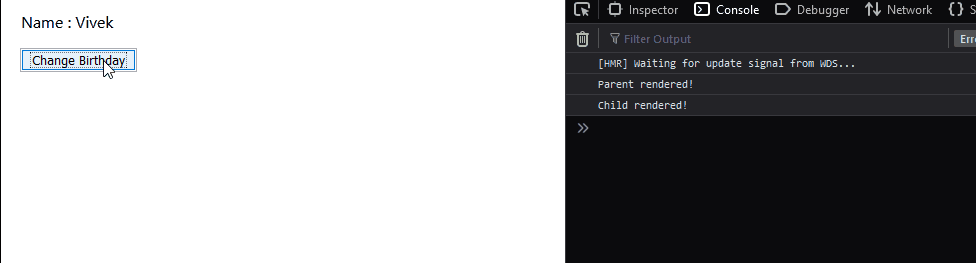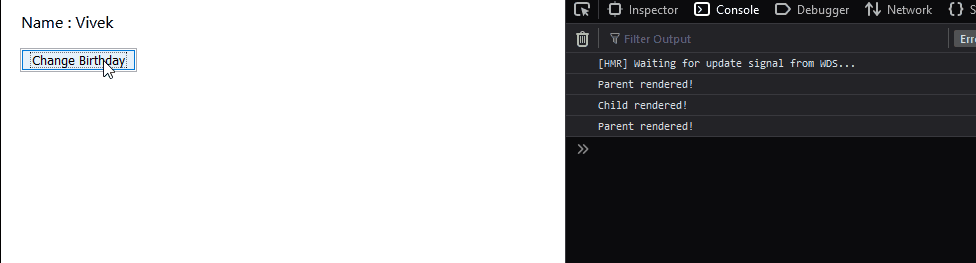
Now, we observe that by using React.PureComponent, the child component does not get rendered if its props or state remains unchanged. This is the advantage of using React.PureComponent extension. We considered straight forward components in this case but, imagine having child components that render many elements, in that case, using React.PureComponent extension helps in preventing unnecessary re-renders which might hamper the performance of your application. **Note- The functional component alternative of React.PureComponent is React.memo.
Colocating State
Use-case: Improves the speed of a React application. In general terms, Colocation means to put your code as close to where it is relevant as possible. So considering the definition of Colocation, State Colocation means to put your state as close to where it is needed as possible.
Why should we colocate state?
While developing React applications, it is extremely important to consider how an application is handling the global state. We need to handle global state in such a way that any component does not have access to states which it doesn’t need to know about i.e every component needs to handle states which are used by it or which are required by it in some way. Making a component handle states which are not used by it, makes the component more complex and therefore, difficult to maintain. Along with complexity, in most cases, it also hampers the speed of your application. Let’s understand the need for colocating state by an example:
Consider the following component:
unction Component1(){
let [countries,setCountries] = useState([]);
let [countriesByRegion, setCountriesByRegion] = useState([]);
let [inputVal,setInputVal] = useState('');
useEffect(()=>{
async function fetchCountries(){
const countriesList = await Axios.get('https://restcountries.eu/rest/v2/all');
const countriesList2 = await Axios.get('https://restcountries.eu/rest/v2/region/africa');
if(countriesList && countriesList2){
setCountries(countriesList.data);
setCountriesByRegion(countriesList2.data);
}
}
fetchCountries();
},[])
let changeInput = (e) => setInputVal(e.target.value);
let allCountriesOptions = countries.map((country)=>({
key:country.name,
value: country.name,
text: country.name
}));
let countriesByRegionOptions = countriesByRegion.map((country)=>({
key:country.name,
text:country.name,
value:country.name
}));
return(
<div>
<div className="input-element">
<label>Search Country:</label>
<input type="text" value={inputVal} onChange={changeInput}></input>
</div>
<div className="all-countries">
<Dropdown placeholder="Search All Countries" selection options={allCountriesOptions}/>
</div>
<div>
<Dropdown placeholder="Search Countries in Africa" selection options={countriesByRegionOptions}/>
</div>
</div>
)
}
I’m using the Rest Countries API along with two endpoints, all countries and countries by region (africa in this case) for the following example.
**Note- For demonstration purposes, I have written the API calls in the component itself. Let’s quickly understand what this component consists of. It contains three states, inputVal (bound to the input element), countries (it’s an array which holds the value received by the API call for all countries), countriesByRegion (array holding the value received by the API call for country by region). changeInput( ) function handles any change in the input-element and sets the new value. There are two other variables, countriesOptions and countriesByRegionOptions which are used as the options attribute of both DropDown elements. We can observe how complex the component looks. It has access to multiple states. Let’s see what happens when we try to render such a complex component:
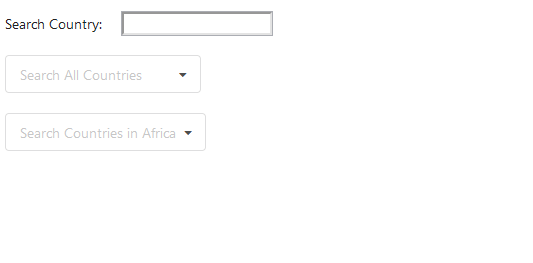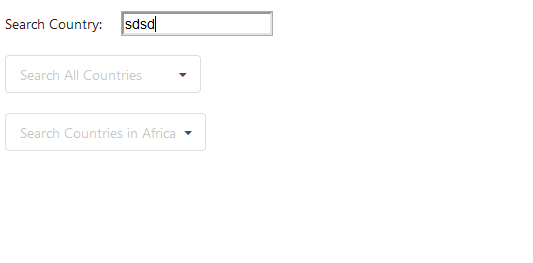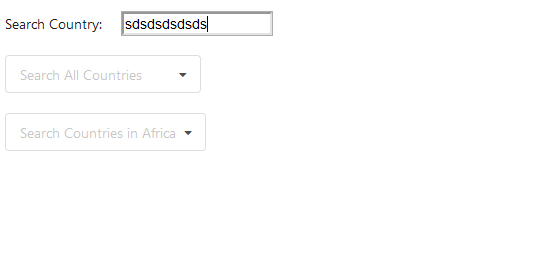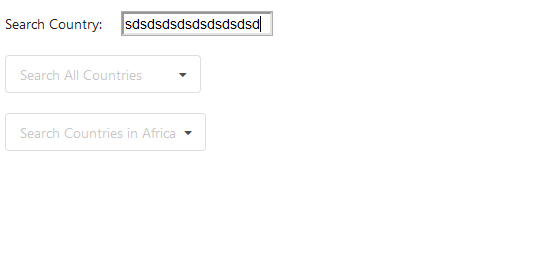
Above is the GIF of the rendered component. Can you notice a lag, which happens when I start typing letters rapidly inside the input-element? If you are not able to notice the lag inside the GIF, try the live demo below:
https://codesandbox.io/s/state-colocation-1-rcosi?file=/src/Component1.js
Did you notice the lag now? So let’s understand why is the input-element lagging. The reason behind is how we are managing the global state. In the above component, we are calling an API endpoint which responds with 250 countries code, along with this, we are also calling the countriesByRegion end-point which responds with another 54 countries code. Since all this code and multiple states reside in the same component, every time we type inside the input-element, the component re-renders the complete component which consists of mapping those 284 country names so that we produce it in the dropdowns. changeInput function listens to the changes made in the input-element and updates the state of the inputVal, along with this, the mapping of country names by countriesOptions and countriesByRegionOptions is done every single time. Therefore, we experience considerable lag in the input-element. So how do we fix this? Obviously by colocating state, let’s put each of the states along with their respective functions inside separate components:
function InputComponent(){
let [inputVal,setInputVal] = useState('');
let changeInput = (e) => setInputVal(e.target.value);
return(
<div>
<p>Search Countries</p>
<input type="text" value={inputVal} onChange={changeInput}/>
</div>
)
}
function CountriesComponent(){
let [countries,setCountries] = useState([]);
let allCountriesOptions = countries.map((country)=>({
key:country.name,
value: country.name,
text: country.name
}));
useEffect(()=>{
async function getAllCountries(){
const countriesList = await Axios.get('https://restcountries.eu/rest/v2/all');
if(countriesList){
setCountries(countriesList.data);
}
};
getAllCountries();
console.log("rendered")
},[]);
return(
<div>
<Dropdown placeholder="Search All Countries" selection options={allCountriesOptions}/>
</div>
)
}
function CountriesByRegionComponent(){
let [countriesByRegion, setCountriesByRegion] = useState([]);
useEffect(()=>{
async function getCountriesByRegion(){
const countriesList = await Axios.get('https://restcountries.eu/rest/v2/region/africa');
if(countriesList){
setCountriesByRegion(countriesList.data);
}
}
getCountriesByRegion();
},[]);
let countriesByRegionOptions = countriesByRegion.map((country)=>({
key:country.name,
text:country.name,
value:country.name
}));
return(
<div>
<Dropdown placeholder="Search Countries in Africa" selection options={countriesByRegion}/>
</div>
)
}
Now let’s render these components individually:
<InputComponent/> <CountriesComponent/> <CountriesByRegionComponent/>
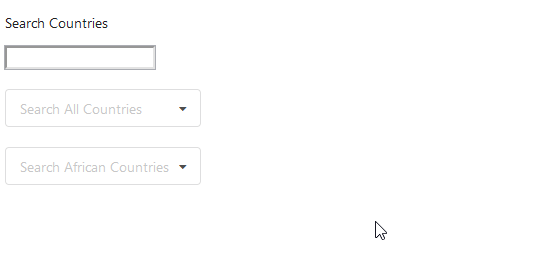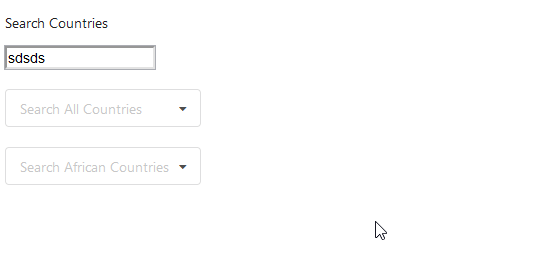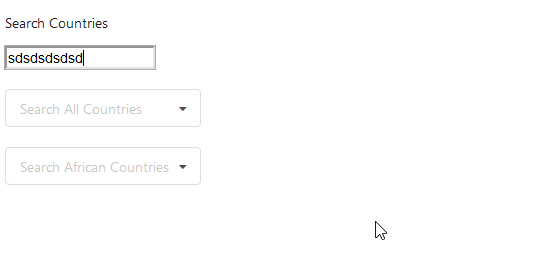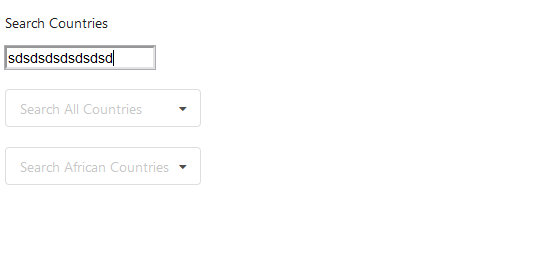
The input-element does not lag anymore:
To see the live demo:
https://codesandbox.io/s/state-colocation2-185d3
By this small example, we have demonstrated why state colocation is important. Not maintaining State Colocation leads to more complex and lagging components therefore, it is always advised to put all the states as close to where they are needed as possible.
Using useMemo hook
Use-case: Can be used to speed up an application.
What is useMemo?
It is a React hook used to memorize the return value of a function. It accepts two parameters, a function and an array of dependencies. Whatever function is given as a parameter to the useMemo hook, it memorizes the return value of the function, so next time when the same function gets called, instead of implementing the whole function, it just returns the output of the function.
Example:
useMemo(() => fn(),[]);
It is important to provide the second parameter to the useMemo hook, an array of dependencies. If the array is not provided, the return value of a function will not be memorized. We can also pass parameters to the function, along with that we also need to pass the parameters to the array dependencies:
useMemo(() => fn(parameter1,parameter2),[parameter1,parameter2]);
Now, the function inside the useMemo callback will get called only if the value of parameters change and if they don’t change, the memorized values will be returned. This way, we can make functions perform faster.
When is the useMemo hook used?
The obvious use case will be for computationally expensive operations. Computationally expensive operations may include calculating prime numbers, calculating factorials, finding all the paths in a network, an expensive query inside the database etc.. Whenever we need to perform expensive operations, the function might become slow gradually therefore, with the useMemo hook, we can memorize most of the return values of the function.
Example:
**Note- For demonstration purposes, I will be using a simple function (instead of a computationally expensive function).
Consider the following component:
function Component1(){
let [inputVal,setInputVal] = useState();
let changeInput = (e) => setInputVal(e.target.value);
let fn1 = multiplyBy1024(inputVal);
return(
<div>
<label>Enter number:</label>
<input type="number" value={inputVal} onChange={changeInput} />
</div>
)
}
It’s a simple component which renders an input element. We have a variable called fn1 which calls the function multiplyBy1024 with the inputVal. The important point to remember while creating a functional component is that every line inside the functional component comes under the render method i.e each time a state or a prop gets changed/updated, every line inside the functional component gets executed. Therefore, in the above example, each time a user types inside the input-element, the state changes and every line inside the functional component gets executed(rendered) again. I mentioned before that I will be using a simple function (multiplyBy1024) for the example, but, consider having an expensive function in the same place, each time the input-element changes the expensive function gets executed again and again which might hamper the speed of the application. To improve the speed we can use useMemo hook:
let fn1 = useMemo(()=>multiplyBy1024(inputVal),[inputVal]);
Now, the function multiplyBy1024 will get executed only when the inputVal changes. For example, If I enter “4” inside the input-element, the multiplyBy1024 function gets executed and the return value gets stored. If I enter “4” again inside the input-element, instead of executing the multiplyBy1024 function again, the useMemo hook just returns the value of the output since the inputVal has not changed. **Note- In practical cases, use the useMemo hook only when the optimization makes your application considerably faster. If the optimization using useMemo hook is minimal, then it is better to avoid using useMemo since it might make your application more complex. There is another hook called useCallback in React, it is similar to the useMemo hook, the only difference is that instead of memorizing the return value, it memorizes the callback function itself. So we have discussed three ways to optimize a React application. My suggestion will be to use these optimization techniques only when it has a considerable effect on your app.