
In this article, we’ll explore Progressive Web Apps and Service Workers.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Progressive Web Applications
- Introduction
- Requirements
- Benefits
- Setting up a PWA
- Service Workers
- What they are
- How they apply to PWA
- Setting up a Service Worker
- Conclusion
Progressive Web Applications
Introduction
The term Progressive Web Apps was first coined by Frances Berriman and Alex Russell in 2015, as a way of describing applications that take advantage of new features supported by modern browsers, including service workers and web app manifests, and also let users upgrade web apps to progressive web applications regardless of their native operating system. (Source: blog.pusher.com)
Progressive Web Applications use Modern Web APIs to create cross-platform applications. They are web applications that work like native applications. These work on computers, androids and iOS devices thereby giving the same user experience as native apps.
Requirements of a PWA
– HTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure is required because of security. This makes it impossible for intruders to disrupt or alter communications between the websites and user’s browsers
– Installable
PWAs are installable. These are different from page shortcuts. When installed, such applications can be shared with another user.
– Network Independent
Offline experience, which is aided by service workers.
– Responsive
PWAs must be responsive. You would never see a native application that would behave like a desktop-view website causing the user to swipe left and right to see the contents.
Benefits of Building PWAs
– Placed on the home screen (Installation)
These kinds of applications are very similar to native applications such that they can be installed on a device and placed on a screen.
– Secured online experience
– Faster webpage load time.
Since pages are cached, the user has a faster experience with the site except for cases where a new resource would be fetched.
Setting up a PWA
A service worker
This aids in offline experience. More on this topic later.
Web App Manifest
This controls what the user sees when launching the application after installation. This includes splash screens, themes and so on. It is saved as manifest.json.
{
// manifest.json
"short_name": "My App",
"name": "My Application",
"icons": [
{
"src": "./path/to/icon.png",
"sizes": "192x192",
"type": "image/png"
}
],
"start_url": "/",
"display": "standalone",
"theme_color": "#ff0000",
"background_color": "#ffffff"
}- ‘short_name’ is the name of the application that appears on the home screen.
- ‘name’ is the name appeared on the application.
- ‘icons’ are used when the application is added to the home screen.
- ‘start_url’ is the URL that loads when the application launches.
- ‘display’ defines the preferred mode of display for the application.
- ‘theme_color’ defines the default theme of the application.
- ‘background_color’ defines the background of the application
Remember to add your manifest file in the head tag of your HTML document.
If your manifest file is not configured correctly or you’re missing a configuration, you will not get the add to home screen prompt. However, if you manually choose the add to home screen option, you may get the application on your home screen but with the chrome logo on it.
Service Workers
What they are
Service workers are scripts written in Javascript which manages caching and responding to resource requests. This helps in reducing the dependence on the network as cached contents would be loaded until a new resource is acquired.
They have access to Cache API (the interface that provides a storage mechanism for Request / Response object pairs that are cached) and Fetch API (interface for fetching resources) which helps in storing data for offline access.
They also support Background Sync which postpones actions or requests sent by a user until there is stable network connectivity. This ensures that whatever the user wants to send is actually sent.
How they apply to PWA
As seen above, service workers help in offline experience. In most native applications (including those which require an internet connection for some operations), users could still perform some other activities without network. Popular native applications with this enabled are twitter, facebook, Whatsapp. Though you cannot post a tweet, follow a facebook friend or add a user to a WhatsApp group without a network connection, but the applications are still accessible.
The same goes for Progressive Web Applications. When you have been able to enable one on your previous Web application, you’d need a service worker to improve the offline experience.
The maximum scope of a service worker is the folder level at which it is located. It cannot be used for any file higher than the level it is placed. For example, A folder structure such as
Let’s examine this diagram
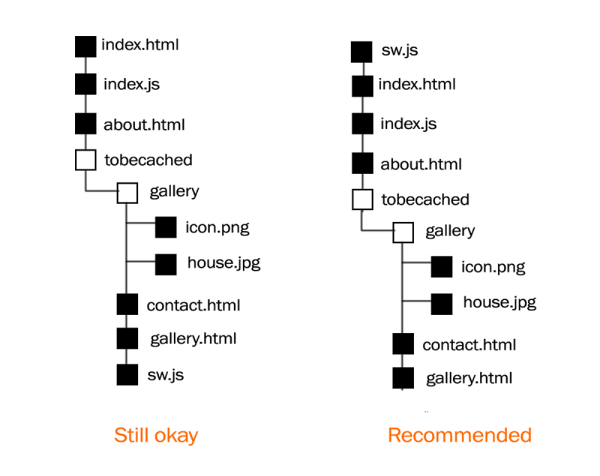
In the first illustration,
The service worker cannot be used for index.html and about.html because they are beyond its scope. It can only be used for the contents of the folder, tobecached.
The second illustration is recommended because,
When using a service worker for a web application, it is good practice to use it at the root level so that everything in the application is within its scope. Moreover, this is a requirement for a progressive web application.
Setting up a Service Worker
Registering the worker
All work is done in the worker file but the registration is done is a javascript file (index.js in our own case) which would be required in our application.
Once the service worker is registered, the service worker waits for a page to load. When any page within its scope loads, it is installed to work on that page. Although it is installed for a page load, it doesn’t install uniquely for that page. All installations still combine to form the whole service worker.
if('serviceWorker' in navigator) {
window.addEventListener('load', function() {
navigator.serviceWorker.register('/sw.js', {scope: '/'})
.then((reg) => {
// registration success
console.log('Registration success');
}).catch((err) => {
//registration failed
console.log('Registration failed: ' + err);
});
});
}First, we confirm if service workers are supported by the browser after which we define a scope. The scope option is though option as it defaults to the level of the service worker. You could define a level (which is within the worker) that you want the service worker to serve. Service workers will only intercept requests with URL that starts with the scope hence as defined above, everything within the whole application (‘/…’). If you want service workers to listen to requests starting with /blog/tags/ then your scope would be scope: '/blog/tags/'.
In the next line of code, the worker is registered which returns a promise. We then handle the successful registration or the failure with .then and .catch respectively.
Worker configuration
After registration, the installation of the service worker begins which occurs only once per scope. If a service worker is already installed in the browser for that scope, the installation process would be skipped unless we are trying to install a new or modified service worker.
During installation, the install event is triggered by which we can listen to and execute some codes.
// sw.js
// files array to cache
let filesArr = [
'/',
'./tobecached/contact.html',
'./tobecached/about.html',
'./tobecached/gallery/icon.png'
]
self.addEventListener('install', function(e) {
console.log('Service Worker installed : )');
// delay the event until promise is resolved
e.waitUntil(
// open the cache
caches.open('v1').then(function(cache) {
// add the files that you want to cache
return cache.addAll(filesArr);
})
);
})When the service worker is installed, we create a new cache which is called v1 (like version 1). Then, we add all our files to the cache using the addAll() method with the array of files passed as argument. An activate event is also triggered after installation. If no install event is triggered, activate event will not be triggered.
The activate event is used to do things that would have broken the previous cache version while it was running. Here, we can remove old cached files or versions that are no longer needed to free storage.
Next, we can use the fetch event to tell service workers to do something with the cached resources when a resource controlled by the service worker is requested.
self.addEventListener('fetch', function(e) {
e.respondWith(
caches.match(e.request)
.then(function(response) {
return response || fetch(event.request).then(function(response) {
return caches.open('v1').then(function(cache) {
cache.put(event.request, request.clone());
return response;
});
});
})
.catch(function(err) {
console.log('Error fetching resources')
})
)
})We first check if our cache matches the request before responding. With the OR (||) operator, we are able to fetch the request from the network if the cache does not match the request. After fetching, we then store the request in cache by cache.put() (which takes the request and the clone from the network). This is good practice so as to retrieve later requests of that resource offline.
Updating your service worker
You can go through the same installation process above but with a new version, say, v2.
By listening to the activate event, we are able to delete versions which do not appear in the list of versions we want to keep.
self.addEventListener('activate', (event) => {
var cacheKeeplist = ['v2'];
event.waitUntil(
caches.keys().then((keyList) => {
return Promise.all(keyList.map((key) => {
if (cacheKeeplist.indexOf(key) === -1) {
return caches.delete(key);
}
}));
})
);
});Read more about service workers in the MDN Documentation.
Conclusion
With the above steps applied correctly, you have created your progressive web application. The next time you (or anyone) opens your website, an ‘Add to Home Screen’ prompt is opened. If the action is accepted, the website is installed on the device. The worker caches all pre-defined resources (filesArr in the example above) as soon as they are loaded. To test it, you could disconnect from the network and try opening the following links: ‘/’ or ‘./tobecached/contact.html’. You’d discover that they opened without network.
You can know the service workers registered on your browser by entering chrome://serviceworker-internals/ in chrome and about:debugging#/runtime/this-firefox in firefox.
You can also check if the features of your PWA are in order by analysing the application with Chrome Lighthouse.
If you aren’t using one already, I guess you have seen the reasons why you should. Users tend to use native applications compared to websites because they remain accessible with or without a network connection. Do not limit the potentials of your web applications.
Thanks for reading : )

