Our next step will be using the streams to work with network connections. And we will start from delivering files to a visitor. As you may remember, we’ve already had a task like this: if a visitor requires the following url, you will give him the file. Let us create a file pipe.js with the following code (for your convenience, you can download code’ lesson from the repository because we’ll need an HTML file from there):
var http = require('http');
var fs = require('fs');
new http.Server(function(req, res) {
// res instanceof http.ServerResponse < stream.Writable
if (req.url == '/big.html') {
fs.readFile('big.html', function(err, content) {
if (err) {
res.statusCode = 500;
res.end('Server error');
} else {
res.setHeader("Content-type", "text/html; charset=utf-8");
res.end(content);
}
});
}
}).listen(3000);A solution example to this task without streams may be as follows, read the file:
fs.readFile('big.html', function(err, content) {once the file is read, call callback:
function(err, content) {
if (err) {
res.statusCode = 500;
res.end('Server error');
} else {
res.setHeader("Content-type", "text/html; charset=utf-8");
res.end(content);
}
});Next, if we’ve got an error, we send an alert, but if everything’s ok, we put a title specifying what file it is. And in response we write the file content as a call res.end(content) that gives back the content and closes the connection. This solution generally works, but its problem is extended memory consumption because if a file is heavy, readFile will first read it and then call a callback. As a result, if the client is slow, the whole read content will hang up in the memory, until the client gets it.
But what if we’ve got a lot of slow clients of this kind? And what if a file is big? It turns out, a server can occupy the whole available memory in just a few seconds, which is not good for us. In order to avoid it, we will change the file return code to another one that uses streams. We can already read from the file using ReadStream:
var file = new fs.ReadStream('big.html');It will be an input-data stream. While an output-data stream will be a response object res, which is an object of the http.ServerResponse class that inherits from stream.Writable.
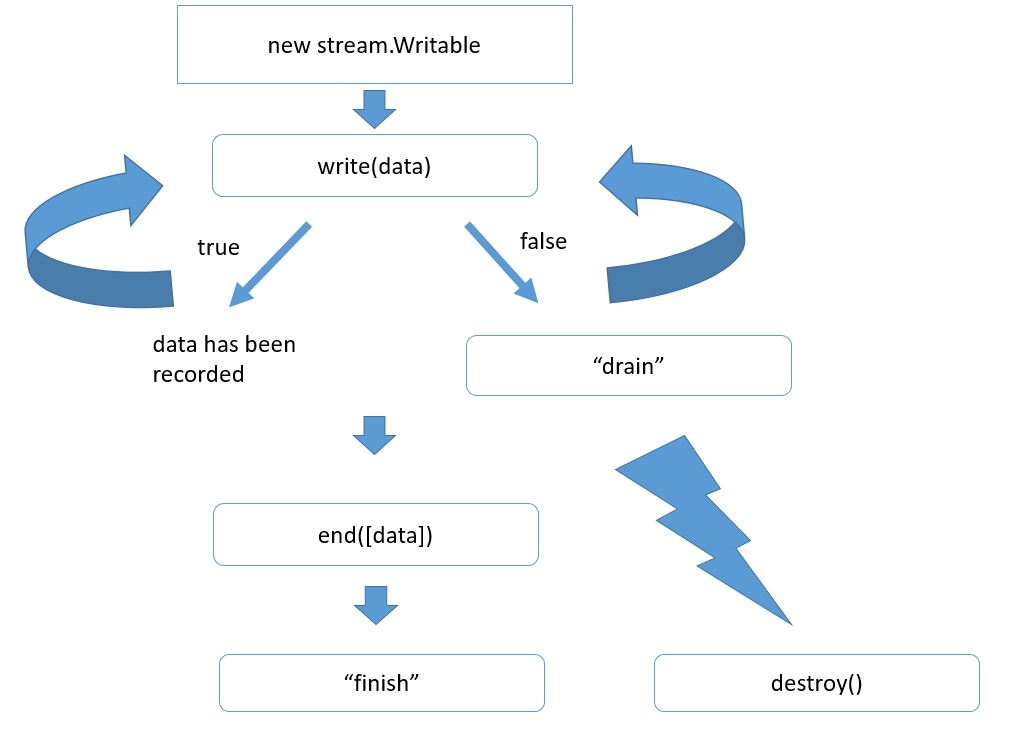
The overall algorithm of using the streams for recording cardinally differs from those things that we’ve analyzed earlier. It looks like that.
First, we create a stream object. If we’ve got an http server, the object is already created. That is res. Next we want to send something to a client. We can do it by calling res.write and deliver our data there. It is generally a buffer or a string. Our data get added to a special stream parameter that is called a buffer. If this buffer is not that big yet, our data get added to it, and write returns true, which means we can write more. In this case, the stream itself becomes responsible for sending data. In general, the sending occurs asynchronously.
Another variant is possible, too. For example, we’ve delivered too much data at a time or if a buffer is already occupied with something, the write method can return false, which means the internal stream buffer is overloaded and you can add your record at the moment, but it will be senseless because it all will be contained in the buffer. That’s why getting false оne does not continue recording waiting for a special event called drain that will be generated with a stream, when it sends everything and the internal buffer gets empty.
Thus, we can call write multiple times, and whenever we realize all data are written down, we should call the end method. Here you can also transfer your data with the first argument. In this case, it will just call write . The most important task of end is to end the record. The stream does it and calls internal operations of closing resources (files), connections, etc., if needed. Then it generates the finish events, which means the record is finally ended.
Note that a similar event at stream.writable is called end. This difference is not just a coincidence because there are duplex streams that can read and write. Respectively, they can generate both of these events.
A stream can be destroyed at any time by calling the method destroy(). When calling this method the stream work gets ended, and all the resources associated to it get free. Of course, the finish event will never happen because this is already a successful ending for a stream work and successful delivery of all data.
We provide the right file output by using the inquiry scheme as our crib sheet. Let us do it within a separate function named sendFile.
It will get one stream for a file and the second one for its response.
At first, pipe.js will look just like that:
var http = require('http');
var fs = require('fs');
new http.Server(function(req, res) {
// res instanceof http.ServerResponse < stream.Writable
if (req.url == '/big.html') {
var file = new fs.ReadStream('big.html');
sendFile(file, res);
}
}).listen(3000);
function sendFile(file, res) {
file.on('readable', write);
function write() {
var fileContent = file.read();
res.write(fileContent);
}
}The first thing we will do with such function is to wait for its data:
function sendFile(file, res) {
file.on('readable', write);
Later, when all data is received, inside a handler readable , we will read them and send the following as the response:
function write() {
var fileContent = file.read();
res.write(fileContent);
}Of course, it doesn’t stand any criticism because if a client cannot receive these data (for instance, due to a slow Internet connection), they will be stuck within the object res buffer:
res.write(fileContent)
So, if a file is quickly read, but isn’t sent yet, it will occupy a lot of memory, and we would like to avoid a scenario of this kind. Within this short code we see an example of a versatile solution for this task. Copy this code part instead of the previous one:
function sendFile(file, res) {
file.on('readable', write);
function write() {
var fileContent = file.read(); // read
if (fileContent && !res.write(fileContent)) { // send
file.removeListener('readable', write);
res.once('drain', function() { //wait
file.on('readable', write);
write();
});
}
}
}We also read the file content on the readable event, but we do not only send it with a call res.write, but also analyze what this call will return. If res accepts data very fast, then res.write will return true. It means, the branch if will never be performed
if (fileContent && !res.write(fileContent)) {...}Respectively, we will get read-write, read-write and so on.
A more interesting occasion is when res.write returns false. It means, when a buffer is overloaded, we temporarily reject handling readable events from the file.
file.removeListener('readable', write);This stop of a handler does not mean the file stream will quit reading data. On the contrary, it will read the data, but will do it till a certain level, fill in its inside buffer of a file object, and then, as no one requests read, this internal buffer will stay loaded till a certain level. It means, a file stream will read up something and stop there. Next we will wait for a drain event.
res.once('drain', function() {
file.on('readable', write);
write();
});It means, whenever the data will be successfully delivered in response (it means, we can accept something else from the file), we demonstrate our interest in readable events again and immediately call the write method. Why? Just because when we’ve waited for this drain, new data can easily come. This means, you can immediately read them:
var fileContent = file.read();
The read call will return null, if you’ve got no data. Otherwise, they will be simply handled in the same way we’ve been talking about earlier in if.
So, we get this kind of a recursive function: to read, send whatever has been read, waite for drain whether necessary, read again, send and wait – the same actions on loop until the file ends.
The article materials were borrowed from the following screencast.
We are looking forward to meeting you on our website blog.soshace.com