
Introduction
Utilizing React Query for data fetching is simple and effective. By removing the complexity of caching, background updates, and error handling, React Query streamlines and improves data retrieval.
As a React engineer, it’s critical to grasp the various methods for fetching and managing data in your application. The method you employ to acquire and manage data has a significant impact on your application’s performance, scalability, and overall user experience.
In this post, we will look at several popular methods for retrieving and handling data in React, such as utilizing the built-in fetch function, a library like axios, and the latest and most powerful library React Query. By downloading and employing code in the form of applets or scripts, the React Query description expands client capabilities to save and reload data at a faster runtime. As a result, you will be able to manage the state of your React apps consistently and reliably. Redux was succeeded by a React query. It quickly manages the side effects of the API, caching, etc. using a simple boilerplate. Contrarily, caching refers to keeping the server response in the client itself so that a client does not have to send server requests for the same resource repeatedly. React Query is often described as the missing data-fetching library for React.
In more technical terms, it makes fetching, caching, synchronizing, and updating server state in your React applications a breeze.
Data from hardware or software can be cached and retrieved later. The API response can be cached when a client (like a browser) submits a REST API request.
Fetch Function
The simplest method for retrieving data is to use the built-in fetch function. Most current browsers support this web standard for sending network requests. The response data can be accessed using the Response object that resolves the fetch function’s promise, which is returned. It does not, however, offer a graceful method of handling mistakes or canceling requests. Furthermore, it lacks built-in support for caching, a capability that many applications depend on.
const fetchData = async () => {
try {
const response = await fetch('https://example.com/data');
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error('Failed to fetch data');
}
const data = await response.json();
console.log(data);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
};
fetchData();
Axios Library
Using a library such as axios gives you more control over network queries. It offers a more powerful and adaptable method of dealing with failures, timeouts, and other network-related difficulties. Furthermore, axios includes interceptor support, allowing you to simply add cross-cutting concerns like authentication, logging, or error handling to your requests.
import axios from 'axios';
const fetchData = async () => {
try {
const response = await axios.get('https://example.com/data');
console.log(response.data);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
};
fetchData();
While these approaches are solid solutions, they still have some limitations. For example, caching and pagination are not handled by default, and you have to implement them yourself, which can be time-consuming and error-prone. This is where React query comes into play.
How React Query Works Under The Hood
React Query’s useQuery hook, which makes it simple for developers to fetch data, is the foundation of the entire architecture.
Developers provide a function that will retrieve the data when they execute useQuery, and React Query will take care of caching the results and automatically managing data freshness.
Likewise, the library allows background data prefetching depending on cache settings, guaranteeing that data is kept current without needless accesses.
If this is your first encounter with React Query, I assure you will leave this tutorial with one of the best tools for data retrieval. You could agree that data fetching in React is a pain. You attempt numerous hooks or even devise your own solution, but it appears that you are continuously returning to the same vulnerability.
When interacting with an API, for example, there are numerous things you want to track, such as the loading state and data state. While most standard state management libraries work well with client states, they are less effective with async or server states.
Let’s take a deeper look into the React developer tool to understand what exactly goes on.
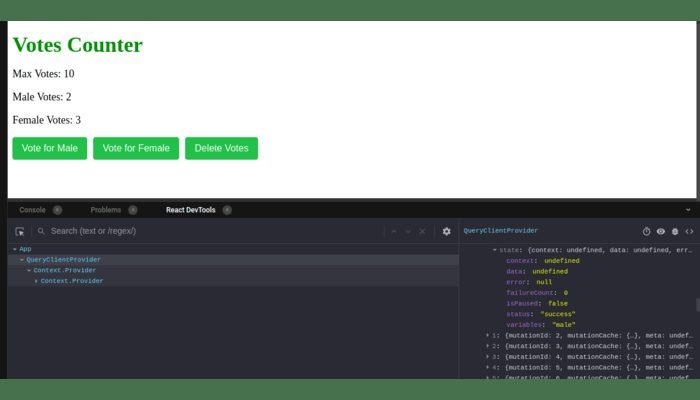
The terms you stated are related to distinct elements of mutations in the context of React Query, which is a library for managing remote and local data fetching and caching in React applications:
Context: “context” in React Query refers to the information or data passed to a modification function. This could include data that the mutation need to function, such as input values or authentication tokens.
Error: In the context of a mutation, “error” refers to any issues or problems encountered while attempting to execute the mutation. These failures could be caused by a variety of factors, including network issues, server-side faults, or validation flaws.
IsPaused: The “isPaused” attribute specifies whether a mutation should be paused or executed. This is useful when you wish to temporarily pause the execution of a mutation, possibly based on some specific criteria, and then continue it later.
The “status” of a mutation refers to the current state of execution of the mutation. React Query supports numerous status values, including:
“idle” indicates that the mutation is ready to be executed.
“loading” indicates that the mutation is currently being executed.
“success”: The mutation was executed and completed successfully.
“error”: An error occurred during the execution of the mutation.
More complications may develop as you proceed once the server status of your application is obtained. As an example:
- Reducing Server Load
- Optimizing Data Fetching
- Error Handling and Retries
- Pagination and Data Pre-fetching
React Query offers a variety of customization options, including the ability to define query dependencies, handle retries on errors, and configure cache lengths, providing flexibility in addressing varied data circumstances.
useQuery() Hook
For communicating with APIs, React Query provides useQuery. It is a custom React Hook with two arguments. It appears as follows:
const {data, error, isLoading} = useQuery(key, fetcher);
Here, key refers to anything that uniquely identifies the query, and fetcher refers to a function that will access the API using Fetch or another library, such as Axios.
The hook returns the properties data, error, and isLoading. The following are all of the available properties:
const {
data,
error,
isError,
isFetchedAfterMount,
isFetching,
isLoading,
} = useQuery(key, fetcher);Now we can fetch and handle data using the useQuery hook, as so:
// File.js
import {useQuery} from 'react-query';An example code snippet demonstrating data fetching with React Query is provided below. In this example, we’ll utilize React Query’s useQuery hook to get a list of users from a fake API.
import { useState } from "react";
import { useQuery } from "react-query";
const fetchUsers = async () => {
const response = await fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users");
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error("Failed to fetch users");
}
return response.json();
};
const UsersList = () => {
const { data, isLoading, error } = useQuery("users", fetchUsers);
if (isLoading) {
return <div>Loading...</div>;
}
if (error) {
return <div>Error: {error.message}</div>;
}
return (
<div>
<h1>User List</h1>
<ul>
{data.map((user) => (
<li key={user.id}>{user.name}</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
};
Creating an Application Using React Query
In this tutorial, we will demonstrate the potential of React query by creating a robust voting application. Let’s use React Query to create a “Votes Counter” application.
Users can vote or delete a vote on the counter in our app, and we’ll use React Query to manage data fetching and updating.
Setting Up Our Project:
Create a new React project by using the Create React App or another technique of your choice.
npx create-react-app react-query-votes-app cd react-query-votes-app npm install react-query
To use React-Query in a React application, wrap the App.js component with the QueryClientProvider component from React-Query, which gives us access to all of React-Query’s hooks.
//index.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import './index.css';
import App from './App';
import reportWebVitals from './reportWebVitals';
import { QueryClient, QueryClientProvider } from 'react-query';
const queryClient = new QueryClient();
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<QueryClientProvider client={queryClient}>
<App />
</QueryClientProvider>
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
reportWebVitals();
import { useState } from "react";
import { useQuery, useMutation, useQueryClient } from "react-query";
const fetchVotes = async () => {
// Simulate fetching vote count from the server
const response = await fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users/");
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error("Failed to fetch votes");
}
const data = await response.json();
return { count: data.length }; // Use the number of users as the vote count for simulation
};
const Counter = () => {
const [localVotes, setLocalVotes] = useState(0);
const queryClient = useQueryClient();
const { data, isLoading, error } = useQuery("votes", fetchVotes);
const voteMutation = useMutation(
() => {
// Simulate updating vote count on the server (in this case, the client-side)
return { count: localVotes + 1 };
},
{
onSuccess: (data) => {
// Update the local state and invalidate the query to refetch data
setLocalVotes(data.count);
queryClient.invalidateQueries("votes");
},
onError: (error) => {
console.error("Failed to vote:", error);
}
}
);
const handleVote = () => {
voteMutation.mutate();
};
if (isLoading) {
return <div>Loading...</div>;
}
if (error) {
return <div>Error: {error.message}</div>;
}
return (
<div>
<h1>Votes Counter</h1>
<p>Total Votes : {data.count}</p>
<p>Local Votes : {localVotes}</p>
<button onClick={handleVote}>Vote</button>
</div>
);
};
export default Counter;
We can make a separate CSS file and style the borders and buttons in the Votes Counter app, then apply the styles to the appropriate elements. Let’s make a new file called styles.css and specify the border and button styles in it:
/* Styles for the container */
.container {
max-width: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
border: 2px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 8px;
}
/* Styles for the headings */
h1 {
font-size: 36px;
color: green;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
/* Styles for the vote counts */
p {
font-size: 18px;
}
/* Styles for the buttons */
button {
padding: 10px 16px;
font-size: 16px;
margin-right: 10px;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
cursor: pointer;
background-color: #4caf50;
color: #fff;
}
/* Hover effect for buttons */
button:hover {
background-color: #45a049;
}
/* Styles for the error message */
.error {
color: #f44336;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
/* Styles for the dismiss button */
.dismiss-btn {
background-color: #f44336;
}
Making Mutations
When you need to change data on the server, React Query provides the useMutation() hook. This hook is used to perform create, update, or delete operations.
To make requests and wrap values while requests are being made, we’ll utilize the useMutation() hook, which returns an isLoading, error, and modify function. The argument also accepts an Asynchronous function.
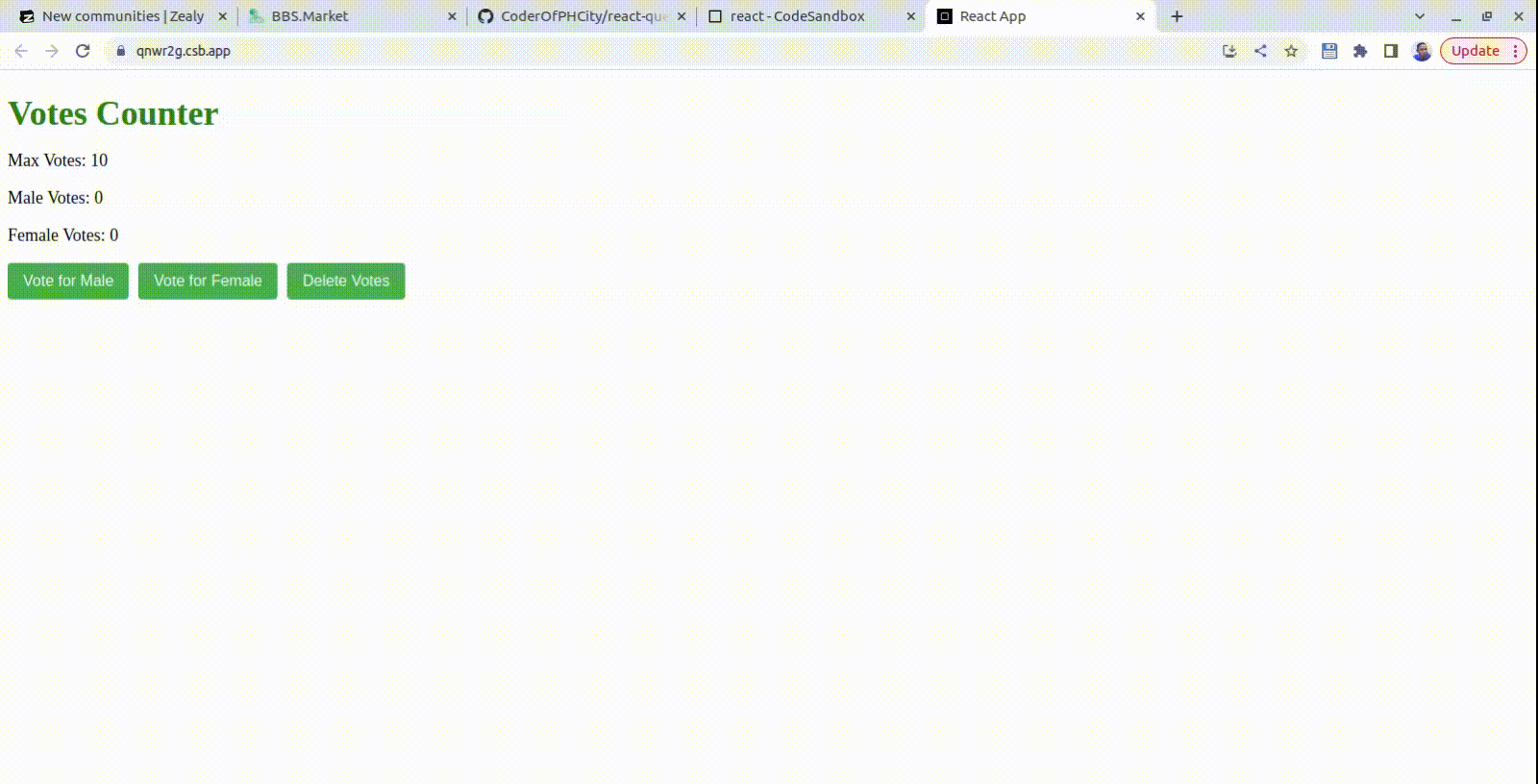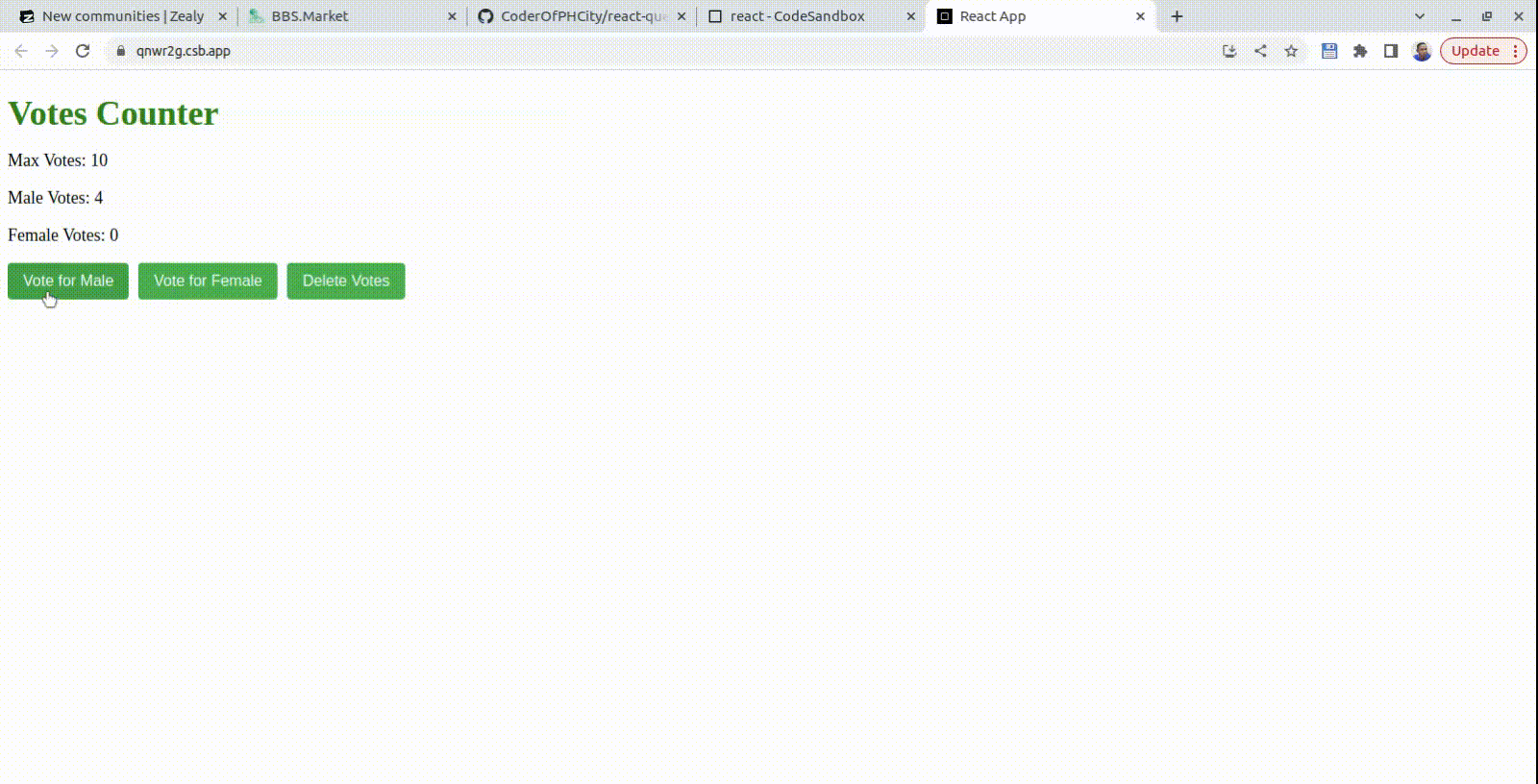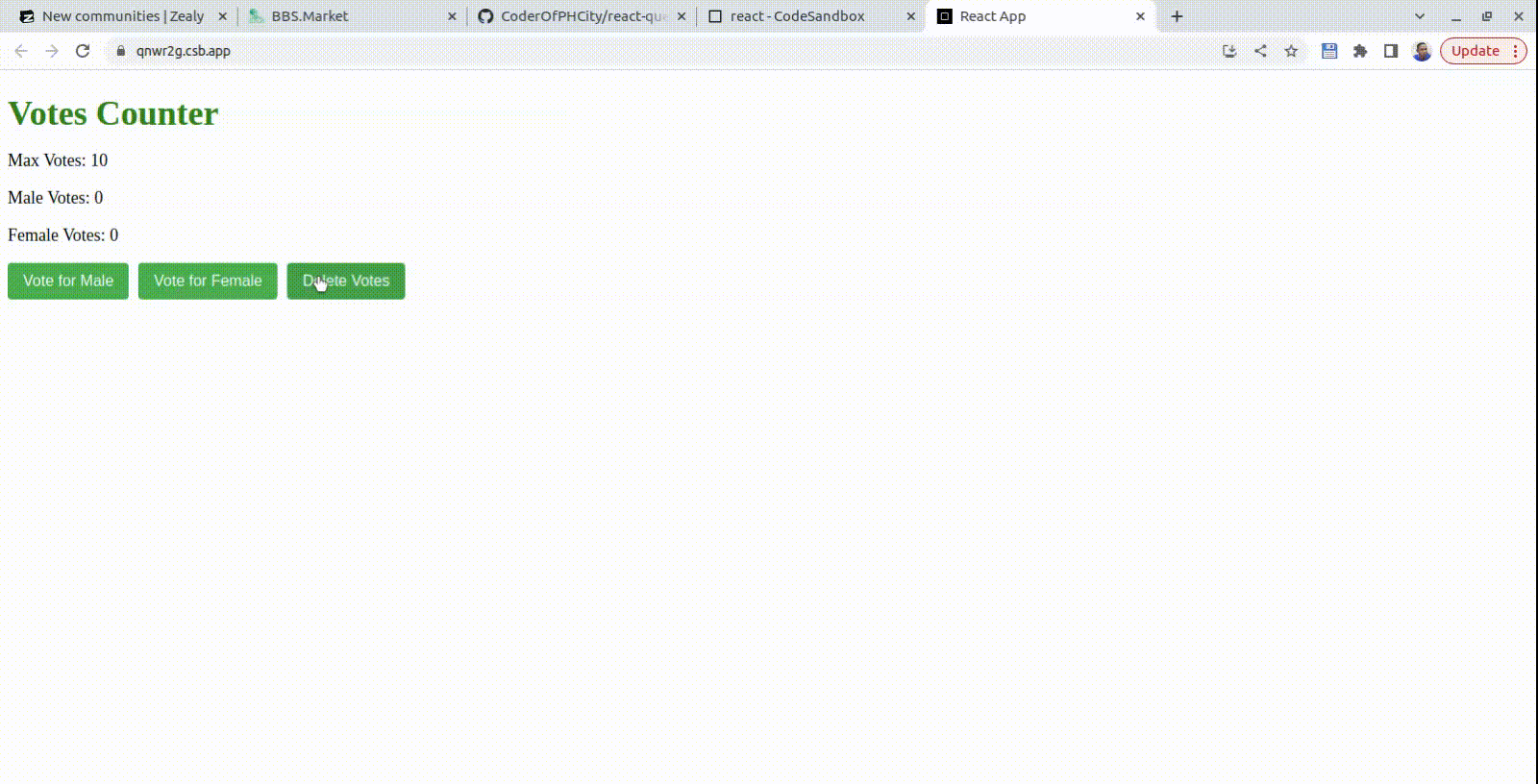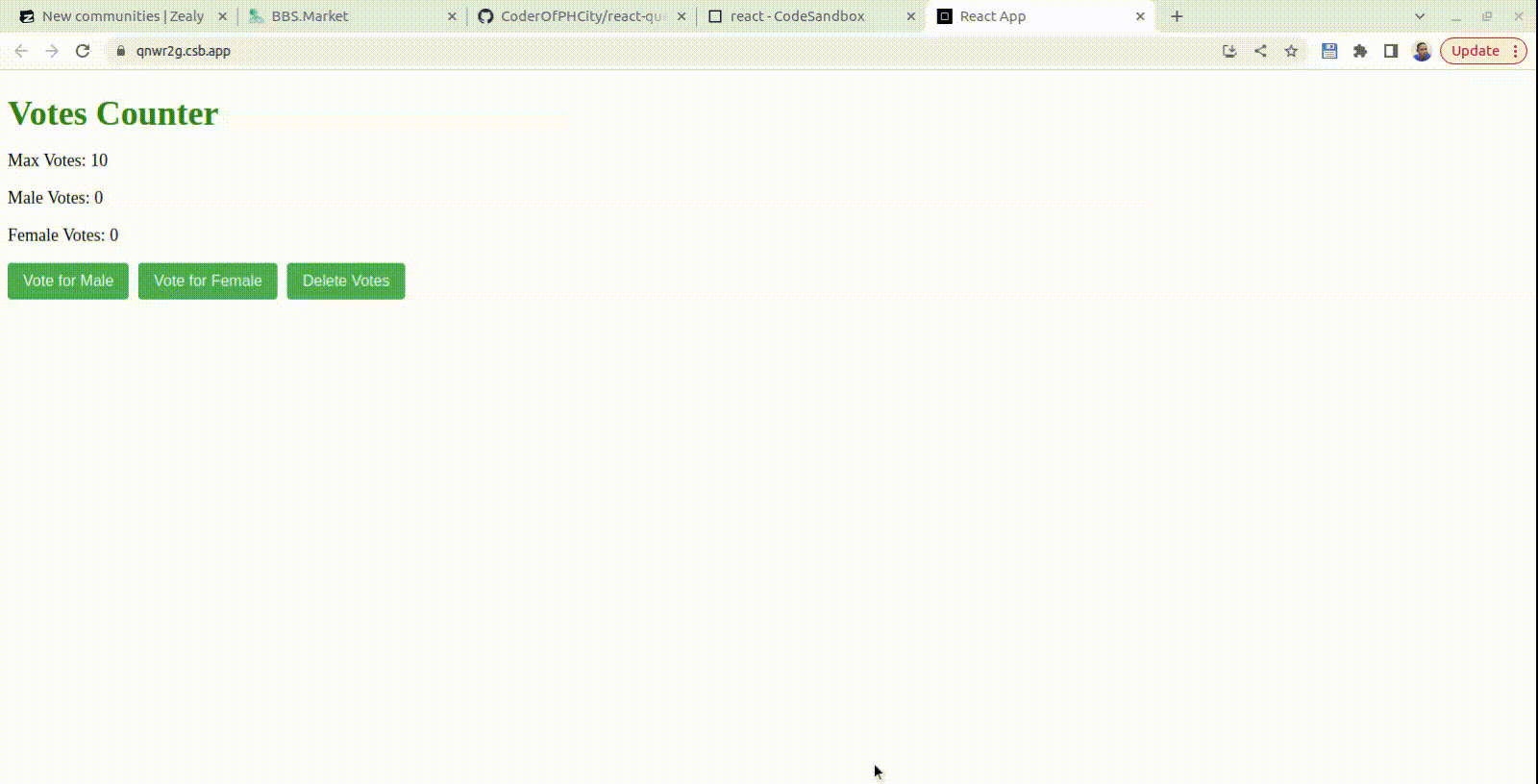
For our voting app, let’s utilize the power of React query mutation to initiate both male and female votes as so:
import { useState } from 'react';
import { useQuery, useMutation, useQueryClient } from 'react-query';
const fetchVotes = async () => {
// Simulate fetching vote count from the server
const response = await fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users/');
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error('Failed to fetch votes');
}
const data = await response.json();
return { count: data.length }; // Use the number of users as the vote count for simulation
};
const Counter = () => {
const [localVotes, setLocalVotes] = useState({ male: 0, female: 0 });
const queryClient = useQueryClient();
const { data, isLoading, error } = useQuery('votes', fetchVotes);
const voteMutation = useMutation(
(type) => {
// Simulate updating vote count on the server (in this case, the client-side)
if (type === 'male') {
return { count: localVotes.male + 1 };
} else if (type === 'female') {
return { count: localVotes.female + 1 };
}
return { count: localVotes.male + localVotes.female };
},
{
onSuccess: (data, type) => {
// Update the local state and invalidate the query to refetch data
if (type === 'male') {
setLocalVotes((prevVotes) => ({ ...prevVotes, male: data.count }));
} else if (type === 'female') {
setLocalVotes((prevVotes) => ({ ...prevVotes, female: data.count }));
}
queryClient.invalidateQueries('votes');
},
onError: (error) => {
console.error('Failed to vote:', error);
},
}
);
const handleVote = (type) => {
voteMutation.mutate(type);
};
if (isLoading) {
return <div>Loading...</div>;
}
if (error) {
return <div>Error: {error.message}</div>;
}
return (
<div>
<h1>Votes Counter</h1>
<p>Max Votes : {data.count}</p>
<p>Male Votes : {localVotes.male}</p>
<p>Female Votes : {localVotes.female}</p>
<button onClick={() => handleVote('male')}>Vote for Male</button>
<button onClick={() => handleVote('female')}>Vote for Female</button>
</div>
);
};
export default Counter;
The localVotes state is used in this enhanced version as an object with properties for male and female votes. The type parameter in the voteMutation function now determines whether the vote is for a man or a woman.
useMutation hook is used to create a mutation function for voting, and this function can be customized to handle different types of votes, such as male and female votes.
Let’s break down how the mutation makes male and female votes possible:
Customized Mutation Function:
The useMutation hook is used to define the mutation function. In this case, the mutation function accepts a type parameter, which represents the type of vote (male or female). Based on this type, the mutation function determines how the vote count should be updated.
Simulating Server-side Update:
Since JSONPlaceholder is a read-only API and doesn’t support actual data updates, the mutation function in this example simulates the server-side update by updating the local state instead.
For instance, when the type is ‘male’, the mutation function increments the localVotes.male count. Similarly, when the type is ‘female’, the mutation function increments the localVotes.female count.
Optimistic Update:
The mutation function uses an optimistic update approach. This means that it immediately updates the local state before the actual server request is completed
Error Handling

We’ll build a special hook that isolates the logic for managing errors and returns the pertinent error messages or error status in order to perform error handling in a separate file.
We may reuse the error handling mechanism in our Votes Counter app’s various components in this way.
For the special hook, let’s make a new file called useVotesError.js:
//useVotesError.js
import { useState } from 'react';
const useVotesError = () => {
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
const handleVoteError = (error) => {
setError(error);
// You can also add additional error handling logic here
console.error('Failed to vote:', error);
};
const clearError = () => {
setError(null);
};
return {
error,
handleVoteError,
clearError,
};
};
export default useVotesError;
The useVotesError custom hook, which controls the error state and offers the two functions handleVoteError and clearError, is created in this file.
error: If there isn’t an error, it stores the current error message as null.
handleVoteError: When a vote mutation fails, it sets the error state. If more error handling logic is required, you can alter this method.
When handling or dismissing an error situation, you normally utilize the clearError function to clear the error state.
Now we can import this custom error into the counter.js file using the code below
//counter.js import useVotesError from './useVotesError';
In this configuration, the useVotesError custom hook is used by the Counter component to handle error states when voting modifications fail. The hook offers tools for setting and removing error statuses.
The handleVoteError function is called by the onError callback when a voting mutation fails in order to set the error state and the appropriate error message. The component will show the error message, and users can choose to ignore it by clicking the “Dismiss” button.
It is simpler to manage and maintain the error handling behavior when the error handling logic is separated into a custom hook. This also simplifies the organization of the code and enables us to reuse the error handling logic across many components.
Reference Links
https://tanstack.com/query/v3/
https://tkdodo.eu/blog/mastering-mutations-in-react-query
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn/JavaScript/Client-side_web_APIs/Fetching_data
Conclusion
In this tutorial, We learned how React query as a data queue and data mutation works as well as illustrated how to build a simple votes counter application with React query.
For managing server state in your React applications, use React Query. Background updates, mutations, query invalidation, prefetching and endless queries are all capabilities that are available right out of the box.
You can find the link to the complete project codebase here.

