Repository with the code – https://github.com/soshace/graphql-sample
Back-end is the place where web development started. Nowadays it is more minimalistic and many things are left for front-end. Sometimes you can even avoid implementation of back-end logic at all and use, for example, Firebase for all your needs. But there’re lots of innovations in this field and we’re going to talk about one of them. This technology allows you to have typing in your API, use a universal query language that can have any kind of server language behind and batch your requests to API easy as pie. Interested? Then keep reading!
Our today’s guest is GraphQL (Graph Query Language). One of its unique parts is obvious. This technology uses queries to get resources from the API, that’s an absolutely different way to describe to the server, comparing it with commonly used REST, but what kind of action it should perform and the most important part – how.
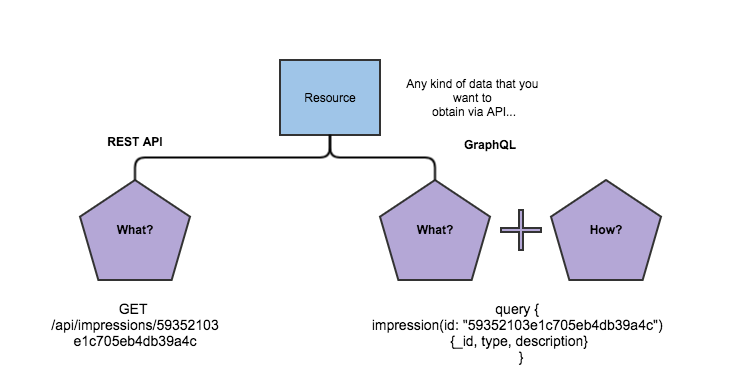
As you can see on the chart above, in the most common case of REST methodology usage, you specify just resource and operation that you want to perform upon it. However, for GraphQL by default you specify how the end data will be represented in the response.
In this tutorial, we’re going to use a small impression application as a sample (common app with only one type of resource – impression (about anything that you prefer: restaurant, hotel, whatever) to simplify the whole process. Let’s say you want to get information about a specific impression in the system:
GET /api/impressions/59352103e1c705eb4db39a4c
After the server responses with the data, but you can’t know the end result, you can expect a specific one, but you can’t change the form of data (technically you can with query string parameters, but from the box it’s just GET request, and operations with query params are the extra complications inside request handler). GraphQL allows you to specify how to get the data; in our case, what kind of properties we want to see in the response.
query {
impression(id: "59352103e1c705eb4db39a4c")
{_id, type, description}
}So in this case our query says to the GraphQL server that we want to take only id, type and description of our impression. That’s it, no extra implementation is required, just to specify what you want to get and how.
That’s a simple but significant different between GraphQL and REST. But how does this magic work? Let’s take a look at the top level of the whole process: client-server communication.
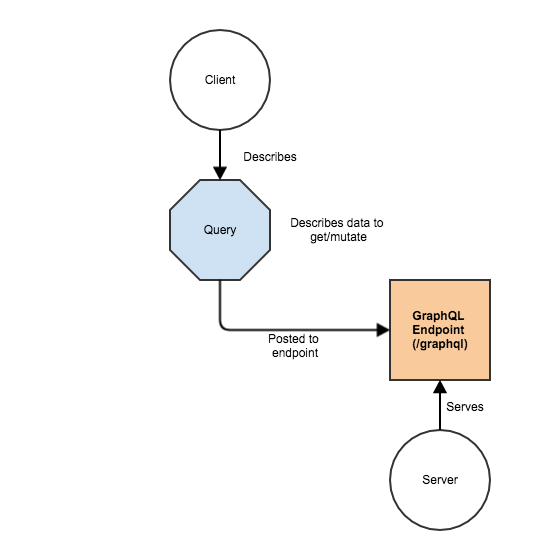
So the whole process is:
- Server supports the endpoint (/graphql) – in our case we’ll use extension for nodejs express, but there’re lots of other possibilities;
- Client describes in the form of query – what and how to get from the server;
- Client sends this query to GraphQL endpoint;
- Server performs the query;
- Client gets expected data;
One request to rule them all.
Now you don’t need to specify each resource as a separate endpoint and have an overkill trying to support a large number of those resources. The only thing that you need is to have a different query described on the client side. But what about POST/PUT/DELETE operations? We can get whatever we want, but we can perform those side effects as well, can’t we? Indeed. If you’d been attentive enough, you might’ve seen a small spoiler inside the chart above. GraphQL has a separate type of query for performing of side effects on the data – mutation.
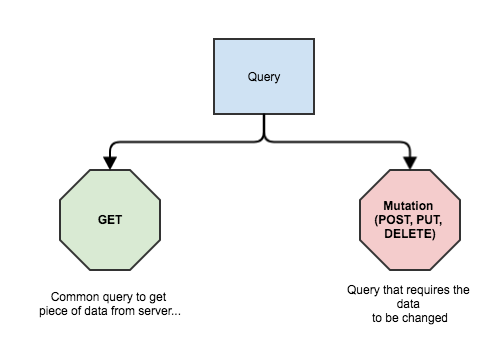
So using this type of query, you can perform any kind of side effect on the data. Let’s add a new impression:
mutation {
impressionAdd(impression: {title: "New", type: "good", description: "Absolutely new impression."}) {
_id
}
}As you can see, the name of this query is not query anymore, but mutation so GraphQL server can know how to resolve our query.
Now we are going to look into server typing. For GraphQL, it’s critical to have types specified for each kind of resource. The name of such types is schema. So for our impression resource it looks something like this:
export let ImpressionType = new GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'impression',
fields: function () {
return {
_id: {
type: new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLID)
},
title: {
type: new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLString)
},
type: {
type: new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLString)
},
description: {
type: GraphQLString
}
}
}
});So we can specify when properties shouldn’t be empty inside data and have exact type for each of them, e.g. title is always a string, while id has its own ID type (there’re lots of others types and data structures inside GraphQL, you can start research from here). Here I need to emphasize that query and mutation have different schema for the same resource. While query has ObjectType schema, mutation has ObjectInputType. It is logical, especially when some of the properties in the end data are auto-generated (e.g. in our case MongoDB generates _id automatically, but you can also generate creation date, index and many other things that won’t ever be included in initial entity data). Our mutation schema looks like this:
export let ImpressionInputType = new GraphQLInputObjectType({
name: 'impressionInput',
fields: function () {
return {
title: {
type: new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLString)
},
type: {
type: new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLString)
},
description: {
type: GraphQLString
}
}
}
})So after we understood how exactly GraphQL uses typing on its end, we can see the full picture of client-server communication:
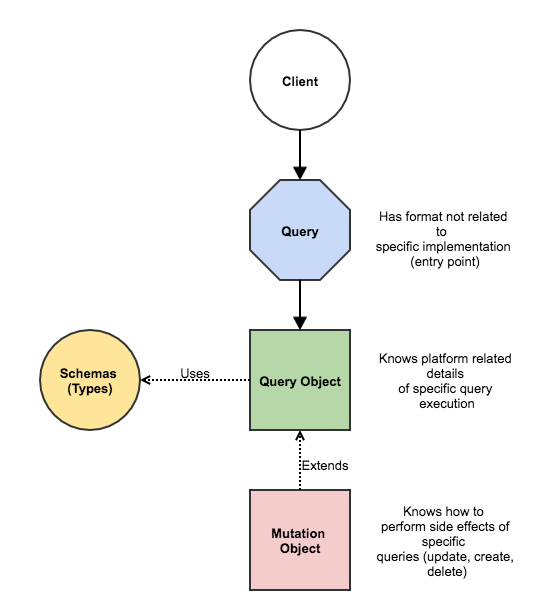
- Server supports the endpoint (/graphql) – in our case we’ll use extension for nodejs express, but there’re lots of other possibilities;
- Client describes in the form of a query – what and how to get from the server;
- Client sends this query to GraphQL endpoint;
- Server verifies input of the query according to specified schema (if data doesn’t meet the schema, you see appropriate error message);
- Server resolves the query (if query is a mutation then server performs side effects as well);
- Client gets expected data;
So it’s a bit more complicated than the first impression. The last mystery of the article is how GraphQL resolves queries. Actually no surprises here. Let’s take a look into GET impression query:
export let Impression = {
type: new GraphQLList(ImpressionType),
args: {
id: {
name: 'Impression ID',
type: new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLString)
}
},
resolve: function (root, args) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
ImpressionModel.find({_id: args.id}).then(impressions => resolve(impressions));
})
}
};- You specify type of the query based on schema;
- You specify arguments of the query with typing (so for our GET impression query it’s id only of corresponding type – impression(”));
- Finally, you specify resolve function that will be called to perform your query. The only purpose here is to return the valid piece of data with logic based on your database/server language choice (that’s the place where the logic of the each query lives);
For mutation the whole structure looks almost the same, yet it is different:
export let AddImpression = {
type: ImpressionType,
description: 'Add Impression',
args: {
impression: {
name: 'Impression Object',
type: ImpressionInputType
}
},
resolve: (root, args) => {
const impression = new ImpressionModel(args.impression);
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
impression.save().then(ent => resolve(ent));
})
}
};For type specification of input argument here we use our input schema. All other rules are the same as for the common query. My only advice here is don’t mix up Read-only requests with requests that have side effects because it’s conceptually wrong.
One last trick for today is batch request in GraphQL:
query {
impressions {_id, title}
impression(id: "59352103e1c705eb4db39a4c") {_id, type, description}
}So you can just specify any number of queries to be performed at once and get all the results as a response at once as well. Batching has never been so easy to understand and use.
I’ll be glad to see your questions in the comments below, guys. And thank you for your patience, this article might not have been easy. See you soon in our blog.
Instead of P.S.
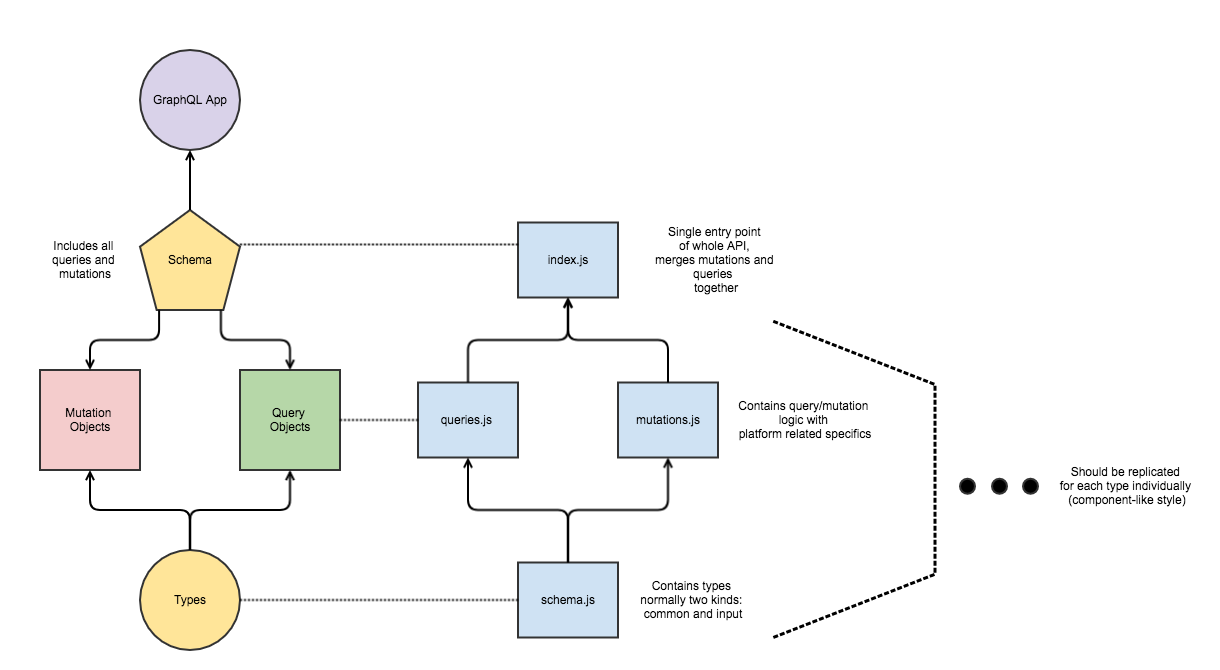
The more experienced of you should’ve had a question how to structure code with such number of abstractions: schemas, queries, mutations, etc. Firstly, here is the link to GitHub repository with a full sample, so you can play with it and see everything in action. Secondly, my suggestion related to structure is to use component-like structure, where for each resource you specify mutations, schemas and queries separately and merge them all at once in index file. Check the chart below for details:
We are looking forward to meeting you on our website blog.soshace.com

