
Introduction
As a Flask developer, I understand the importance of creating robust, scalable, and maintainable web applications. Test Driven Development (TDD) is a powerful approach that helps achieve these goals. In this article, I will share my comprehensive guide to implementing TDD in Flask development, complete with code examples and best practices.
Developing web applications using Flask, a lightweight Python web framework, has become increasingly popular due to its simplicity and flexibility. As a Flask developer, it is essential to create high-quality, maintainable, and scalable web applications that meet users’ needs and withstand the test of time. One effective way to achieve these goals is by adopting Test Driven Development (TDD), which emphasises writing tests before implementing the functionality.
In this comprehensive guide, I will share my extensive experience in implementing TDD in Flask development, providing you with practical tips, code examples, and best practices. The guide covers essential aspects of TDD, including setting up the development environment, configuring Flask for testing, writing various types of tests, implementing features using the TDD workflow, and integrating continuous integration and deployment.
Whether you are a seasoned Flask developer or just starting, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to develop robust Flask applications using the TDD approach. By following this guide, you will not only improve the quality of your Flask applications but also enhance your skills as a developer, ensuring that you are well-prepared to tackle increasingly complex web development challenges.
Setting up the Flask development environment
Before diving into TDD, let’s first set up our Flask development environment.
Install Python and Flask:
$ pip install python $ pip install flask
Create a virtual environment:
$ python -m venv venv $ source venv/bin/activate
Install necessary packages and dependencies:
$ pip install flask-testing pytest
Understanding Test-Driven Development
Test Driven Development (TDD) is a software development methodology that emphasizes writing tests before writing the actual code for the desired functionality. This approach shifts the focus from merely implementing features to ensuring that the implemented features work correctly and meet the desired requirements. By adhering to TDD, developers can achieve a higher level of code quality and maintainability.
TDD is built on three fundamental principles:
1. Red-Green-Refactor cycle: The TDD process follows a cycle of writing a failing test (red), implementing the feature to make the test pass (green), and refactoring the code to improve its quality without changing its functionality.
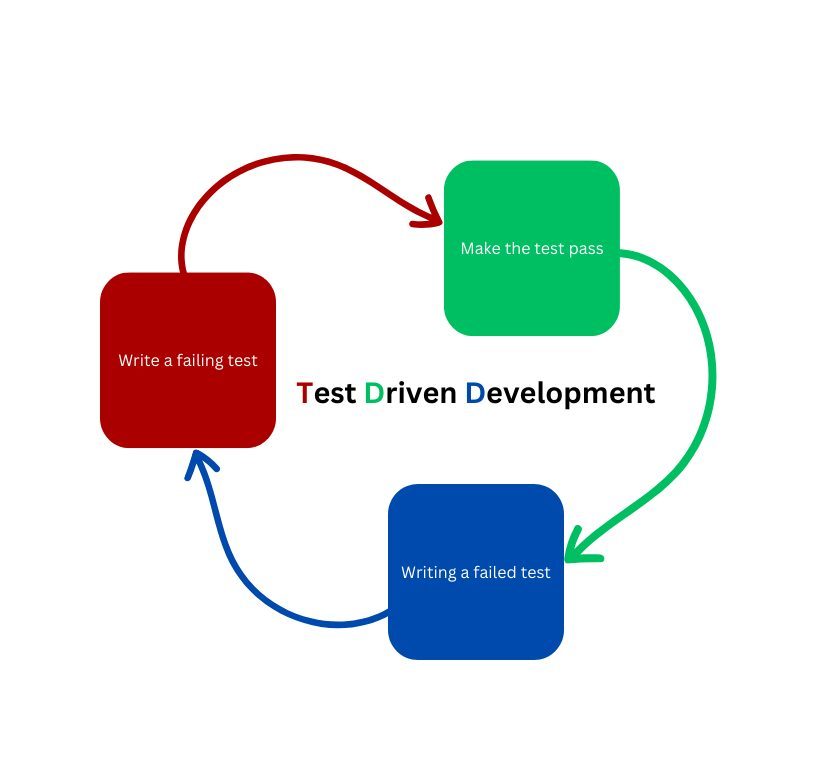
2. Incremental development: TDD promotes developing small, incremental features, making it easier to manage and maintain the codebase. This approach allows developers to catch issues early in the development process and reduce the risk of introducing new bugs.
3 Test-first approach: Writing tests before implementing the code encourages developers to think about the desired behaviour of the application, ensuring that they fully understand the requirements before starting the implementation. This approach also ensures that the test suite comprehensively covers the application’s functionality.
By adopting TDD in Flask development, developers can reap numerous benefits, such as:
- Fewer bugs: Writing tests before implementing the functionality helps catch potential issues early in the development process, reducing the number of bugs that make it into production.
- Better collaboration: TDD promotes a shared understanding of the application’s requirements and expected behaviour among team members, leading to smoother collaboration.
- Easier maintenance: Comprehensive test suites make it easier to refactor and improve the codebase without introducing new issues, ensuring that the application remains maintainable and scalable over time.
- Improved code quality: The TDD approach forces developers to think about their code’s design and structure, leading to cleaner, more modular, and better-organized code.
In this guide, I will demonstrate how to effectively apply TDD principles to Flask development, covering various aspects such as configuring Flask for testing, writing different types of tests, and implementing features using the TDD workflow. By mastering these concepts, you will be well-equipped to create high-quality, maintainable, and scalable Flask applications.
Configuring Flask for TDD
To configure Flask for TDD, I follow these steps:
Flask application structure for TDD:
myapp/
|- myapp/
|- __init__.py
|- views.py
|- models.py
|- tests/
|- __init__.py
|- test_views.py
|- test_models.py
|- config.py
|- run.py
Configuration files and settings for testing:
In config.py, I define the testing configuration:
class TestingConfig(Config):
TESTING = True
SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI = 'sqlite:///:memory:'
Setting up Flask extensions for testing:
In myapp/__init__.py, I initialize the Flask-Testing extension:
from flask_testing import TestCase
class MyAppTestCase(TestCase):
def create_app(self):
app.config.from_object('config.TestingConfig')
return app
Writing Flask tests
Now, let’s explore the different testing tools available and how to use them in Flask applications.
Overview of Flask testing tools:
- Flask-Testing: A Flask extension for testing
- pytest: A popular Python testing framework
- unittest: Python’s built-in testing library
Writing test cases for Flask routes:
In tests/test_views.py, I write a test case for a simple “Hello, World!” route:
from myapp import MyAppTestCase
class TestViews(MyAppTestCase):
def test_hello_world(self):
response = self.client.get('/')
self.assert200(response)
self.assertEqual(response.data, b'Hello, World!')
Testing database models and operations:
In tests/test_models.py, I write tests for a User model:
from myapp.models import User, db
from myapp import MyAppTestCase
class TestModels(MyAppTestCase):
def test_create_user(self):
user = User(username='John', email='john@example.com')
db.session.add(user)
db.session.commit()
result = User.query.filter_by(username='John').first()
self.assertIsNotNone(result)
self.assertEqual(result.email, 'john@example.com')
Testing Flask forms:
Let’s say I have a LoginForm with a custom validator. In tests/test_forms.py, I write tests for the form validation:
from myapp.forms import LoginForm
from myapp import MyAppTestCase
class TestForms(MyAppTestCase):
def test_valid_login_form(self):
form = LoginForm(username='John', password='mypassword')
self.assertTrue(form.validate())
def test_invalid_login_form(self):
form = LoginForm(username='', password='')
self.assertFalse(form.validate())
def test_custom_validator(self):
# Assuming a custom validator that checks for banned users
form = LoginForm(username='banned_user', password='mypassword')
self.assertFalse(form.validate())
self.assertIn('This user is banned.', form.username.errors)
Testing API endpoints:
Let’s say I have an API endpoint that returns user information. In tests/test_api.py, I write tests for the endpoint:
from myapp import MyAppTestCase
import json
class TestAPI(MyAppTestCase):
def test_user_info(self):
response = self.client.get('/api/user/1')
self.assert200(response)
data = json.loads(response.data)
self.assertEqual(data['username'], 'John')
self.assertEqual(data['email'], 'john@example.com')
def test_user_not_found(self):
response = self.client.get('/api/user/99')
self.assert404(response)
Implementing features using TDD
Let’s implement a new feature using the TDD workflow. For example, adding user registration functionality to our application.
Write test cases for the new feature:
In tests/test_registration.py, I write tests for the registration view and form:
from myapp import MyAppTestCase
class TestRegistration(MyAppTestCase):
def test_registration_form_submission(self):
response = self.client.post('/register', data={
'username': 'Alice',
'email': 'alice@example.com',
'password': 'mypassword',
'confirm_password': 'mypassword'
})
self.assertRedirects(response, '/')
def test_existing_username(self):
# Assuming a user 'John' already exists
response = self.client.post('/register', data={
'username': 'John',
'email': 'john@example.com',
'password': 'mypassword',
'confirm_password': 'mypassword'
})
self.assert400(response)
Implement the feature:
Now, I create the registration view and form to pass the tests.
Refactor and improve code quality:
Once the tests pass, I refactor the code to improve its quality while ensuring the tests still pass.
Advanced testing techniques in Flask
Mocking external dependencies:
Mocking is a powerful technique in Test-Driven Development (TDD) that allows you to isolate and test individual components of your application. In Flask development, you can use the unittest.mock module to create mock objects for testing.
For my tests, I use Python’s unittest.mock library to mock external dependencies, such as APIs, databases, or services, to isolate the components being tested.
In the example below, I created a Flask script for registering a user and adding the user to a database:
# myapp.py
from flask import Flask, redirect, request
from werkzeug.security import generate_password_hash, check_password_hash
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'sqlite:///test.db'
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
class User(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
username = db.Column(db.String(80), unique=True, nullable=False)
email = db.Column(db.String(120), unique=True, nullable=False)
password_hash = db.Column(db.String(128), nullable=False)
def register_user(username, email, password):
# Check if the username already exists
existing_user = User.query.filter_by(username=username).first()
if existing_user:
return None # Return None to indicate that registration failed
# Hash the password before saving it to the database
hashed_password = generate_password_hash(password, method='sha256')
# Create a new user
new_user = User(username=username, email=email, password_hash=hashed_password)
# Add the new user to the database
db.session.add(new_user)
db.session.commit()
return new_user # Return the user object to indicate successful registration
@app.route('/register', methods=['POST'])
def register():
username = request.form['username']
email = request.form['email']
password = request.form['password']
confirm_password = request.form['confirm_password']
if password != confirm_password:
return "Password and confirm password do not match", 400
user = register_user(username, email, password)
if user:
return redirect('/')
else:
return "Username already exists", 400I then created a test that mocks the “register_user” function
# test_myapp.py
import unittest
from unittest.mock import patch
from myapp import app, register_user
class TestRegistration(unittest.TestCase):
@patch('myapp.register_user')
def test_registration_form_submission(self, mock_register_user):
# Mock the register_user function to return a user object
mock_user = register_user(username='Alice', email='alice@example.com', password='mypassword')
mock_register_user.return_value = mock_user
# Use the Flask test client to simulate a registration form submission
with app.test_client() as client:
response = client.post('/register', data={
'username': 'Alice',
'email': 'alice@example.com',
'password': 'mypassword',
'confirm_password': 'mypassword'
})
# Assert that the response is a redirect
self.assertRedirects(response, '/')
@patch('myapp.register_user')
def test_existing_username(self, mock_register_user):
# Mock the register_user function to return None (indicating failure)
mock_register_user.return_value = None
# Use the Flask test client to simulate a registration form submission with an existing username
with app.test_client() as client:
response = client.post('/register', data={
'username': 'John',
'email': 'john@example.com',
'password': 'mypassword',
'confirm_password': 'mypassword'
})
# Assert that the response is a 400 Bad Request
self.assert400(response)
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
In this example, the “register_user” function is mocked using the @patch(‘myapp.register_user’) decorator. I then set the return value of the mock to control the behaviour of the mocked function during the test. This allows to test the registration form submission and the case where the username already exists without actually hitting the database.
Test coverage analysis:
Test coverage analysis measures the percentage of your codebase that is exercised by your tests. It identifies areas of code that are tested and those that are not.
Test coverage analysis acts as a guide for testing by highlighting areas where your code lacks test coverage. This is crucial for catching potential bugs early and making sure that when you modify your code, existing functionality remains stable. It fosters a safer environment for making changes, and by encouraging continuous improvement in testing practices, it contributes to the overall reliability and robustness of your codebase.
I use a popular Python library called Coverage.py. it provides tools for measuring code coverage during test execution. Here’s how you can use coverage.py in Flask development for TDD:
Install Coverage.py:
pip install coverage
Write test case:
from myapp import MyAppTestCase
class TestRegistration(MyAppTestCase):
def test_registration_form_submission(self):
response = self.client.post('/register', data={
'username': 'Alice',
'email': 'alice@example.com',
'password': 'mypassword',
'confirm_password': 'mypassword'
})
self.assertRedirects(response, '/')
def test_existing_username(self):
# Assuming a user 'John' already exists
response = self.client.post('/register', data={
'username': 'John',
'email': 'john@example.com',
'password': 'mypassword',
'confirm_password': 'mypassword'
})
self.assert400(response)Run tests with Coverage:
coverage run -m unittest test_myapp.py
Generate coverage report:
coverage report -m
I am also able to generate a coverage report that shows which lines of code were executed during the tests.
Using coverage.py in conjunction with TDD helps you identify areas of your codebase that lack test coverage, ensuring that you write tests for critical parts of your application.
Load and stress testing:
Load Testing in TDD with Flask:
With Load testing, I can evaluate how well your Flask app handles concurrent users or requests. Test cases simulating high-traffic scenarios are written using tools like locust. I can then monitor metrics such as response time and throughput and thereafter identify bottlenecks and optimize for scalability.
Stress Testing in TDD with Flask:
Stress testing assesses app stability under extreme conditions. I can create scenarios simulating sudden traffic spikes or resource-intensive operations utilizing tools like locust to stress specific functionalities. I then analyze results to identify breaking points and areas for optimization.
Considerations:
It helps with evaluating database capacity, middleware impact, and caching efficiency. Also, allows you to assess scalability by testing additional resources. I implement robust monitoring during tests and integrate load and stress testing into my continuous integration pipeline for early issue detection. A tool I commonly use for implementing and automating these tests into my continuous integration pipeline is Jenkins.
Best practices for Flask TDD
Organizing test cases and modules:
I keep my test cases organized by separating them into different modules based on the components being tested.
Writing maintainable and reusable tests:
I strive to write maintainable and reusable tests by following these practices:
- Use descriptive test names: Test function names should clearly describe the purpose of the test, making it easier for others to understand and maintain.
- Keep tests simple and focused: Each test should focus on a single aspect of the application. This makes it easier to debug and maintain tests.
- Use setUp() and tearDown() methods: These methods, available in testing frameworks like unittest, help set up necessary objects and clean up resources after each test, promoting reusability and reducing duplication.
Keeping test suites up to date:
As the application evolves, it’s essential to keep the test suite up to date. I regularly add new tests for new features, update existing tests to reflect changes in functionality, and remove obsolete tests that no longer apply.
Collaborating on TDD projects:
When working in a team, I follow these practices to ensure smooth collaboration:
- Share test suite setup and configuration: I ensure everyone on the team uses the same testing setup and configuration to maintain consistency across development environments.
- Communicate test failures and successes: When tests fail, I quickly notify team members and work together to resolve the issue.
- Review test cases during code reviews: I incorporate test case review into the code review process to ensure test quality and adherence to best practices.
- Also with the help of automated pipeline tools, every member of the team can see what tests passed or failed even without having to run the tests on their local machine. Hence, better code reviews are done and the team is able to know what code works or not in the integration and deployment pipeline.
Software Architecture:
Software architecture is crucial for creating testable systems. To achieve this,
- learn good programming practices, like writing clean code and understanding SOLID principles.
- learn how to build effective software architecture and put these ideas into practice in your code.
Common mistakes to avoid when using TDD with Flask
There are several common mistakes to avoid when using TDD with Flask:
- Avoid writing tests that are too complex. Complex tests can be difficult to maintain and may not cover all possible scenarios.
- Avoid relying too heavily on mocking. Mocking can be useful, but it is important to ensure that your tests are still testing the actual behaviour of your application.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Test Driven Development (TDD) is a powerful and effective approach for creating high-quality, maintainable, and scalable Flask web applications. By following the principles and best practices outlined in this comprehensive guide, you can leverage TDD to significantly improve your Flask development process and the resulting applications.
In this comprehensive guide, I shared my insights and experiences in implementing Test Driven Development for Flask applications. By following these principles and best practices, you can create robust, maintainable, and scalable Flask applications with confidence. I encourage you to apply TDD in your future Flask projects and experience the benefits it offers.
By embracing TDD in your Flask development projects, you will not only improve the overall quality of your applications but also foster a mindset focused on code quality and maintainability. This mindset is invaluable as you tackle more complex web development challenges and work with teams to create successful applications. Keep honing your TDD skills and continue to explore new testing techniques and tools to stay at the forefront of Flask development and deliver exceptional web applications to your users.

