
Over the past four years, I’ve gained extensive experience building products with Expressjs, Vue.js and React. As I delved deeper into these frameworks, I uncovered fascinating implementation details hidden beneath the surface. For instance, Vue 3’s reactivity system relies on Proxies instead of Object.defineProperty() used in Vue 2, while React employs Proxies in implementing the Virtual DOM. My initial encounter with Proxies was limited to proxy servers, which I mainly used to bypass CORS issues. However, I soon realized that JavaScript Proxies offer the power to observe and manipulate various actions, such as getting or setting a property or invoking a function.
In a previous large-scale JavaScript project, I was tasked with revamping the data validation and error management for a Vue.js client. This undertaking exposed me to computed properties and watchers in Vue and the Reflect.defineProperty() method. Computed properties derive their values from other component data properties, while watchers are functions triggered when a data property changes. This exploration ultimately led me to the JavaScript Reflect API, which simplifies working with Proxies and modifying objects through its built-in methods.
Admittedly, Proxies might seem intimidating for JavaScript beginners. They act like concealed intermediaries between an object and its properties or methods. Nevertheless, gaining proficiency in Proxies and the Reflect API is invaluable for JavaScript developers. Their versatile applications include object inspection, data storage and connection, security enhancement, and problem resolution. By harnessing these features, you can craft clean, easily readable code that maintains a well-organized separation between distinct application components.
In this article, we’ll examine the fundamentals of Proxies and the Reflect API, discuss their benefits in JavaScript applications, and demonstrate their real-world utility by constructing a book rating application.
JavaScript Proxies
A JavaScript Proxy serves as an intermediary between an object and its properties or methods. It allows you to intercept and modify actions performed on the object, such as getting or setting properties, calling functions, or checking if a property exists.
Imagine you have a simple JavaScript object called book:
const book = {
title: 'JavaScript: The Good Parts',
author: 'Douglas Crockford',
rating: 4.5
};You can create a Proxy for the book object that intercepts attempts to read or modify its properties:
const handler = {
get(target, prop) {
console.log(`Getting the ${prop} property.`);
return Reflect.get(target, prop);
},
set(target, prop, value) {
console.log(`Setting the ${prop} property to ${value}.`);
return Reflect.set(target, prop, value);
}
};
const bookProxy = new Proxy(book, handler);Now, when you interact with the bookProxy object, the Proxy will log your actions:
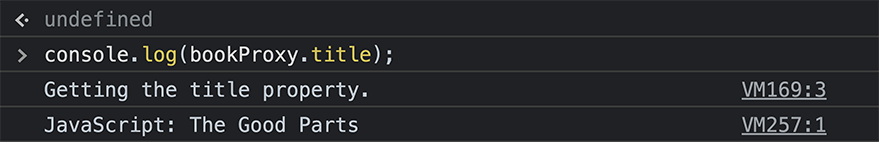
Reflect API
The Reflect API is a built-in JavaScript object that provides methods for performing low-level operations on objects. It works seamlessly with Proxies, allowing you to access and modify properties, invoke functions, or perform other operations on objects more intuitively.
For example, you can use the Reflect API to check if a property exists in an object and, if not, set a default value:
const book = {
title: 'JavaScript: The Good Parts',
author: 'Douglas Crockford'
};
const defaultRating = 4;
if (!Reflect.has(book, 'rating')) {
Reflect.set(book, 'rating', defaultRating);
}
Benefits of Proxies and the Reflect API
By incorporating JavaScript Proxies and the Reflect API into your applications, you can achieve several benefits:
- Enhanced validation and error handling: Proxies can intercept and validate property assignments or function calls, ensuring they adhere to business rules and constraints.
- Better encapsulation: Proxies can hide implementation details by intercepting property access or method calls and redirecting them to the appropriate handler.
- Code maintainability and readability: Proxies and the Reflect API can streamline complex operations on objects, making the code more maintainable and easier to understand.
In the next section, we’ll put these concepts into practice by building a simple book rating application that leverages the power of Proxies and the Reflect API.
Building a Book Rating Application
Now that we have a solid understanding of JavaScript Proxies and the Reflect API, let’s put them to use by building a simple book rating API. This API will allow users to rate books on a scale of 1 to 5.
Let’s break down the features/functionalities.
The API will be built using Node.js and Express, with MongoDB and Mongoose as ORM. It will consist of the following components:
- User Accounts and Authentication: User registration and authentication will be implemented using JSON Web Tokens (JWT), to protect the API endpoints.
- Book Data: A list of books will be stored in the database, along with user ratings.
- API Endpoints: The backend will expose API endpoints for user registration, authentication, fetching book data, and submitting book ratings.
Pre-requisites
You need to have the following:
- Nodejs ≥v16
- Code editor (VS code preferably)
- Knowledge of JavaScript and React
- MongoDB installed
- Postman, ThunderClient (on VSCode), or any API client of your choice
The complete code is on GitHub.
Setting up
First, let’s create a new folder for our project and initialize a new Node.js application:
mkdir book-rating-app cd book-rating-app npm init -y
Next, install the required dependencies:
yarn add express mongoose dotenv nodemon body-parser
Spin up your local MongoDB interactive shell with this command on your terminal.
mongosh
Create a DB by running these prompts:
use bookratingapp;
db.user.insert({title: "About JavaScript", author: "John Stemos", rating: 3})Now you’ve created the DB, head back to the code editor and create a .env file to store environment variables such as the MongoDB connection string.
MONGODB_URI=mongodb://localhost:27017/bookratingapp
Create this directory structure with your terminal from the root of your application.
touch server.js authenticateJWT.js mockData.js seed.js; mkdir modules; cd modules; mkdir book user; cd book; touch book.controller.js book.model.js book.routes.js; cd ..; cd user; touch user.controller.js user.model.js user.routes.js
The directory tree will look like this:
├── authenticateJWT.js ├── mockData.js ├── modules │ ├── book │ │ ├── book.controller.js │ │ ├── book.model.js │ │ └── book.routes.js │ └── user │ ├── user.controller.js │ ├── user.model.js │ └── user.routes.js ├── package.json ├── seed.js ├── server.js └── yarn.lock
For the purpose of this article, we will not go through the implementation details of all the files. You can find that on this GitHub repo.
This is what each of these files does:
authenticateJWT.js: This file contains a middleware function calledauthenticateJWTthat is responsible for verifying and decoding JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) attached to incoming requests. It ensures that users are authenticated before they can access protected routes.mockData.js: This file contains an array of book objects generated using a list of titles, authors, and descriptions. This data is used for seeding the database with some initial book entries.modules/book/book.controller.js: This file contains the controller functions for managing books, including adding a book rating and getting a book by its ID.modules/book/book.model.js: This file defines the Book model and its schema for the MongoDB database, using Mongoose as an ORM. It includes the book’s title, description, author, and an array of ratings.modules/book/book.routes.js: This file contains the routes related to book management, including endpoints for adding a rating to a book and fetching a book by its ID.modules/user/user.controller.js: This file contains the controller functions for managing users, including registering a new user and logging in to an existing user.modules/user/user.model.js: This file defines the User model and its schema for the MongoDB database, using Mongoose as an ORM. It includes the user’s username, email, and password.modules/user/user.routes.js: This file contains the routes related to user management, including endpoints for registering a new user and logging in to an existing user.seed.js: This file is a script that seeds the MongoDB database with the initial book data from themockData.jsfile.server.js: This file is the main entry point of the application. It sets up the Express.js server, connects to the MongoDB database, and imports and uses the routes defined in thebook.routes.jsanduser.routes.jsfiles. It also starts the server and listens for incoming requests on a specified port.
This is the database schema for the application.
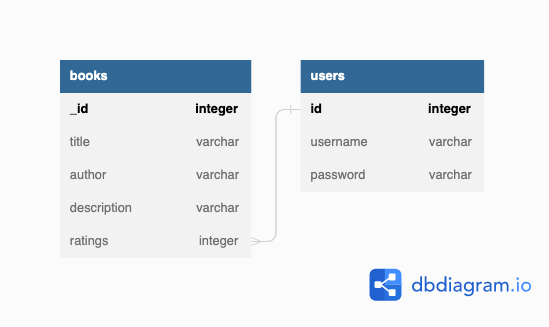
database schema
Testing the API works
After you’ve cloned the repo, install the packages by running:
yarn install OR npm install
Update the .env keys with the appropriate values.
I generated the
JWT_SECRETusing openssl. The command for generating the secret isopenssl rand -hex 16
Generate seed data by running this command
yarn seed
Then start the app server by running:
yarn start
Open your API client and make the following requests:
Register user:
http://localhost:3000/api/users/register
Login User
List books
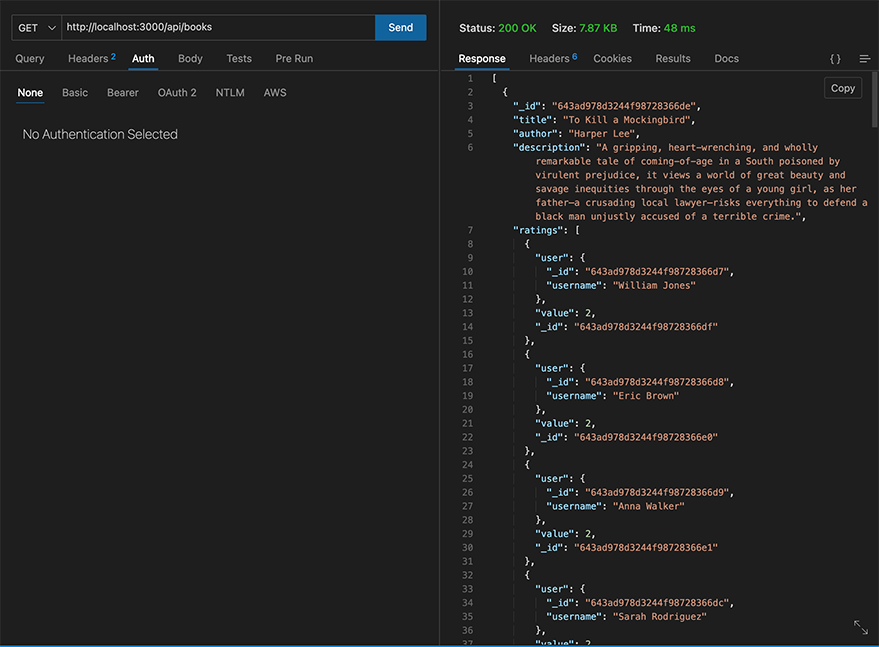
Rate Book
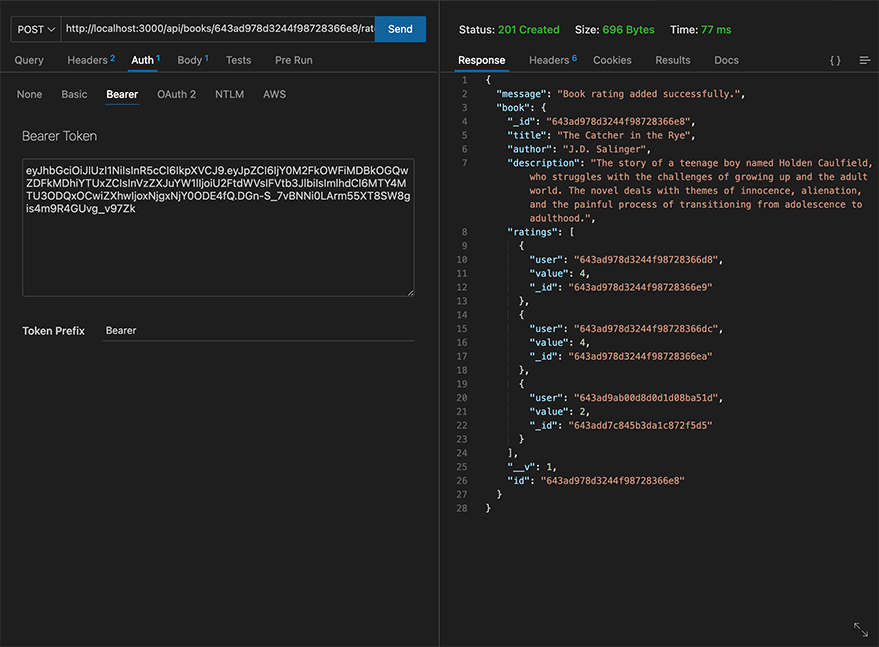
http://localhost:3000/api/books/:bookId/rate
{
"value": 2
}
Enforcing Business Rules Using Proxies
In this section, I’ll show you how Proxies help us ensure that users are logged in before rating a book and that the rating values are within the allowed range.
Creating a Proxy to Intercept Book Rating Requests
Instead of directly interacting with the Book model when a user attempts to rate a book, we can create a Proxy to intercept the rating request. This Proxy can be used to enforce the business rules before allowing the request to proceed. First, let’s create a function that will handle the rating logic and wrap it with a Proxy:
const rateBookHandler = {
apply: async function (target, thisArg, argumentsList) {
// Business rules will be enforced here
return target.apply(thisArg, argumentsList);
},
};
const rateBookFunction = async (userId, bookId, value) => {
// Perform the actual rating logic here
};
const rateBookProxy = new Proxy(rateBookFunction, rateBookHandler);Ensuring the User Is Logged In Before Allowing Them to Rate a Book
With the Proxy in place, we can now enforce our first business rule: ensuring the user is logged in before they can rate a book. We’ll check the userId parameter and make sure it’s a valid user ID:
const rateBookHandler = {
apply: async function (target, thisArg, argumentsList) {
const [userId, bookId, value] = argumentsList;
if (!userId) {
throw new Error("User must be logged in to rate a book.");
}
return target.apply(thisArg, argumentsList);
},
};Validating That the Rating Is Within the Allowed Range (1 to 5)
Next, we’ll enforce our second business rule: validating that the rating value is within the allowed range (1 to 5). We’ll add this check to the apply method of our rateBookHandler:
const rateBookHandler = {
apply: async function (target, thisArg, argumentsList) {
const [userId, bookId, value] = argumentsList;
if (!userId) {
throw new Error("User must be logged in to rate a book.");
}
if (value < 1 || value > 5) {
throw new Error("Rating value must be between 1 and 5.");
}
return target.apply(thisArg, argumentsList);
},
};Now, when a user attempts to rate a book, the Proxy will first enforce the business rules and only allow the request to proceed if the rules are met. This ensures that the application remains consistent and adheres to the desired constraints.
This is the complete code for ./modules/book/book.controller.js
const Book = require("./book.model");
// Fetch the list of books
exports.getBooks = async (req, res) => {
try {
const books = await Book.find().populate("ratings.user", "username");
res.status(200).json(books);
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ message: "Error fetching books.", error });
}
};
// Rate book handler
const rateBookHandler = {
apply: async function (target, thisArg, argumentsList) {
const [userId, bookId, value] = argumentsList;
if (!userId) {
throw new Error("User must be logged in to rate a book.");
}
if (value < 1 || value > 5) {
throw new Error("Rating value must be between 1 and 5.");
}
return target.apply(thisArg, argumentsList);
},
};
const rateBookFunction = async (userId, bookId, value) => {
// Check if the book exists
const book = await Book.findById(bookId);
if (!book) {
throw new Error("Book not found.");
}
// Check if the user has already rated the book
const existingRating = book.ratings.find(
(rating) => rating.user.toString() === userId
);
if (existingRating) {
throw new Error("You have already rated this book.");
}
// Add the new rating to the book
book.ratings.push({ user: userId, value });
await book.save();
return book;
};
const rateBookProxy = new Proxy(rateBookFunction, rateBookHandler);
// Add a rating to a book
exports.rateBook = async (req, res) => {
try {
const userId = req.user.id;
const bookId = req.params.bookId;
const value = req.body.value;
const book = await rateBookProxy(userId, bookId, value);
res.status(201).json({ message: "Book rating added successfully.", book });
} catch (error) {
res
.status(500)
.json({ message: "Error rating book.", error: error.message });
}
};When the rating is above 5 or less than 1:
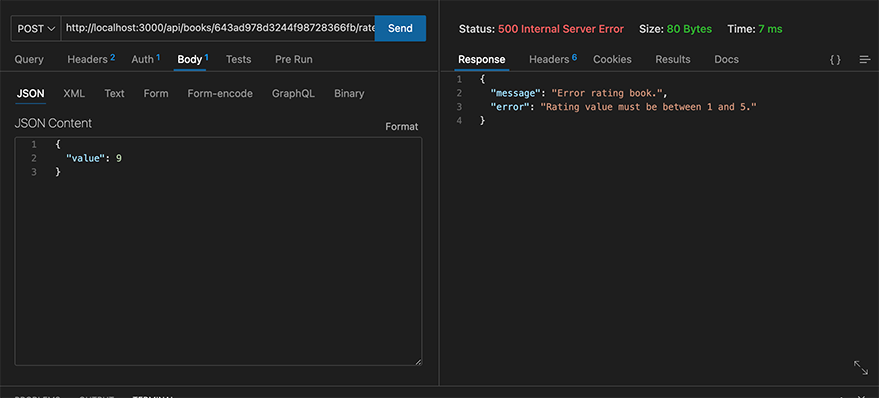
When you’ve already rated a book:
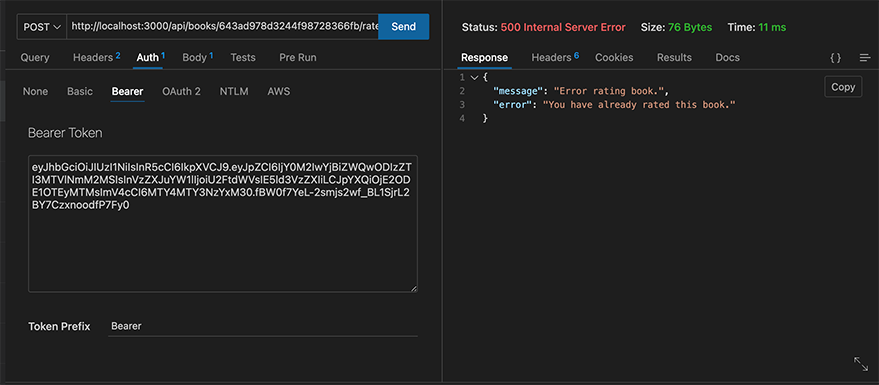
Awesome. Notice how adding more business cases is simple, and the code is readable. The more your code grows, you can create a directory for proxies.
Implementing Validation Logic Using the Reflect API
This section will explore how the Reflect API can help us implement validation logic in the book rating application.
Checking for Existing Book Ratings
One of the use cases for the Reflect API in this application is to check for existing book ratings. Instead of using the traditional approach with find or filter, we can use the Reflect object to inspect the book object’s ratings.
For example, let’s say we rewrite the check for “if a user has already rated a book”. We can use Reflect.get() to retrieve the ratings property of a book object and then use the find() method to check if the user has already rated the book:
const existingRating = Reflect.get(book, 'ratings').find( (rating) => rating.user.toString() === userId );
Preventing Users from Rating the Same Book Multiple Times
Using the Reflect API, we can prevent users from rating the same book multiple times. To enforce this constraint, we will use Reflect.has() method to check if a user’s rating already exists in the book’s ratings array.
// Inside the rateBookFunction
const ratings = Reflect.get(book, 'ratings');
const hasRated = ratings.some((rating) => rating.user.toString() === userId);
if (hasRated) {
throw new Error("You have already rated this book.");
}
// Add the new rating to the book
ratings.push({ user: userId, value });
await book.save();Here, the Reflect.get() method is used to retrieve the ratings array from the book object, and then the some() method to check if the user has already rated the book. If they have, an error is thrown; otherwise, add the new rating to the book and save it.
Best Practices and Pitfalls to Avoid
When working with JavaScript proxies and the Reflect API, it’s important to follow best practices to ensure your code is maintainable and efficient.
Proper error handling: When using Proxies and the Reflect API, ensure you handle errors correctly. This includes catching exceptions, returning meaningful error messages, and using the appropriate HTTP status codes.
Code maintainability and readability: Use Proxies and Reflect API to make your code more maintainable and easier to read. This means using descriptive variable names, commenting your code, and following consistent coding conventions.
Thorough testing: Test your Proxy and Reflect API implementations thoroughly to ensure they are working as expected. This includes unit, integration, and end-to-end testing, as appropriate for your project.
Pitfalls to Avoid
Performance issues: Overusing Proxies or implementing them incorrectly can lead to performance issues in your application. Be mindful of how many Proxies you create and ensure that you are using them efficiently.
Complexity and confusion: Using Proxies and the Reflect API without clear intent or justification can make your code harder to understand. Only use these features when they clearly benefit your application and ensure their purpose is well-documented.
Conflicts between Proxy traps and Reflect API: When using Proxies and the Reflect API together, be aware of potential conflicts between Proxy traps and Reflect methods. Ensure that your code handles these conflicts gracefully and in a way that is consistent with your application’s requirements.
Wrapping up…
JavaScript Proxies and the Reflect API are powerful tools that can significantly enhance the functionality and maintainability of your applications. Through exploring these features and implementing a book rating app, we’ve demonstrated the capabilities and benefits of both Proxies and the Reflect API.
Proxies provide an excellent way to intercept and manipulate operations on objects, while the Reflect API offers a more functional and standardized approach to handling objects and their properties. By using these features in tandem, you can create clean, efficient, and modular code that is easy to understand and maintain.
Throughout this article, we’ve discussed the importance of following best practices, such as proper error handling, code maintainability, and thorough testing, as well as avoiding pitfalls like performance issues, unnecessary complexity, and conflicts between Proxy traps and Reflect methods. By considering these considerations, you can confidently incorporate Proxies and the Reflect API into your projects, unlocking their full potential and elevating your JavaScript development skills.
As you continue to grow as a developer, embracing the power of JavaScript Proxies and the Reflect API will not only enable you to create more robust and adaptable applications but also equip you with a deeper understanding of the language itself.
Resources
- MDN Web Docs – JavaScript Proxies: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Proxy
- MDN Web Docs – Reflect API: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Reflect
- Metaprogramming with Proxies: https://exploringjs.com/deep-js/ch_proxies.html#proxies-explained
- Using the JavaScript Proxy API for Fun and Profit: https://medium.com/dailyjs/how-to-use-javascript-proxies-for-fun-and-profit-365579d4a9f8
- Introduction to “Reflect” API for Metaprogramming in JavaScript: https://medium.com/jspoint/introduction-to-reflect-api-for-metaprogramming-in-javascript-8b5a2bb84282

