JavaScript has become a popular programming language for building engaging and responsive web applications.. As a language that continuously evolves, JavaScript has undergone significant updates and improvements in syntax and functionality, resulting in enhanced power and efficiency. This guide offers a thorough examination of the latest version of JavaScript, including ES6 and other recent advancements.
Why Learn Modern JavaScript?
There are multiple reasons to consider learning up-to-date JavaScript. Firstly, it serves as the foundation for web development, making it essential for creating web applications. Secondly, contemporary JavaScript is more potent and streamlined than its predecessors, enabling the development of intricate applications using fewer code lines. Lastly, JavaScript continually progresses, with novel features and syntax emerging annually. Staying current with contemporary JavaScript allows you to maintain a competitive edge and develop state-of-the-art applications.
What is ES6?
ES6, short for ECMAScript 2015, represents the most recent version of the JavaScript language. It was unveiled in 2015 and brought about various improvements to the language, such as advanced syntax and enhanced functionality. Among the new features that ES6 introduced are:
- Block-scoped variables:Block-scoped variables: ES6 introduced the ‘let’ and ‘const’ keywords for declaring variables, which have block scope instead of function scope, unlike ‘var’. As a result, ‘let’ and ‘const’ can only be accessed within the specific code block where they were defined.
// ES5 (function-scoped)
function myFunction() {
if (true) {
var myVariable = "Hello";
}
console.log(myVariable); // Output: Hello
}
myFunction();
// ES6 (block-scoped)
function myFunction() {
if (true) {
let myVariable = "Hello";
}
console.log(myVariable); // Output: Uncaught ReferenceError: myVariable is not defined
}
myFunction();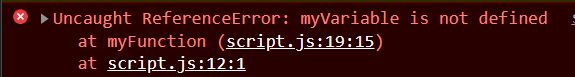
- Arrow functions: These offer a concise way to develop functions utilizing the => operator. Arrow functions exhibit key differences from conventional functions, including the handling of the ‘this’ keyword and the treatment of parameters.
// Regular function
function regAdd(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
console.log(regAdd(2, 3)); // Output: 5
//
const arrAdd = (a, b) => a + b;
console.log(arrAdd(2, 3)); // Output: 5
- Template literals: ES6 brought forth template literals as an alternative way to create strings in JavaScript. They enable more adaptable and legible string manipulation by directly incorporating variables and expressions into the string. Before ES6, string creation required concatenating variables and strings using the plus (+) operator, often resulting in cluttered and difficult-to-read code, particularly with lengthy or intricate strings. Employing template literals, developers can utilize backticks (`) rather than single or double quotes, and directly integrate variables and expressions into the string, enhancing code readability and comprehension.
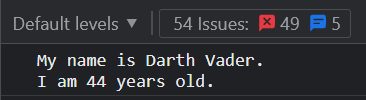
const name = "Darth Vader";
const age = 44;
console.log(`My name is ${name}.
I am ${age} years old.
`)
- Destructuring: ES6 introduced destructuring, providing a new syntax for extracting values from arrays and objects and assigning them to variables. Prior to ES6, values needed to be extracted from arrays and objects by directly accessing their keys or indices, which could lead to verbose and repetitive code, especially when working with complex data structures.
// Without destructuring const myArray = [1, 2, 3]; const firstValue = myArray[0]; const secondValue = myArray[1]; const thirdValue = myArray[2]; console.log(firstValue, secondValue, thirdValue); // Output: 1 2 3 // With destructuring const myArray = [1, 2, 3]; const [firstValue, secondValue, thirdValue] = myArray; console.log(firstValue, secondValue, thirdValue); // Output: 1 2 3
Destructuring objects takes a similar approach by referencing the key name in the object.
const myObject = { name: "Bruce Wayne", age: 48 };
const { name, age } = myObject;
console.log(name, age); // Output: Bruce Wayne 48- Spread and rest operators: These advancements present a new method for managing arrays and objects in JavaScript. They enable the dispersion of array elements and object attributes across other arrays or objects. The spread operator is symbolized by three consecutive dots (…) and can be employed to distribute an array’s elements into another array or an object’s properties into another object.
const myArray = [1, 2, 3]; const newArray = [...myArray, 4, 5, 6]; console.log(newArray); // Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
The rest operator is also denoted by three dots (…) and can be used to gather up the remaining arguments in a function into an array or to gather up the remaining properties of an object into a new object.:
const myObject = {
name:"Saul Goodman",
age: 48,
occupation: "Legal Practitioner" };
const { name, ...rest } = myObject;
console.log(rest); // Output: { age: 48, occupation: "Legal Practitioner"Working with Functions and Classes
ES6 additionally incorporated numerous novel aspects associated with functions and classes.
- Default function parameters enable the definition of default values for function parameters. These help to prevent undefined values when no argument is passed in.
function greet(name = "World") {
console.log(`Hello, ${name}!`);
}
greet(); // Output: Hello, World!
greet("Shelby"); // Output: Hello, Shelby!
- ES6 additionally incorporated classes, facilitating object-oriented programming in JavaScript. Classes offer a means to establish objects with attributes and methods while supporting inheritance and static methods. This enables developers to construct more intricate and structured code arrangements in JavaScript, streamlining their work and maintenance.
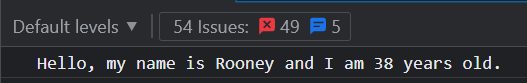
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
sayHello() {
console.log(`Hello, my name is ${this.name} and I am ${this.age} years old.`);
}
}
const Rooney = new Person("Rooney", 38);
Rooney.sayHello(); // Output: Hello, my name is Rooney and I am 38 years old.In this example, ES6 syntax is employed to define a Person class containing a constructor method and a sayHello method. The constructor method establishes the name and age properties for the instance, while the sayHello method outputs a greeting message, inclusive of the instance’s name and age, to the console. Subsequently, we generate an instance of the Person class using the ‘new’ keyword and provide the name and age arguments. Lastly, we invoke the sayHello method on the instance, logging the greeting message to the console. This example exemplifies the definition of a class with properties and methods using ES6 syntax, as well as the creation of a class instance and the invocation of its methods.
Managing Asynchronous Code using Promises and Async/Await
Asynchronous programming is vital in JavaScript, since many tasks, such as retrieving data from a server, demand time to finish.. A difficulty emerges when the remainder of the program must proceed without interruption as the operation takes place, with the operation’s outcome only becoming available once it is completed. Consequently, developers must address asynchronous code without obstructing the program’s execution. ES6 introduced Promises, a potent and adaptable construct that enables more efficient and legible asynchronous code. Promises enable developers to execute asynchronous tasks and handle their results with greater precision and simplicity. Promises also allow for chaining multiple asynchronous operations while handling errors more effectively. Additionally, ES6 presented the Async/Await syntax, which streamlines working with Promises. Async/Await makes writing asynchronous code resemble synchronous code, facilitating easier comprehension and maintenance. This method enables developers to create more succinct and comprehensible code by eliminating callback functions, leading to a more streamlined code organization.
Here’s an example of using promises.
function fetchData() {
console.log("It worked #1");
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
const data = { name: "John Wick", age: 42 };
resolve(data);
}, 3000);
});
}
fetchData()
.then((data) => {
console.log(data);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log(error);
});
console.log("It worked #2");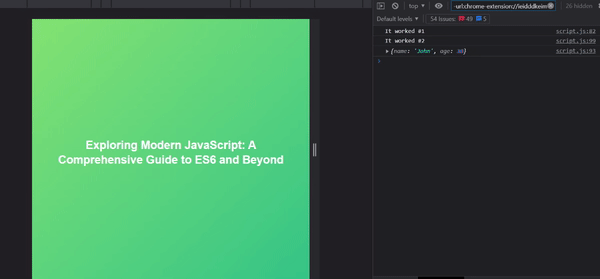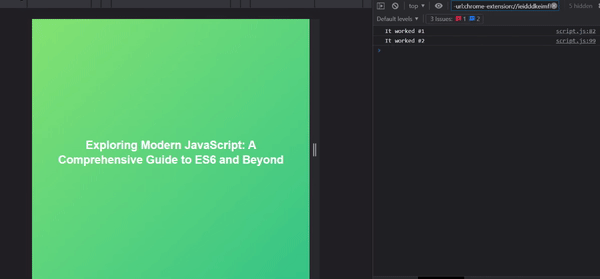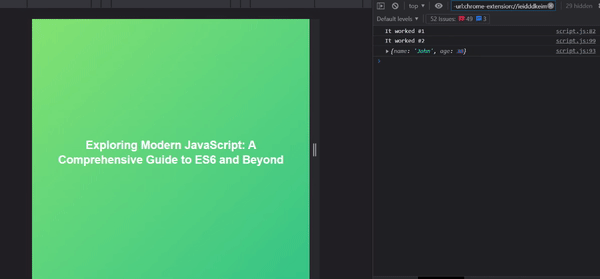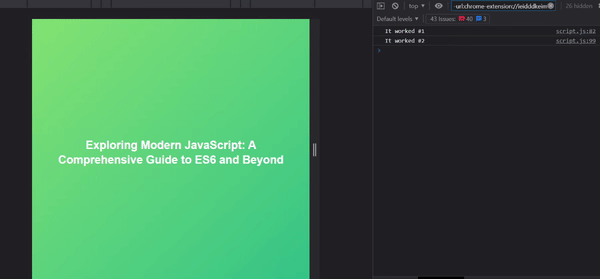
As you can see, we were able to chain methods (the then and catch methods) to our async operation, properly dispatching actions based on the result of the async operation.
Here’s an example of using async/await.
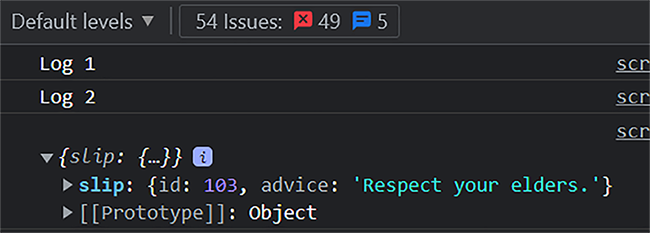
console.log("Log 1");
async function fetchData() {
try {
const response = await fetch("https://api.adviceslip.com/advice");
const data = await response.json();
console.log(data);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
}
console.log("Log 2");
fetchData();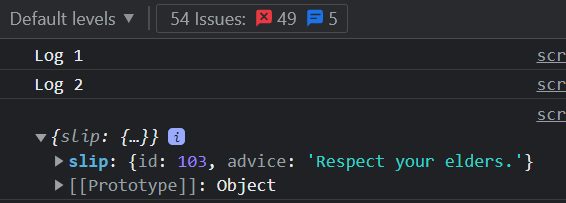
By employing async/await and the try-catch block, we composed asynchronous code that appears synchronous, enhancing its readability and removing the necessity for callback functions.
Modules and Imports
Modules and Imports are essential concepts in JavaScript that assist in arranging and structuring code to be more reusable and modular.. ES6 introduced an improved syntax for creating, exporting, and importing modules across different files, facilitating better code organization and upkeep. ES6 presented a new syntax for exporting and importing modules, encompassing both default and named exports. These capabilities provide enhanced versatility in module creation, allowing for the export of either a single default item or several named items from a module.
// module.js
export const add = (a, b) => a + b;
export const subtract = (a, b) => a - b;
// main.js
import { add, subtract } from './module';
console.log(add(2, 3)); // Output: 5
console.log(subtract(5, 2)); // Output: 3In this example, a module.js file exports two functions: add and subtract. These functions can be imported into other files utilizing the import statement, as demonstrated in the main.js file. Curly braces {} are employed to import named exports from the module. The console.log() statements in the main.js file showcase how the imported functions can be incorporated into the code. In summary, this example illustrates the application of modules and imports in JavaScript to enhance code organization and structure, facilitating more modular and reusable applications.
Advanced Topics in Modern JavaScript
ES6 also introduced several advanced features that can be used to solve more complex programming problems. These features include
- Symbols: Symbols facilitate the creation of distinct object keys that other keys cannot overwrite. This is useful in creating objects that need to have unique keys.
const mySymbol = Symbol("mySymbol");
const myObj = {};
myObj[mySymbol] = "Hello, World!";
console.log(myObj[mySymbol]); // Output: Hello, World!- Iterators: Iterators offer a groundbreaking method for managing data collections in JavaScript. An iterator constitutes an object that supplies a series of values, sequentially, from a collection. This enables more adaptable control over the access and iteration of the values.
const myArray = [1, 2, 3]; const myIterator = myArray[Symbol.iterator](); console.log(myIterator.next().value); // Output: 1 console.log(myIterator.next().value); // Output: 2 console.log(myIterator.next().value); // Output: 3
- Maps: ES6 introduced Maps, a novel data structure that enables the storage of key-value pairs, similar to object literals in JavaScript. Maps present various advantages compared to object literals, including flexible key types and a built-in approach to iterating over entries.
const myMap = new Map();
myMap.set("key1", "value1");
myMap.set("key2", "value2");
console.log(myMap.get("key1")); // Output: value1- Sets: ES6 unveiled Sets, a fresh data structure that facilitates storing collections of distinct values in JavaScript. In contrast to arrays, Sets only allow distinct values, which makes them useful for removing duplicate entries.
const mySet = new Set([1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3]);
console.log(mySet); // Output: Set { 1, 2, 3 }
In this example, a new Set called mySet is created with an array of values, including some duplicates. Nevertheless, the Set maintains only unique values while discarding duplicates. Sets offer multiple built-in methods for data manipulation, such as add() to include new values, delete() to remove values, and has() to verify the presence of a value in the Set.
- Proxies: ES6 introduced Proxies, a potent feature that enables intercepting and modifying operations carried out on JavaScript objects. A Proxy object wraps around another object, providing an abstraction layer that can be employed to control and modify the original object’s actions.
const myObj = {
name: "John",
age: 30
};
const handler = {
get(target, prop) {
console.log(`Getting property "${prop}"`);
return target[prop];
},
set(target, prop, value) {
console.log(`Setting property "${prop}" to "${value}"`);
target[prop] = value;
}
};
const myProxy = new Proxy(myObj, handler);
console.log(myProxy.name); // Output: Getting property "name" n John
myProxy.age = 40; // Output: Setting property "age" to "40"
console.log(myProxy.age); // Output: Getting property "age" n 40In this example, we generate a Proxy object named myProxy, which intercepts and alters the get and set operations performed on the original object myObj. We employ the handler object to specify the custom behavior for each operation and provide it as an argument to the Proxy constructor. In the handler’s get() method, we log a message signifying the accessed property, and then return the property value from the original object. In the set() method, we log a message indicating the property being set, followed by updating the property value in the original object. In summary, Proxies offer a robust method for managing and tailoring object behavior in JavaScript, facilitating advanced meta-programming and reflection. Proxies can intercept and modify operations such as property access, assignment, deletion, function calls, and more.
Beyond ES6: Exploring Modern JavaScript
As a developer, I value the addition of advanced features in modern JavaScript that streamline intricate programming tasks. These features, when combined with a robust understanding of the language, empower developers to address various challenges and devise inventive solutions. In the rapidly changing realm of web development, continuous learning is crucial, and keeping abreast of the most recent JavaScript trends and technologies is vital for generating high-quality code.
ES6 acts as the cornerstone of current JavaScript, with new versions of the language being launched each year, incorporating additional functionality and syntax. ES7 and ES8 introduced further enhancements, such as async iterators and object spread syntax. The JavaScript community is in constant flux, with a multitude of cutting-edge technologies and frameworks building upon the language, including Node.js, React, and Vue.js. Remaining updated with modern JavaScript demands continuous learning and practice, resulting in more potent and efficient code.
The introduction of new features simplifies the creation of concise, understandable, and maintainable code, refining the entire development experience. For example, ES10 presented optional chaining and nullish coalescing operators, which can aid in reducing code complexity when dealing with optional or missing data. In summary, venturing into modern JavaScript beyond ES6 is crucial for any dedicated JavaScript developer who seeks to stay informed about the latest trends and technologies in the language. Persevering in learning and practicing is key to staying relevant and enhancing the quality of your code.
Conclusion
Modern JavaScript has become a critical tool for developers seeking to create efficient, scalable, and maintainable applications in today’s technology-driven world. The language’s constant evolution and transformation are evident in the numerous updates and advancements that have been introduced in recent years, with ES6 and beyond being the most significant milestones. This guide has explored the various features and enhancements introduced in modern JavaScript, from the basics of ES6 to advanced topics such as iterators, generators, and proxies. We have discussed the benefits of using functions and classes, managing asynchronous code with promises and async/await, and utilizing modules and imports for better code organization and reusability. By understanding and mastering the concepts covered in this guide, developers can unlock the full potential of modern JavaScript and leverage its power to build applications that meet the needs of today’s dynamic and ever-changing technological landscape. Embracing a lifelong learning mindset and staying up-to-date with the latest innovations in the language will enable developers to stay ahead of the curve and continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in web development.