As a JavaScript developer, I’ve learned firsthand the importance of mastering error-handling techniques. I’ve seen how even small errors can cause major issues in an application, and how a solid understanding of error handling can prevent those issues from occurring.
However, my personal view is that error handling is not just a necessary component of programming, but an indispensable one. In fact, I believe that mastering error-handling techniques is crucial to building robust, fault-tolerant applications that can gracefully recover from unexpected issues. It’s not just about improving application stability; it’s also about enhancing the overall user experience by ensuring that applications remain responsive and informative even in the face of unforeseen circumstances.
That’s why I am excited to present this comprehensive guide on error handling in JavaScript. It aims to provide an in-depth understanding of error handling in JavaScript by exploring various aspects, such as try/catch statements, throw statements, and custom error classes. Additionally, it delves into best practices and advanced error-handling concepts that developers should be familiar with to create applications capable of handling a wide range of scenarios.
I believe at the conclusion of this guide, you will have the knowledge needed to effectively tackle and resolve errors, allowing you to develop applications that will stand the test of time and provide a seamless experience to users across multiple platforms and environments.
Common JavaScript Errors and Their Causes
JavaScript errors can be broadly categorized into several types, each with its distinct causes and implications. Understanding these errors and their origins is essential to effectively handling and preventing them. These errors include:
- Syntax Errors
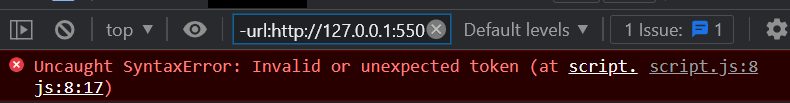
Syntax errors arise when there is a violation of the language’s grammar rules, such as a missing closing bracket, an unclosed string, or a misplaced semicolon. I’ve encountered my fair share of syntax errors in my code, such as forgetting to close a bracket or missing a semicolon. These errors may seem minor, but they can cause major issues in your application if left unchecked. These errors prevent the code from being parsed and executed.
- Missing closing curly brackets
const greet = function(name) {
console.log("Hello, " + name);
// Missing closing bracket here
- Unclosed string
const message = "This is an unclosed string;
2. Type Errors
Type errors occur when a variable or object is used in an improper or incompatible manner, such as calling a non-existent function, attempting toinvoke a non-function value, or accessing a non-existent property.
- Invoking a non-existent function
const person =
{ name: "John Doe",}
;person.greet();
// TypeError: person.greet is not a function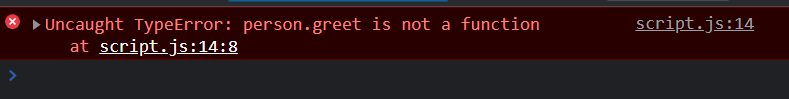
- Accessing a non-existent property
const person =
{ name: "John Doe",};
console.log(person.age.toUpperCase());
// TypeError: Cannot read property 'toUpperCase' of undefined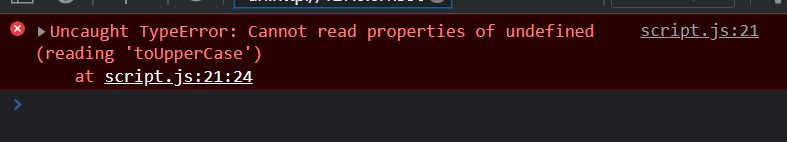
3. Reference Errors
Reference errors happen when a variable is used before it has been declared or is out of scope, resulting in an attempt to access an undefined reference.
- Using an undeclared variable
console.log(undeclaredVariable); // ReferenceError: undeclaredVariable is not defined

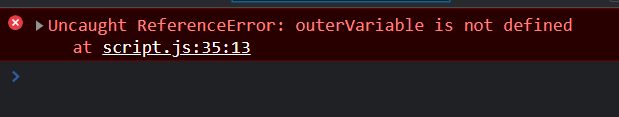
- Accessing a variable out of scope
function outerFunction() {
const outerVariable = "I am outside the inner function.";
function innerFunction() {
console.log(outerVariable); }}
console.log(outerVariable);
// ReferenceError: outerVariable is not definedNote: It is important to note that accessing a variable out of scope throws the same error as using an undeclared variable.
The try/catch Statement: Syntax and Usage
The try/catch statement serves as a robust mechanism for catching and handling exceptions in JavaScript. It comprises a try block, which contains the code that could potentially throw an exception, and a catch block, where the error is addressed. The syntax for the try/catch statement is as follows:
try {
// Code that might throw an exception}
catch (error) { // Handle the error}Let’s examine the following code snippet to better understand the try/catch statement:
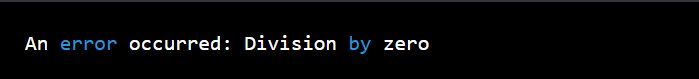
try {
let result = 10 / 0;}
catch (error)
{ console.error("An error occurred:", error.message);}In this example, the try block contains the code that may potentially throw an error, which in this case is dividing 10 by 0. Since dividing by zero is not allowed, an exception is thrown. Consequently, the catch block executes, logging the error message to the console.
In one of my recent projects, I used the try/catch statement to handle errors that occurred when making API calls. By wrapping the API call in a try block and handling the error in the catch block, I was able to gracefully handle any errors that occurred and prevent my application from crashing.
The throw Statement: Creating and Throwing Custom Errors
The throw statement empowers developers to create and throw custom errors, allowing for more granular control over error handling. When an error is thrown, the current execution halts, and control is passed to the nearest catch block. The syntax for throwing an error is as follows:
throw new Error("Error message");Let’s modify the previous example to better understand how the throw statement works:
function divide(a, b)
{ if (b === 0) {
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
} return a / b;}
try { let result = divide(10, 0);
console.log(result);}
catch (error)
{ console.error("An error occurred:", error.message);}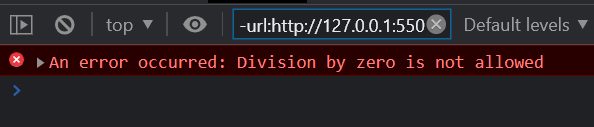
Implementing Custom Error Classes
Custom error classes can be created by extending the built-in Error class, allowing for more specific error types and additional functionality. To create a custom error class, use the following syntax:
class CustomError extends Error {
constructor(message) {
super(message);
this.name = "CustomError";
}}For example, let’s create a custom DivisionByZeroError class:
class DivisionByZeroError extends Error {
constructor() {
super("Division by zero is not allowed");
this.name = "DivisionByZeroError";
}}Now, we can throw and catch our custom error:
function divide(a, b)
{ if (b === 0) {
throw new DivisionByZeroError(); }
return a / b;}
try {
let result = divide(10, 0);
console.log(result);}
catch (error) {
if (error instanceof DivisionByZeroError) {
console.error("Custom error occurred:", error.message); }
else
{ console.error("An unknown error occurred:", error); }}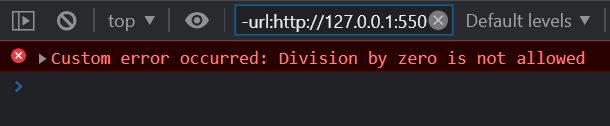
In this example, the catch block checks if the caught error is an instance of DivisionByZeroError and handles it accordingly by logging a specific error message. If it’s not, it assumes an unknown error occurred and logs a more generic error message. In a project I worked on recently, I created a custom error class to handle errors related to user authentication. This allowed me to easily identify and handle authentication errors in my code, improving the overall user experience.
Error Handling Best Practices
To ensure effective error handling in your JavaScript applications, it’s essential to follow best practices. Here are some recommendations, along with examples:
- Always use try/catch blocks to handle errors gracefully and provide useful feedback to the user.
try { let result = divide(10, 0); console.log(result);} catch (error) { console.error("An error occurred:", error.message); // Inform the user about the error and provide guidance}
2. Avoid using empty catch blocks, as they can make debugging difficult.
try {
// Some code that might throw an error}
catch (error) {
// Avoid leaving the catch block empty
console.error("An error occurred:", error);}3. Throw custom errors for better error classification and handling.
function divide(a, b)
{ if (b === 0) {
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
} return a / b;}4. Use custom error classes for more specific error types and additional functionality.
class DivisionByZeroError extends Error {
constructor() {
super("Division by zero is not allowed");
this.name = "DivisionByZeroError"; }}5. Log errors for debugging and monitoring purposes.
try { let result = divide(10, 0);}
catch (error) {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
// Log the error to an external logging service for monitoring}By following these best practices, you can create JavaScript applications that are more resilient to errors, easier to debug, and provide a better user experience.
Advanced Error Handling: Unhandled Promise Rejections
In modern JavaScript, asynchronous operations are often managed using Promises. It is important to fix errors that can come up during these operations. When a Promise rejects and there is no .catch() handler or a try/catch block with async/await, an unhandledrejection event is emitted. You can handle this event with the following syntax:
window.addEventListener("unhandledrejection",
(event) => {
console.error("Unhandled rejection:", event.reason);});This code will log unhandled Promise rejections, enabling you to identify and rectify issues in your code.
Here’s an example demonstrating the handling of unhandled Promise rejections:
function fetchData(url) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// Simulate a rejected Promise
reject(new Error("Network error"));
});}
// fetchData is called without a catch
handlerfetchData("https://api.example.com/data");
// Handle unhandled Promise
rejectionswindow.addEventListener("unhandledrejection", (event) => {
console.error("Unhandled rejection:", event.reason);});In this example, the fetchData function returns a rejected Promise with a “Network error” message. Since there’s no .catch() handler, the unhandledrejection event is emitted. The event listener catches this event and logs the error to the console.
To ensure proper error handling in your JavaScript applications, make sure to handle Promise rejections using .catch() handlers, try/catch blocks with async/await, or by listening for unhandledrejection events.
Debugging Techniques for Error Identification and Resolution
Debugging plays a vital role in identifying and resolving errors in your JavaScript code. Here are some practical techniques and examples that can help you effectively debug your applications:
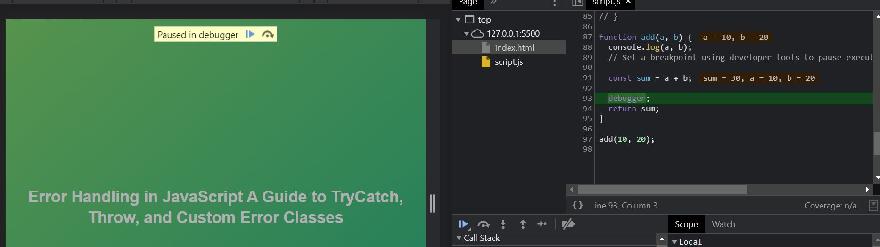
- Use browser developer tools (such as Chrome DevTools or Firefox Developer Tools) to inspect the code, set breakpoints, and step through execution. To view the developer tools on Google Chrome, press the f12 button on our keyboard and a sidebar containing all the developer tools will pop up. On Mac OS, the equivalent keyboard shortcut to access the developer tools in most web browsers is Option + Command + I.

Error Handling in JavaScript Alternatively, you can right-click on your browser page and click on the Inspect option.Developer tools offer features such as breakpoints, step-by-step execution, and call stack inspection, which can help you identify and fix errors in your code.
function add(a, b) { // Set a breakpoint using developer tools to pause execution here const sum = a + b; debugger; return sum}add(10, 20);
Error Handling in JavaScript A Guide to TryCatch, Throw, and Custom Error Classes Viewing this code in a console becomes
- Add console.log() or console.error() statements to trace variable values and errors. Inserting console.log() or console.error() statements in your code can help you monitor the values of variables and track down errors.
function fetchData(url) { // Log the URL being fetched console.log("Fetching data from:", url); // Simulate a network request setTimeout(() => { console.error("Network error"); }, 1000);} fetchData("https://api.example.com/data"); - Use the debugger statement to pause execution at a specific point in the code.
The debugger statement can be used to pause the execution of your code and automatically open developer tools, allowing you to examine variables, step through the code, and more.function processData(data) { // Pause execution using the debugger statement debugger; const processedData = data.map((item) => item.toUpperCase()); return processedData;}processData(["apple", "banana", "orange"]);By employing these debugging techniques, you can identify and resolve errors more efficiently and effectively, resulting in more robust and reliable JavaScript applications.
Practical Examples of Error Handling in JavaScript
- Handling JSON parsing errors
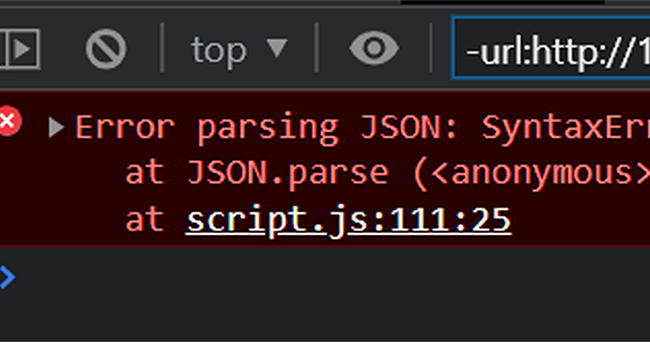
In this example, we demonstrate how to handle errors that may occur while parsing a JSON string.let jsonString = '{"name": "John Doe"}'; try { let jsonObject = JSON.parse(jsonString); console.log("Parsed JSON object:", jsonObject);} catch (error) { console.error("Error parsing JSON:", error);}If the JSON string is malformed or contains errors, the JSON.parse() method will throw a SyntaxError. The try/catch block will catch and handle the error, logging it to the console. Testing this using an object instead of a JSON string;
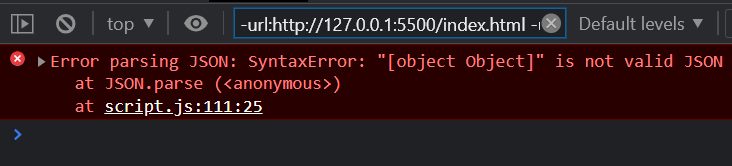
let jsonString = { name: "John Doe" }; try { let jsonObject = JSON.parse(jsonString); console.log("Parsed JSON object:", jsonObject);} catch (error) { console.error("Error parsing JSON:", error);}
Error parsing JSON - Handling network request errors using Promises: In this example, we demonstrate how to handle network request errors using the fetch() API and Promises.
fetch("https://api.example.com/data") .then((response) => { if (!response.ok) { throw new Error("Network response was not ok");} return response.json(); }) .then((data) => { console.log("Fetched data:", data); }) .catch((error) => { console.error("Error fetching data:", error); });If the network request fails or the response is not ok, the error will be caught and handled in the .catch() block.
Handling network request errors using async/await
In this example, we demonstrate how to handle network request errors using the fetch() API and the async/await syntax.
async function fetchData() {
try {
const response = await fetch("https://api.example.com/data");
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error("Network response was not ok");
} const data = await response.json();
console.log("Fetched data:", data);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error fetching data:", error);
}}fetchData();Similar to the previous example, if the network request fails or the response is not ok, the error will be caught and handled in the try/catch block.
Sources
- A Definitive Guide to Handling Errors in JavaScript
- Error handling, “try…catch.
- The Ultimate Guide to JavaScript Error Handling
- JavaScript Try-Catch Error and Exception Handling Guide
- JavaScript Errors Throw and Try to Catch
- Error Handling in JavaScript: a Quick Guide
- Js Docs
- DevDocs
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective error handling is essential in JavaScript programming. Employing try/catch blocks, throw statements and custom error classes enables you to build robust and reliable applications. Furthermore, mastering the handling of unhandled Promise rejections and implementing efficient debugging strategies will significantly enhance your error-handling proficiency.