Defenition: POS – “Point of Sale”. At the point of sale, the merchant calculates the amount owed by the customer, indicates that amount, may prepare an invoice for the customer (which may be a cash register printout), and indicates the options for the customer to make payment.
In the previous chapter, we successfully implemented CRUD operation for the general information of a grocery store. In this chapter, we are going to continue to implement CRUD operation for the Supplier information of a grocery store.
The process is similar to the previous chapter. The idea is to help you understand the CRUD operation in more detail with improvements made in each repeated phase. Repeating Redux operation will surely make us fluent and natural is Redux mechanism use-cases.
Let’s get started!
1. Adding Constants
Similar to our previous tutorials on implementing Redux, we start by defining constants. For that, we need to open ./constants folder and add constants that are used for naming the states as shown in the code snippet below:
// SUPPLIER export const SUPPLIER_FETCHING = "SUPPLIER_FETCHING"; export const SUPPLIER_SUCCESS = "SUPPLIER_SUCCESS"; export const SUPPLIER_FAILED = "SUPPLIER_FAILED"; export const SUPPLIER_CLEAR = "SUPPLIER_CLEAR";
2. Adding Reducer
For implementing reducer, we need to go to ./reducer folder. Then, we need to create a reducer named supplier.reducer.js. The process is similar to previous reducers we have created. In the reducer file, we need to import the constants then define initial state and reducer function as shown in the code snippet below:
import {
SUPPLIER_FETCHING,
SUPPLIER_SUCCESS,
SUPPLIER_FAILED,
SUPPLIER_CLEAR,
} from "../constants";
const initialState = {
isFetching: false,
isError: false,
result: null,
};
export default (state = initialState, { type, payload }) => {
switch (type) {
case SUPPLIER_FETCHING:
return { ...state, isFetching: true, isError: false, result: null };
case SUPPLIER_FAILED:
return { ...state, isFetching: false, isError: true, result: null };
case SUPPLIER_SUCCESS:
return { ...state, isFetching: false, isError: false, result: payload };
case SUPPLIER_CLEAR:
return { ...state, result: null, isFetching: false, isError: false };
default:
return state;
}
};3. Register Reducer
Now, we need to register our reducer to our root reducer in the index.reducer.js file. For that, we need to open index.reducer.js file and include supplierReducer to combineReducers function as shown in the code snippet below:
import supplierReducer from './supplier.reducer'
export default combineReducers({
loginReducer,
registerReducer,
forgotpasswordReducer,
resetpasswordReducer,
posmachineReducer,
branchReducer,
supplierReducer
});4. Creating Action
Next, we need to create a new action file named supplier.action.js file in our ./actions folder. First, we need to import the necessary constants, components, and modules as shown in the code snippet below:
import {
SUPPLIER_FETCHING,
SUPPLIER_SUCCESS,
SUPPLIER_FAILED,
SUPPLIER_CLEAR,
} from "../constants";
import swal from "sweetalert";
import { httpClient } from "./../utils/HttpClient";Now, we need to create a function to trigger the reducer as shown in the code snippet below:
export const setSupplierStateToFetching = () => ({
type: SUPPLIER_FETCHING,
});
export const setSupplierStateToFailed = () => ({
type: SUPPLIER_FAILED,
});
export const setSupplierStateToClear = () => ({
type: SUPPLIER_CLEAR,
});
export const setSupplierStateToSuccess = (payload) => ({
type: SUPPLIER_SUCCESS,
payload,
});Now, we can move to implement the CRUD operation.
4. Create Operation
First, we will implement create operation. For this, we need to create a new component folder named ./supplier and also create a file named action inside it.
One interesting thing about this action is that we will learn to use dispatch to trigger other functions that are not reducer. We are going to use dispatch to reload new data while redirecting back to the index page. The coding implementation is provided in the code snippet below:
export const Create = (values, history) => {
return async (dispatch) => {
dispatch(setSupplierStateToFetching());
const response = await httpClient.post(
process.env.REACT_APP_API_URL + "supplier",
values
);
if (response.data.result == "success") {
dispatch(setSupplierStateToSuccess(response.data));
swal("Success!", response.data.message, "success").then((value) => {
dispatch(setSupplierStateToClear());
history.goBack();
dispatch(Index());
});
} else if (response.data.result === "error") {
dispatch(setSupplierStateToFailed());
swal("Error!", response.data.message, "error");
}
};
};Next, we need to create a new file named create.js and import necessary components as shown ion the code snippet below:
import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react";
import { Formik } from "formik";
import { useDispatch } from "react-redux";
import * as supplierActions from "../../actions/supplier.action";
import * as Yup from "yup";
import { server } from "../../constants";Then, we need to define validation schema using Yup modules as shown in the code snippet below:
const Create_Schema = Yup.object().shape({
name: Yup.string()
.min(2, "name is Too Short!")
.max(50, "name is Too Long!")
.required("name is Required"),
address: Yup.string().required(),
email: Yup.string()
.email("Invalid email")
.required("Email is Required"),
tel: Yup.string().required("Telephone number is required"),
vat: Yup.string().required("VAT number is required"),
});Now for the initial navigation to this component, we want to check user session as shown in the code snippet below:
export default (props) => {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
useEffect(() => {
if (localStorage.getItem(server.TOKEN_KEY) === null) {
return props.history.push("/login");
}
}, []);Next, we need to construct a form using Formik component as shown in the code snippet below:
const showForm = ({
values,
errors,
touched,
handleChange,
handleSubmit,
isSubmitting,
}) => {
return (
<form role="form" onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<div class="card-body">
<div class="row">
<div className="form-group col-md-6 input-group has-feedback">
<input
type="text"
name="name"
onChange={handleChange}
value={values.name}
className="form-control"
placeholder="Supplier Name"
className={
errors.name && touched.name
? "form-control is-invalid"
: "form-control"
}
/>
<div class="input-group-append">
<div class="input-group-text">
<span class="fas fa-user"></span>
</div>
</div>
{errors.name && touched.name ? (
<small id="passwordHelp" class="text-danger">
{errors.name}
</small>
) : null}
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div className="form-group col-md-8 input-group has-feedback">
<textarea
name="address"
onChange={handleChange}
value={values.address}
className="form-control"
placeholder="Supplier Address"
className={
errors.address && touched.address
? "form-control is-invalid"
: "form-control"
}
></textarea>
<div class="input-group-append">
<div class="input-group-text">
<span class="fas fa-building"></span>
</div>
</div>
{errors.address && touched.address ? (
<small id="passwordHelp" class="text-danger">
{errors.address}
</small>
) : null}
</div>
</div>
<div className="form-group input-group has-feedback">
<input
type="text"
name="tel"
onChange={handleChange}
value={values.tel}
className="form-control"
placeholder="Supplier Telephone"
className={
errors.tel && touched.tel
? "form-control is-invalid"
: "form-control"
}
/>
{errors.tel && touched.tel ? (
<small id="passwordHelp" class="text-danger">
{errors.tel}
</small>
) : null}
</div>
<div class="row">
<div className="form-group col-md-6 input-group has-feedback">
<input
type="email"
name="email"
onChange={handleChange}
value={values.email}
className="form-control "
placeholder="Supplier E-mail"
className={
errors.email && touched.email
? "form-control is-invalid"
: "form-control"
}
/>
<div class="input-group-append">
<div class="input-group-text">
<span class="fas fa-envelope"></span>
</div>
</div>
{errors.email && touched.email ? (
<small id="passwordHelp" class="text-danger">
{errors.email}
</small>
) : null}
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div className="form-group col-md-6 input-group has-feedback">
<input
type="text"
name="vat"
onChange={handleChange}
value={values.vat}
className="form-control"
placeholder="Supplier Vat Number"
className={
errors.vat && touched.vat
? "form-control is-invalid"
: "form-control"
}
/>
<div class="input-group-append">
<div class="input-group-text">
<span class="fas fa-user"></span>
</div>
</div>
{errors.vat && touched.vat ? (
<small id="passwordHelp" class="text-danger">
{errors.vat}
</small>
) : null}
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="offset-md-1 col-4">
<button
type="submit"
disabled={isSubmitting}
class="btn btn-primary btn-block"
>
Add
</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form>
);
};Lastly, we need to add the main render() function that wraps all configuration from the object and sends data to the supplierActions.action.js. This will also include validation. The coding implementation inside the render() function is provided in the code snippet below:
return (
<div className="content-wrapper">
<div className="content-header">
<div className="container-fluid">
<div className="row mb-2">
<div className="col-sm-6">
<h1 className="m-0 text-dark">Create Supplier</h1>
</div>
</div>
{/* /.row */}
</div>
{/* /.container-fluid */}
</div>
<div className="content">
<div class="card card-success">
<div class="card-header">
</div>
<Formik
initialValues={{
name: "",
address: "",
tel: '',
}}
onSubmit={(values, { setSubmitting }) => {
console.log(values)
dispatch(supplierActions.Create(values, props.history));
setSubmitting(false);
}}
validationSchema={Create_Schema}
>
{/* {this.showForm()} */}
{(props) => showForm(props)}
</Formik>
</div>
{/* /.card */}
</div>
</div>
);Hence, the resultant form will appear as shown in the screenshot below:
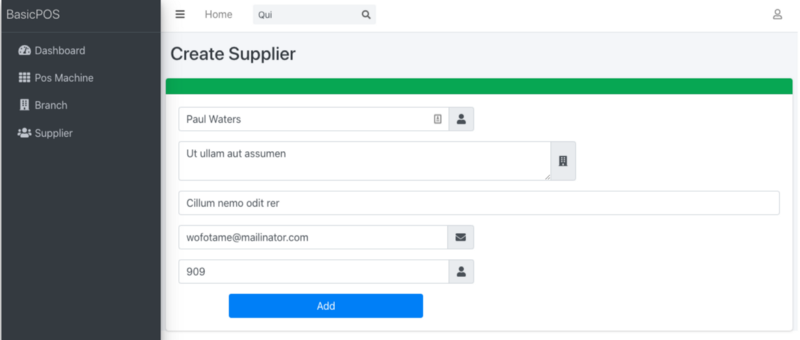
5. Database Schema
Here, we need to open the backend project. For the backend part, we start by creating the new database schema using mongoose package as shown in the code snippet below:
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const schema = mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
address: String,
tel: String,
email: String,
vat: Number,
created: { type: Date, default: Date.now },
});
module.exports = mongoose.model("supplier", schema);Now, we have a new schema to store supplier data.
6. Implementing the Backend API
Next, we need to create a new file named supplier_schema.js and import necessary components for building API endpoint as shown in the code snippet below:
const express = require("express");
const router = express.Router();
const supplier = require("./models/supplier_schema");
const jwt = require("./jwt");Then, we need to a add post method to receive data from the client and create a new row. The implementation of post function is shown in the code snippet below:
router.post("/supplier", async (req, res) => {
try {
let doc = await supplier.create(req.body);
res.json({
result: "success",
message: "Create new Supplier data Successfully",
});
} catch (err) {
console.log(err)
res.json({ result: "error", message: err.msg });
}
});Hence, we can now try to add a new entry from our form as shown in the simulation screenshot below:

Thus, we have successfully implemented the Create operation. Now, we need to get started on Index Operation.
7. Index Operation
Here, what we want to do is to display all of the supplier data after adding new data. Then, we will redirect back to the index page.
We will start on the backend by creating a function that fetches all data from the database as shown in the code snippet below:
router.get("/supplier", jwt.verify, async (req, res) => {
try {
let data = await supplier.find({}).sort({ created: -1 });
res.json({
result: "success",
message: "Fetch Supplier data Successfully",
data: data,
});
} catch (err) {
res.json({ result: "error", message: err.msg });
}
});Now, we need to go back to the supplier component in our React project and create a new index.js. Then, we need to import the necessary functions and packages as shown in the code snippet below:
import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react";
import * as supplierActions from "../../actions/supplier.action";
import { server } from "../../constants";
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from "react-redux";
import { Link } from "react-router-dom";Next, we need to create a new supplier reducer instance. Then, we start by calling the Index function when the component initializes. The coding implementation for this is provided in the code snippet below:
export default (props) => {
const supplierReducer = useSelector(
({ supplierReducer }) => supplierReducer
);
const dispatch = useDispatch();
useEffect(() => {
if (localStorage.getItem(server.TOKEN_KEY) === null) {
return props.history.push("/login");
}
dispatch(supplierActions.Index());
}, []);For UI implementation, we are just going to create a simple table and iterate through the data to display them in the table view. The code to implement the UI portion is provided in the code snippet below:
return (
<div className="content-wrapper">
{/* Content Header (Page header) */}
<div className="content-header">
<div className="container-fluid">
<div className="row mb-2">
<div className="col-sm-6">
<h1 className="m-0 text-dark">Supplier Data</h1>
</div>
</div>
{/* /.row */}
</div>
{/* /.container-fluid */}
</div>
{/* /.content-header */}
<section className="content">
<div className="container-fluid">
<div className="row">
<div className="col-12">
<div className="card">
<div className="card-header">
<h3 className="card-title"></h3>
<div className="card-tools">
<div className="input-group input-group-sm">
<Link to="/supplier/create">
<button type="submit" className="btn btn-default">
<i className="fas fa-plus" />
</button>
</Link>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{/* /.card-header */}
<div className="card-body table-responsive p-0">
<table className="table table-hover text-nowrap">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Vat</th>
<th>Address</th>
<th>Email</th>
<th>TEL.</th>
<th>Action</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{supplierReducer.result ? (
supplierReducer.result.map((data, index) => {
return (
<tr key={index}>
<td>{data.name}</td>
<td>{data.vat}</td>
<td>{data.address}</td>
<td>{data.email}</td>
<td>{data.tel}</td>
<td>
<Link to={"/supplier/update/" + data._id}>
Edit
</Link>
{" | "}
<Link onClick={() => confirmDelete(data._id)}>
Delete
</Link>
</td>
</tr>
);
})
) : (
<td> No data </td>
)}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
{/* /.card-body */}
</div>
{/* /.card */}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</section>
</div>
);Hence, now we can fetch the suppliers data and show it in the table format as shown in the screenshot below:

Hence, our Index operation is complete. Now, we move on to Update/Edit operation.
8. Update Operation
In Update operation, we are required to populate the current data to the form fields.
Re-populating the data…
In the backend project, we need to create an API endpoint for fetching data which is provided in the code snippet below:
router.get("/supplier/:id", async (req, res) => {
try {
let data = await supplier.findById({ _id: req.params.id });
res.json({
result: "success",
message: "Fetch Single Supplier data Successfully",
data: data,
});
} catch (err) {
res.json({ result: "error", message: err.msg });
}
});Back to frontend React project in the supplier action, we need to add the function to fetch the previous data as shown in the code snippet below:
export const getSingleSupplier = (id) => {
return async (dispatch) => {
dispatch(setSupplierStateToFetching());
const response = await httpClient.get(
process.env.REACT_APP_API_URL + "supplier/" + id
);
if (response.data.result == "success") {
dispatch(setSupplierStateToSuccess(response.data.data));
} else if (response.data.result === "error") {
dispatch(setSupplierStateToFailed());
swal("Error!", response.data.message, "error");
}
};
};Next, we need to create a file named update.js. Then, in the supplier component, we need to start by importing necessary components, packages, and modules as shown in the code snippet below:
import React, { useEffect } from "react";
import { Formik } from "formik";
import { useDispatch, useSelector } from "react-redux";
import * as supplierActions from "../../actions/supplier.action";
import * as Yup from "yup";
import { server } from "../../constants";Then, we need to define a new validation schema using Yup module as shown in the code snippet below:
const Create_Schema = Yup.object().shape({
name: Yup.string()
.min(2, "name is Too Short!")
.max(50, "name is Too Long!")
.required("name is Required"),
address: Yup.string().required(),
email: Yup.string()
.email("Invalid email")
.required("Email is Required"),
tel: Yup.string().required("Telephone number is required"),
vat: Yup.string().required("VAT number is required"),
});Now when the component is initially navigated, we need to load the data from API and create supplierReducer instance as shown in the code snippet below:
export default (props) => {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
const supplierReducer = useSelector(
({ supplierReducer }) => supplierReducer
);
useEffect(() => {
if (localStorage.getItem(server.TOKEN_KEY) === null) {
return props.history.push("/login");
}
const { id } = props.match.params;
dispatch(supplierActions.getSingleSupplier(id))
}, []);Then, we need to repopulate the data by using enableReinitialize prop and get data from reducer as shown in the code snippet below:
<Formik
enableReinitialize={true}
initialValues={
supplierReducer.result
? supplierReducer.result
: { name: "", tel: "", address: "", vat: "", email: "" }
}In index.js, we already have a link that we can use to navigate to Update page as shown in the code snippet below:
<Link to={"/supplier/update/" + data._id}>
Edit
</Link>Now, when we click on Edit in the index page, we can navigate to Update page with pre-populated data as shown in the simulation screenshot below:

Next in order to update the data, we need to create a function which accepts PUT request on API and update data using findByIdAndUpdate function provided by mongoose module as shown in the code snippet below:
router.put("/supplier", async (req, res) => {
try {
let doc = await supplier.findByIdAndUpdate(
{ _id: req.body._id },
req.body
);
res.json({
result: "success",
message: "Update Supplier data Successfully",
});
} catch (err) {
res.json({ result: "error", message: err.msg });
}
});Back to the frontend React project, we need to create a new action named Update.js and implement the Update function for updating the data in the database and then navigating back to the index page as shown in the code snippet below:
export const Update = (values, history) => {
return async (dispatch) => {
dispatch(setSupplierStateToFetching());
const response = await httpClient.put(
process.env.REACT_APP_API_URL + "supplier",
values
);
if (response.data.result == "success") {
dispatch(setSupplierStateToClear());
history.goBack();
dispatch(Index());
} else if (response.data.result === "error") {
dispatch(setSupplierStateToFailed());
swal("Error!", response.data.message, "error");
}
};
};Next, we go back to supplier/create.js file and add a new hidden form to receive id that we can use to find the required data as shown in the code snippet below:
<form role="form" onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<div class="card-body">
<div class="row">
<input
type="hidden"
name="_id"
onChange={handleChange}
value={values._id}
/>Lastly, we need to add update action in Formik as well:
<Formik
enableReinitialize={true}
initialValues={
supplierReducer.result
? supplierReducer.result
: { name: "", tel: "",
address: "", vat: "", email: ""
}
}
onSubmit={(values, { setSubmitting }) => {
dispatch(supplierActions.Update(values, props.history));
setSubmitting(false);
}}
validationSchema={Create_Schema}
>Hence, we can now update the data as shown in the simulation screenshot below:

9. Delete Operation
Last but not least is the implementation of the Delete operation. The idea is pretty simple. We just need to create an API endpoint to delete an entry from the table and call the API using the function in the delete button that can be seen in the index page entries.
For Backend API endpoint, we are going to use the delete method which will receive the entry id and delete the data from the table as shown in the code snippet below:
router.delete("/supplier/:id", async (req, res) => {
// console.log(req.params.id);
try {
let response = await supplier.findOneAndDelete({ _id: req.params.id });
res.json({
result: "success",
message: "Delete Supplier data Successfully",
});
} catch (err) {
res.json({ result: "error", message: err.msg });
}
});Then, in the supplier.action.js file, we need to add a new function that sends the delete request to the above API as shown in the code snippet below:
export const Remove = (id) => {
return async (dispatch) => {
console.log("remove");
dispatch(setSupplierStateToFetching());
const response = await httpClient.delete(
process.env.REACT_APP_API_URL + "supplier/" + id
);
if (response.data.result == "success") {
dispatch(setSupplierStateToSuccess());
dispatch(Index());
} else if (response.data.result === "error") {
dispatch(setSupplierStateToFailed());
swal("Error!", response.data.message, "error");
}
};
};In the table from the index page, we need to add a new feature that displays the delete confirmation modal as shown in the code snippet below:
<td>
<Link to={"/supplier/update/" + data._id}>
Edit
</Link>
{" | "}
<Link onClick={() => confirmDelete(data._id)}>
Delete
</Link>
</td>For Modal implementation, we are going to use sweetalert module as shown in the code snippet below:
import swal from "sweetalert";
Now, we need to create a new function that wraps sweetalert module. The function displays the modal and confirms the delete operation. So on the positive confirmation, we need to call the delete operation as shown in the code snippet below:
function confirmDelete(id) {
swal({
title: "Are you sure?",
text: "Once deleted, you will not be able to recover this data!",
icon: "warning",
buttons: true,
dangerMode: true,
}).then((willDelete) => {
if (willDelete) {
dispatch(supplierActions.Remove(id));
swal("Poof! Your Supplier data has been deleted!", {
icon: "success",
});
}
});
}Hence, we will get the result as shown in the simulation screenshot below:

Hence, we can successfully delete an entry now. With this, we have successfully completed the implementation of CRUD operation for Supplier data along with the Redux mechanism.
Conclusion
This chapter can be deemed as a review of the last chapters where we learned how to implement CRUD operation along with Redux functionality. This will make our knowledge on CRUD operation in React using Redux even more fluent and natural. The operations were similar to the previous chapter.
In the next chapter, we will perform CRUD operation again for at least three main data in our app which are Product, Customer, and Employee data. Don’t feel frustrated or bored due to repeated implementation of the same operation and mechanism. For these three important players, we are going to add many tricks for CRUD and improve code quality as well.
All code for this chapter is available on Github for Frontend and Backend.
Stay tuned for the next chapter.
