
Python is well known for its simplicity, readability, and making applications with the fewest lines of code possible. Comprehension is one of Python’s key features that not only targets code simplicity but also better performance. It is a feature of Python by which sequences are constructed from another sequence. It’s critical for us, as Python developers, to understand how comprehensions work. In this article, we will discuss Python Comprehensions and how to optimize your code.
Now, have you seen comprehension anywhere else? Is it something unique to Python?

It is not a new concept as it already had its presence in functional programming (Haskell, Scala, etc). However, it is very rare to find this feature outside of functional programming paradigm.
What is Comprehension?
We have seen some of the definitions of comprehension in Python and its benefits. We saw that we can generate iterable objects in a single expression using comprehensions without regular for loops. But what exactly is a comprehension? How exactly the respective Python implementation looks? To explain them better, let’s talk about different types of comprehensions in Python. Currently, there are four different types of comprehensions supported in Python.
- List comprehensions
- Set comprehensions
- Dictionary comprehensions
- Generator comprehensions
Let’s observe what it looks like to implement comprehension for list creation. We’re using a normal for loop below to iterate through an array and add values in it:
array=[]
for i in range(1000):
array.append(i**2)Below, is the same task done using list comprehension:
array=[i**2 for i in range(1000)]

We effectively reduced the task to a one-liner! Don’t worry about what the above code does for now. The intention was to create an idea of what comprehension can do. We will discuss different types of comprehension in the upcoming sections.
Pre-requisites
This article assumes that you have basic programming knowledge in Python and an understanding of data structures in Python. You need to have Python installed on your system. List comprehension is introduced in Python 2. Set/Dict comprehensions are introduced in Python 3. So, you need to have Python 3 installed on your system in order to try out all the comprehension examples explained in this article.
Why Comprehensions?
One of the benefits of comprehensions is that it will allow us to write less code that is easier to understand. Although programmers from procedural programming background may disagree on this. Programmers who come from a C++/Java background may question the readability of comprehensions. Comprehensions follow the functional programming approach. There’s also performance advantage for comprehensions. It can be proved by calling timeit() method from the timeit package. For example, let us create an array by looping into numbers from 0 to 1000. Below are the two different approaches: One with regular for loop and the other one with comprehensions:
#Use timeit to measure the time required to execute the block of code
import timeit
code1= """
array=[]
for i in range(1000):
array.append(i**2)
"""
print(timeit.timeit(code1,number=1))
code2="""
array=[i**2 for i in range(1000)]
"""
print(timeit.timeit(code2,number=1))Let’s observe the execution time (measured in seconds) for these two code blocks as shown in below snapshot:
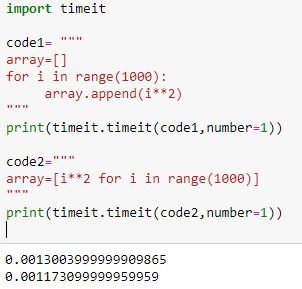
Here we are measuring the time required to execute the code blocks exactly once. The regular for loop (“code1”) takes around 1.3 milliseconds, but the same task with comprehension (“code2”) is accomplished in 1.1 milliseconds. That’s just a matter of 0.2 milliseconds, but it makes sense for a complex application with millions of such computations. Thus comprehension achieves both simplicity and performance at the same time.
List Comprehensions
Now that we have had enough introduction to comprehension, let’s examine how to implement a list comprehensions. Let us take an example where you need to print all prime numbers till number ‘n’. Below is a sample method to check whether the given number is prime:
def isPrime(number):
for i in range(2,number):
if number%i == 0:
return False
return TrueNow, let’s say we need to print all prime numbers that are under n=1000. We can use a list comprehension to create a list of all prime numbers as shown below:
primes = [i for i in range(1,1000) if isPrime(i)] print(primes)
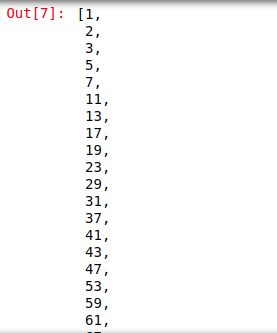
And the output is:
Here, we have only the ‘if’ conditional block, so the actual linking is happening as shown below. Comprehensions start with expressions (‘i’ in the below example).
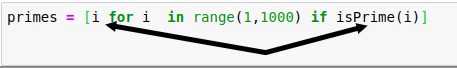
If you need to include both ‘if‘ and ‘else‘ conditional blocks in your comprehension, then you can re-write the code in the below manner. In the below code, we have replaced all non-prime numbers with zero for the demonstration purpose.
primes = [i if isPrime(i) else 0 for i in range(1,1000) ]
At this point, you can think of a list comprehension as a replacement for inbuilt methods such as map(), filter() and lambda functions. We can generate new lists, iterate through existing lists, and perform flattening on multi-dimensional lists using list comprehension.
Set Comprehensions
A set comprehension is no different from a list comprehension except that it creates a set instead of a list. Let’s take the same example discussed earlier and generate a set using a set comprehension.
primes = {i for i in range(1,1000) if isPrime(i)}
print(primes)
And the output is:
At this moment, you would feel like…

Well, we haven’t reached the best part yet. Stay tuned till the end!
Dictionary Comprehensions
Just like we created lists/sets using comprehension, we can also create dictionaries using dictionary comprehensions. Let us consider the below example. We have a list of students and a mark list indicating the scores for each student.
students = ['student1','student2','student3','student4'] marks = [45, 78, 12, 14]
So, our target is to create a dictionary mapping student scores to respective students. The regular approach would be to loop over the list length (student/marks) followed by assigning key values:
size = len(students)
mapping={}
for i in range(size):
mapping[students[i]]=marks[i]The same can be achieved using a dictionary comprehension as shown below:
mapping = {students[i]:marks[i] for i in range(len(students))}Here is what you will see while printing them.
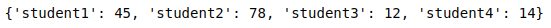
Now let’s say we want to create a dictionary with students who scored more than 40. We can achieve it using a dictionary comprehension as shown below:
students_after_filter = {k:v for k,v in mapping.items() if v>40}Note that mapping.items() will return a list of iterable key-value pairs.
So, now you should see the below output:
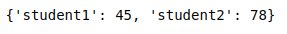
Generator Comprehensions
Generator comprehensions are similar to the list/set comprehensions, the only difference is that we use circular brackets in a generator comprehension. The motive behind the introduction of a generator comprehension in Python is to have a memory-efficient approach in place. In a generator comprehension, memory is allotted on the go and not on the startup. In the list/set comprehensions, we generate the entire elements first and keep them in memory. However, a generator comprehension employs a lazy-loading approach. It is worth talking a bit about a generator before we jump into the discussion of a generator comprehension. A generator is a function with a yield statement instead of returning a value. The peculiarity of a yield statement is that we can pause the method at any time and resume it back at a later point if needed. Let’s create a generator method to generate infinite prime numbers on demand.
import itertools
def genPrime():
for i in itertools.count(1):
if isPrime(i):
yield iWe have imported an itertools package for a specific purpose. Note that, itertools.count() creates an iterable object with a capability of holding infinite series of elements. The idea is to generate a series of elements until a condition is met without mentioning any upper bound.
itertools.count()-> 0,1,2,3,4,5,... itertools.count(1) -> 1,2,3,4,5,6,... itertools.count(1, 2) -> 1,3,5,7,9,...
Let’s create another method to print out prime numbers:
def print_prime_numbers(f,n):
for prime,_ in zip(f, range(n)):
print(prime)We can print prime numbers under the given range as shown below (n=10 in the below example):
print_prime_numbers(genPrime(),10)
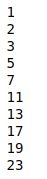
Note that we have two methods here: one to generate infinite prime numbers and the other one to print the prime numbers. Now, what if we don’t have to create those methods with yield statements? Yes, that’s where a generator comprehension comes into play. We can skip creating methods with a yield keyword by using a generator comprehension. Generator method discussed earlier can be converted to a one-liner as shown below:
prime_numbers = (i for i in itertools.count(1) if isPrime(i))
Print the prime numbers to verify the results:
print_prime_numbers(prime_numbers,10)
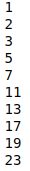
In a nutshell, a generator comprehension deals with only one item at a time and only when there’s a demand. For the same reason, a generator comprehension is memory-efficient in comparison to a list/set comprehension. We can prove this with a timeit package.
import timeit code1=""" numbers = (i for i in range(1,1000)) """ code2=""" numbers = [i for i in range(1,1000)] """ print(timeit.timeit(code1,number=1000)) print(timeit.timeit(code2,number=1000))
We observe below execution time (measured in seconds and for 1000 executions) for the above-mentioned code blocks:
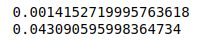
As you can see, that’s a significant difference between these two, which indicates the efficiency of a generator comprehension.

But again, it depends on the requirements. If you prefer performance and only need to iterate once through the objects, then simply use a generator comprehension. If you need to store iterable objects and need to iterate through it multiple times, then better off with a list/set comprehension. And with this, we have discussed all the four comprehension types in Python.
We have discussed very basic examples of comprehension types in Python. For all those procedural programmers out there who are learning Python, the first thing you might want to practice is to write comprehensions instead of regular loop constructs. You may start with a regular procedural approach first and then convert it to use comprehension. Eventually, you will get addicted to the comfort! So, that’s it for now and hope you find this article useful.

