So you have learned the basics of JavaScript and want to move on to learning Data Structures. The motivation for learning/understanding Data Structures can vary since few of us, want to learn to improve our skills, few of us want to learn to get a developer job, and few of us want to learn because well, it seems exciting. Whatever the motivation might be, learning and understanding Data Structures can be a tedious and frustrating task if one does not understand why one should use data structures and when to use them.
This article deals with the when to use them part. In this article, we will learn about Arrays and Objects. We will try to understand when to choose one Data Structure over another by using the Big O notation.
Arrays
One of the most widely used data structures is arrays (also called lists in few languages). Data inside an array gets structured in an orderly fashion i.e the first element inside an array gets stored at index 0, the second element at index 1, and so on. JavaScript provides us with some built-in data structures and an array is one of them.
In JavaScript, the easiest way to define an array is:
let arr = [ ];
The above line of code creates a dynamic array(unknown length). To get the gist of how elements of an array get stored inside memory, let’s take a look at an example:
let arr = ["John", "Lily", "William", "Cindy"];
In the above example, we are creating an array containing names. The names inside the memory get stored like this:
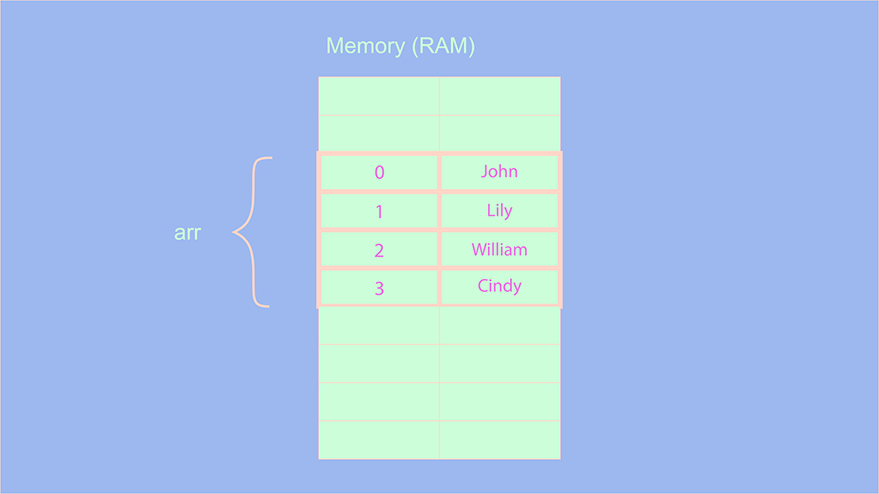
To understand how an array works, let us perform a few operations:
Adding an element:
In a JavaScript array, we have different operations for adding an element at the end, at the front and also, at a specific index.
Adding an element at the end:
JavaScript provides a default property when we define an array that is length property. So presently, the length property holds the value 4, since we have that many elements inside an array. Along with the length property, JS also provides a push( ) method. Using this method, we can directly add an element at the end.
For example:
arr.push("Jake");The name “Jake” gets added to the end:
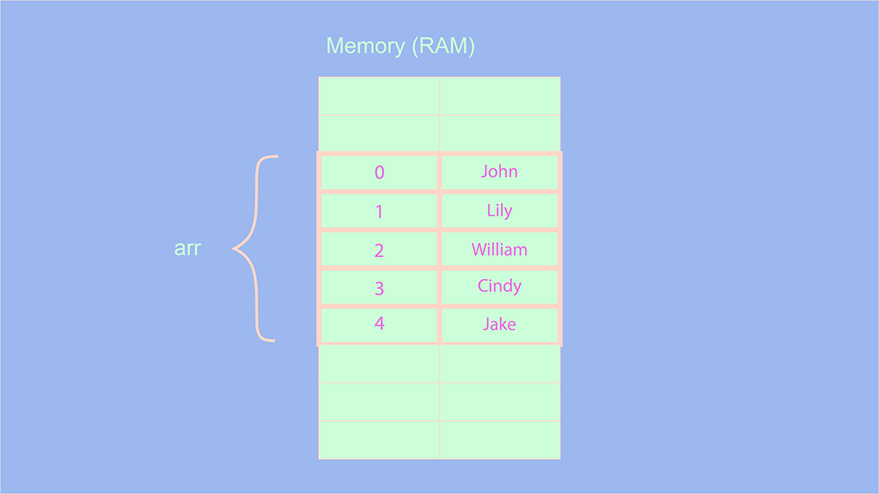
So what will be the complexity of this command? We know that by default, JavaScript provides the length property, the push( ) is equivalent to using the following command:
arr[arr.length-1] = "Jake"
Since we always have access to the length property of an array, no matter how big an array gets, adding an element to the end will always have the complexity of O(1).
Adding an element to the front:
For this operation, JavaScript provides a default method called unshift( ). This method adds an element to the beginning of an array.
let arr = ["John", "Lily", "William", "Cindy"];
arr.unshift("Robert");
console.log(arr); // ["Robert","John", "Lily", "William", "Cindy"];Now, although it might seem like the unshift method, just like the push( ) method has a complexity of O(1) because we are just adding an element to the front. But that’s not the case, let us examine what happens when we use the unshift method:
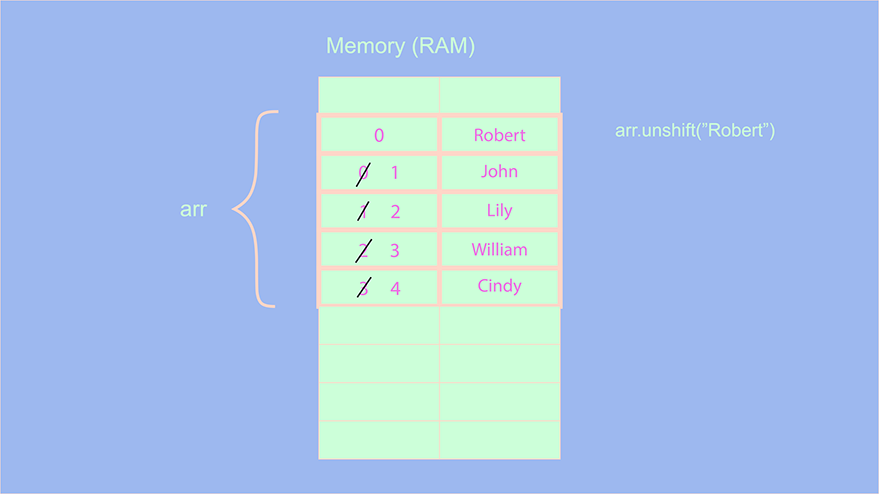
In the above image, when we use the unshift method, the indexes of all the elements should be incremented or shifted by 1. We are using an array that is of shorter length. Imagine using an array of substantial length, then, using a method like unshift leads to delays, since we have to shift indexes of every element of the array. Therefore, the complexity of the unshift operation is O(n). Use the unshift method wisely if you are handling arrays of larger length.Adding an element at a particular index:
For performing this operation, we can use a JavaScript method called splice( ) which has the following syntax:
splice(startingIndex, deleteCount, elementToBeInserted);
Since we are adding an element, the deleteCount will be 0.
Let’s add an element to the index 2:
let arr = ["John","Lily","William","Cindy"]; arr.splice(2,0,"Janice"); console.log(arr); // ["John","Lily","Janice","William","Cindy"];
What do you think the complexity of this operation would be? In the above operation, we are adding the element at index 2, therefore, all the succeeding elements after index 2 will have to be incremented or shifted by 1 (including the element which was previously at index 2).
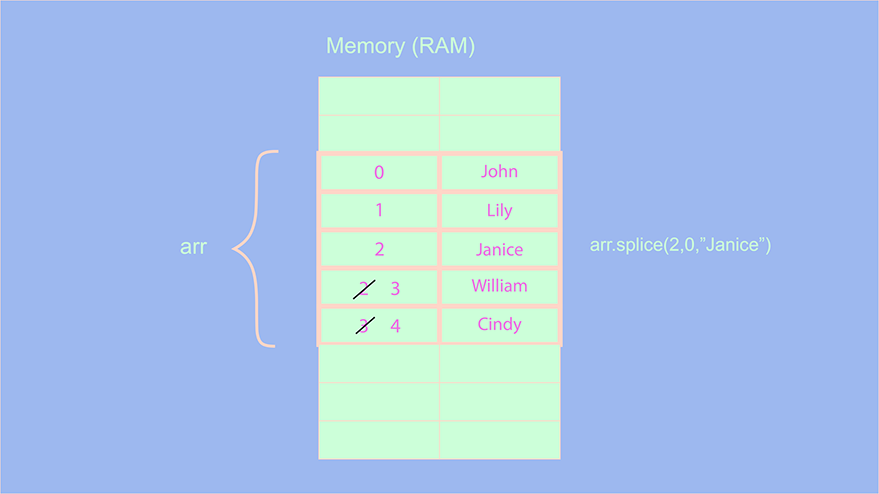
One can observe that we are not shifting or incrementing indexes of all the elements but rather incrementing the indexes of the elements after the index 2. Does this mean that the complexity of this operation is O(n/2)? The answer is no. According to Big O rules,constants get removed from the complexity, and also, we should consider the worst-case scenario. Therefore the complexity of this operation is O(n).
Deleting an element:
Just like adding, deletion of an element can be done at various places, at the end, at the start and a particular index.
Deleting at the end:
Like push( ), JavaScript provides a default method called pop( ) to delete/remove elements at the end of an array.
let arr = ["Janice", "Gillian", "Harvey", "Tom"]; arr.pop( ); console.log(arr); // ["Janice", "Gillian", "Harvey"]; arr.pop( ); console.log(arr); // ["Janice", "Gillian"];
This operation has a complexity of O(1). Since, no matter how big an array gets, removing the last element will not require changing indexes of any element in the array.
Deleting at the front:
For this operation, we have a default method called shift( ). This method deletes the first element of an array.
let arr = ["John", "Lily","William","Cindy"]; arr.shift( ); console.log(arr); // ["Lily","William","Cindy"] arr.shift( ); console.log(arr); // ["William","Cindy"]
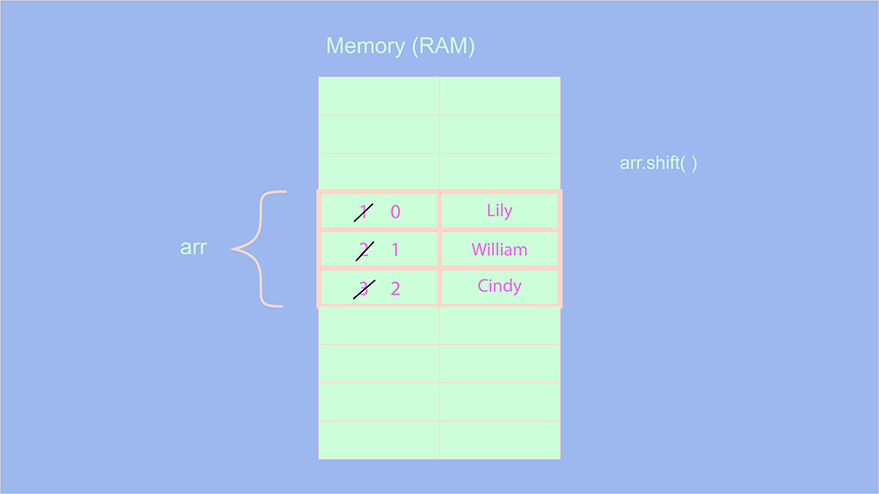
Since we have already covered the unshift method, I think it is quite obvious to guess the complexity of shift( ) operation will be O(n) since after deleting the first element, we have to shift or decrement the indexes of all the elements by 1.
Deleting at a specific index:
For this operation, we are going to the splice( ) method again but, this time, we are going to use only the first two parameters since we are not going to add a new element at that index.
let arr = ["Apple", "Orange", "Pear", "Banana","Watermelon"]; arr.splice(2,1); console.log(arr); // ["Apple", "Orange", "Banana","Watermelon"]
Similar to the splice operation that was performed for adding elements, in this operation we are decrementing or shifting the indexes of elements after the index 2. So this operation has the complexity of O(n).
Lookup:
Lookup is nothing but accessing an element of the array. We can access the elements of an array by using the square bracket notation (ex:- arr[4]).
What do you think is the complexity of this operation? Let’s understand that by an example:
let fruits = ["Apple", "Orange", "Pear"];
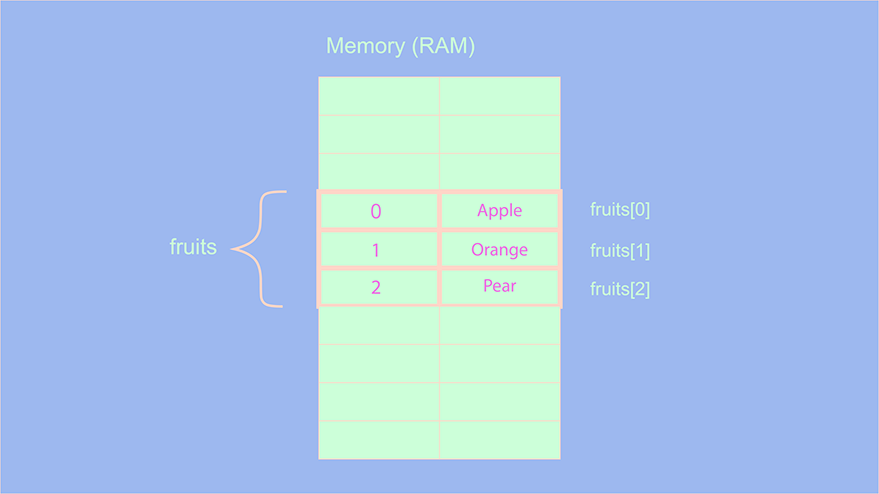
We have seen previously that all the elements of an array are stored in sequential order and are always grouped together. So if we perform the operation fruits[1] we are telling our computer to find the array named fruits and grab the second element (arrays start at index 0). Since they are stored sequentially, the computer does not have to look around the complete memory slot to find the element, it can directly look inside the fruits array since all the elements will be grouped together in order. Therefore, the lookup operation in an array is of complexity O(1).
Now that we have completed the basic operations on an array, let’s conclude when can we use arrays:
Arrays are suitable when you are going to perform operations like push( ) (Adding element at the end) and pop( ) (Removing elements from the end) since these operations are of complexity O(1).
Other than this, lookup operations can be performed really fast in arrays.
Performing operations like adding/deleting elements at a specific index or at the front can be quite slow when you are using arrays since they are of complexity O(n).
Objects
Like arrays, Objects are also one of the most commonly used data structures. Objects are a type of Hash Table that allows us to store key-value pairs instead of storing values at numbered indexes as we have seen in arrays.
The easiest way to define an object is:
let obj1 = { };Example:
let student = {
name: "Vivek",
age: 13,
class: 8
}
Let’s understand how the above object gets stored in memory,
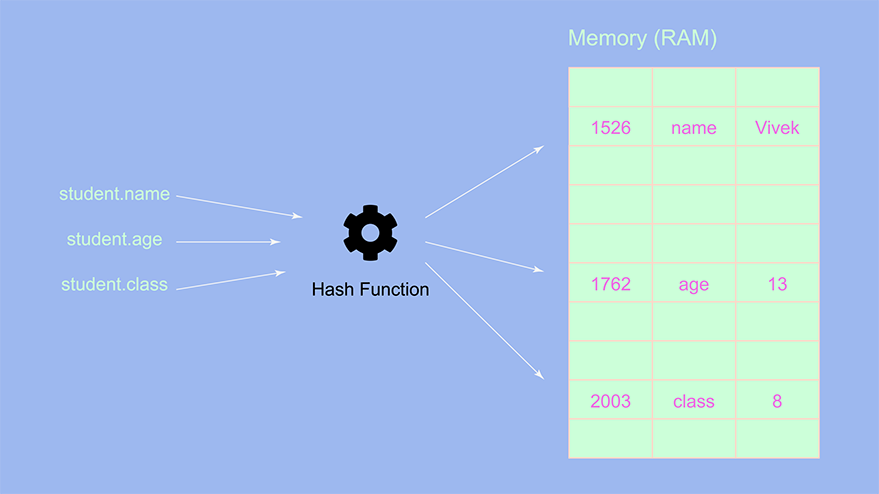
One can observe that the key-value pairs of the object get stored randomly, unlike arrays where all the elements get stored together. That is the main difference when comparing arrays with objects, in objects, the key-value pairs are stored randomly in memory.
We also see that there is a hash function. So what does this hash function do? The hash function takes in each key from the object and, it generates a hashed value, then this hashed value gets converted to an address space where we store the key-value pair.
For example if we add the following key-value pair to the student object:
student.rollNumber = 322;
The rollNumber key goes through the hash function and gets converted to an address space where both the key and value are stored.
Now that we have got a basic idea of how objects get stored in memory, let’s perform some operations.
Adding:
For objects, we don’t have separate methods for adding elements to the front or back, since all the key-value pairs are stored randomly. There is only one operation that is of adding a new key-value pair to the object.
Example:
student.parentName = "Narendra Singh Bisht";
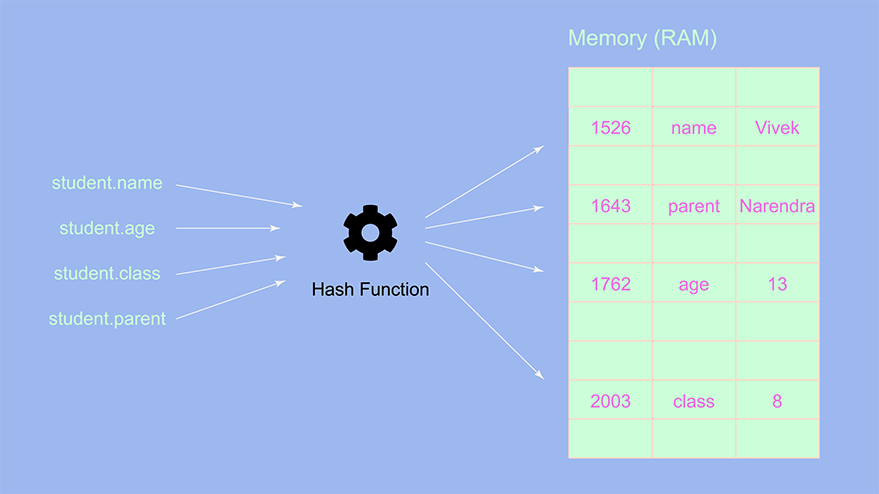
From the above image we can conclude that the complexity of this operation will always be O(1) since we don’t have to change any indexes or manipulate the object itself, we can directly add a key-value pair and it gets stored at a random address space.
Deleting:
Just like adding an element, deletion operation on objects is very simple and is of complexity O(1). Since, we don’t have to change or manipulate objects while deleting.
delete student.parentName
Lookup:
This will be quite obvious now that the lookups as well will be of complexity O(1) since here as well we are just accessing the value with the help of keys.
One of the ways to access value in objects:
student.class
Whoaaa!! adding, deleting, and lookups in objects have a complexity of O(1)??? so can we conclude we should use objects every single time instead of arrays? The answer is no. Although objects are awesome, there is a small condition that needs to be taken into account while using objects. The condition is called Hash Collisions. This condition is not something which should be handled all the time while using objects but understanding this condition will help us understand objects better.
So what are hash collisions?
When we define an object, our computer allocates some space for the object in the memory. We need to remember that the space inside our memory is limited so there are chances that two or more key-value pairs might have the same address space.This condition is called a Hash Collision. To understand it better let’s have a look at an example:
Let’s imagine that 5 blocks of space gets allocated for the following object:
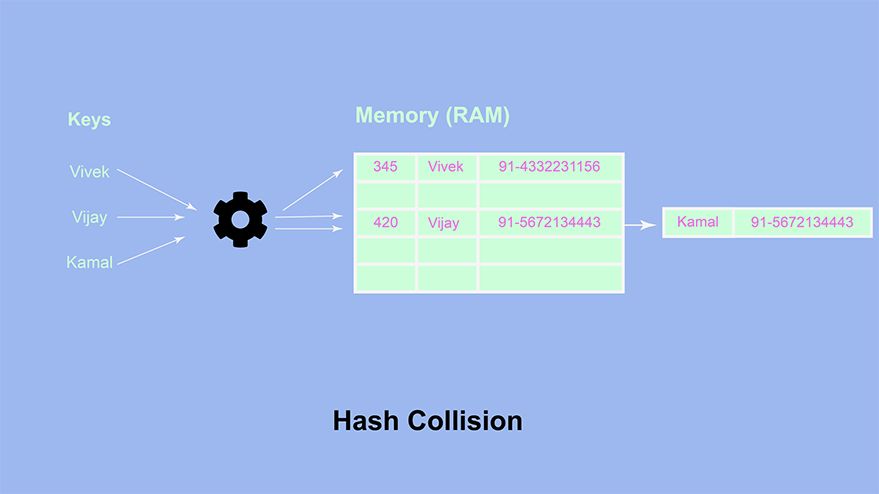
We observe that two key-value pairs are stored at the same address space. How can this happen? This happens when the hash function returns a hash value that converts into the same address space for multiple keys. Due to this, multiple keys get mapped to the same address space. Due to hash collisions, adding and accessing values can be of complexity O(n) since to access a particular value, we might have to loop through various key-value pairs.
Hash collisions are not something that we need to handle every single time we use objects. It is a condition that helps us understand that objects are not a perfect data structure.
Other than Hash Collisions, there is another condition that we have to be careful about when using objects. JavaScript provides us a built-in method for looping through keys of objects called keys( ) method. We can apply this method on any object like this: object1.keys( ). The keys( ) method iterates through the object and returns all the keys. Although this method seems simple, we need to understand that key-value pairs in objects are stored randomly in memory therefore, iterating through the object becomes a slower task unlike iterating through arrays where they are grouped together in order.
So let’s conclude objects. We can use objects when we want to perform actions like adding, deleting and accessing an element but, while using objects we need to be careful about iterating through an object because it can be time consuming. Along with iterating, we should also understand that at times, there are chances that the addition and accessing operations can be of complexity O(n) due to hash collisions.
There you go, we have discussed how arrays and objects work behind the scenes. I wouldn’t say that this is the complete picture of how arrays and objects work but by understanding how basic operations are performed on these data structures we can start analysing when to choose one data structure over another.