Hey all! Our topic for today is Data Streams In Node.js. We will try to learn all the aspects in details for the reason it turns out that on the one hand, common browser JavaScript development lack streams. And on the other hand, knowing and understanding stream principles is necessary for seamless server development because a stream is a versatile way of work with data sources universally used.
We can define two general stream types. The first one is
stream.Readable
It is a built-in class providing streams for reading. Generally, this type itself is never used, while its descendants are quite popular – in particular, we use fs.ReadStream to read from a file. To read from a visitor’s request for its handling, there is a special object familiar to us under its name req, which is the first argument of a request handler.
Stream.Writable
It is a versatile writing method. The very stream.Writable is rarely used, but its descendants – fs.WriteStream and res – are quite common.
There are some other stream types, but the most popular are these two and their variations.
The best way to understand streams is to see how they work in practice. So, right now we’ll start with using fs.ReadStream for reading a file. Let us create a file fs.js:
var fs = require('fs');
// fs.ReadStream nherits from stream.Readable
var stream = new fs.ReadStream(__filename);
stream.on('readable', function() {
var data = stream.read();
console.log(data);
});
stream.on('end', function() {
console.log("THE END");
});So, we get the module fs connected and create a stream:
var fs = require('fs');
var stream = new fs.ReadStream(__filename);Stream is a JavaScript object receiving information about our resource – in our case, it is a path to the file (__filename) – which can work with this resource. fs.ReadStream implements a standard reading interface described in the stream.Readable class. Let us have a detailed look.
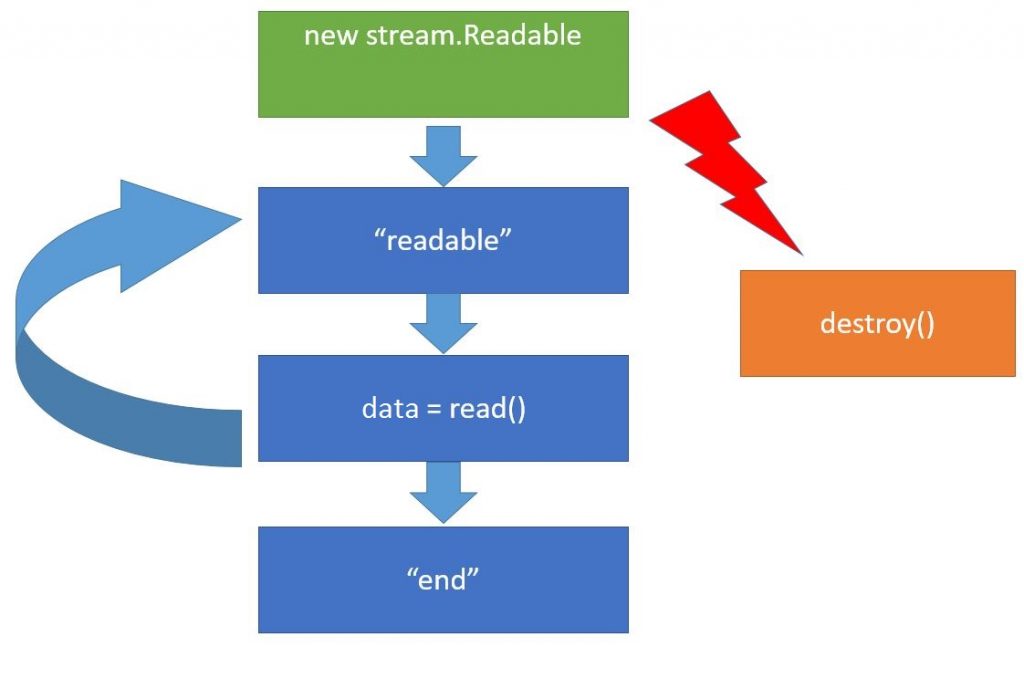
When a stream object new stream.Readable is created, it gets connected to the data source, which is file in our case, and tries to start reading from it. Once it has read something, it imitates the event readable. This event means that all the data have been computed and are contained within an inner stream buffer that can be received using the call read(). Then we can do something with data and wait for the next readable. This cycle will be the same.
Whenever the data source gets empty (however, there are certain sources that never get empty – for example, a random data generator), the file size is limited, so we will have the end, event in the very end meaning there will be no data anymore. Moreover we can call the method destroy() at any step of working with the stream. This method means we do not need the stream anymore and it can be closed, as well as the respective data sources and everything can be cleaned up.
So, let us refer to the original code. Here we create ReadStream, and it immediately wants to open up a file:
var stream = new fs.ReadStream(__filename);
but in our case it doesn’t necessarily mean the same string because any input/output-related operation is performed through libUV. At the same time, libUV has a structure that enables all synchronous input/output handlers to get implemented during the next event loop iteration, or once the current JavaScript has finished its work. It means, we can seamlessly use all handlers knowing that they will be installed prior to the moment the first data fragment gets read. Launch fs.js.
Look at what has appeared in the console. The first one was the event readable. It outputted data. Right now it is an ordinary buffer, but we can transform it to the string by specifying the coding directly upon the stream opening.
var stream = new fs.ReadStream(__filename, {encoding: 'utf-8'});Thus, the modification will be automatic. When a file ends, the event end outputs THE END in the console. Here the file ended almost immediately because it was small at the moment. Let us modify our example a little bit by making a file big.html out of the current file contained in the current directory. Download this HTML file from our repository together with the other lesson materials.
Launch it. The file big.html is big, so the event readable has been initiated several times, and every time we received another data fragment as a buffer. So, let us calculate its length:
var fs = require('fs');
// fs.ReadStream nherits from stream.Readable
var stream = new fs.ReadStream("big.html");
stream.on('readable', function() {
var data = stream.read();
if (data){
console.log(data.length);
}
else {
console.log('data is null')
}
});
stream.on('end', function() {
console.log("THE END");
});
Get it launched. These numbers are the read file fragment length. When a stream opens a file, it reads only its part, but not the whole file, and inserts it into its internal variable. The maximum size is exactly 64 KB. Until we call stream.Read, it won’t read further. Once we’ve received the data, the internal buffer cleans up and can be ready for reading another abstract, etc. The last abstract length is 60,959 B. This example has vividly demonstrated the key advantages of stream usage. They help save memory. Whatever is the size our big file, we still handle only its small part at a moment. The second less obvious advantage is versatility of its interface. Here we use the stream ReadStream from the file. But we can replace it any time by any stream from our resource:
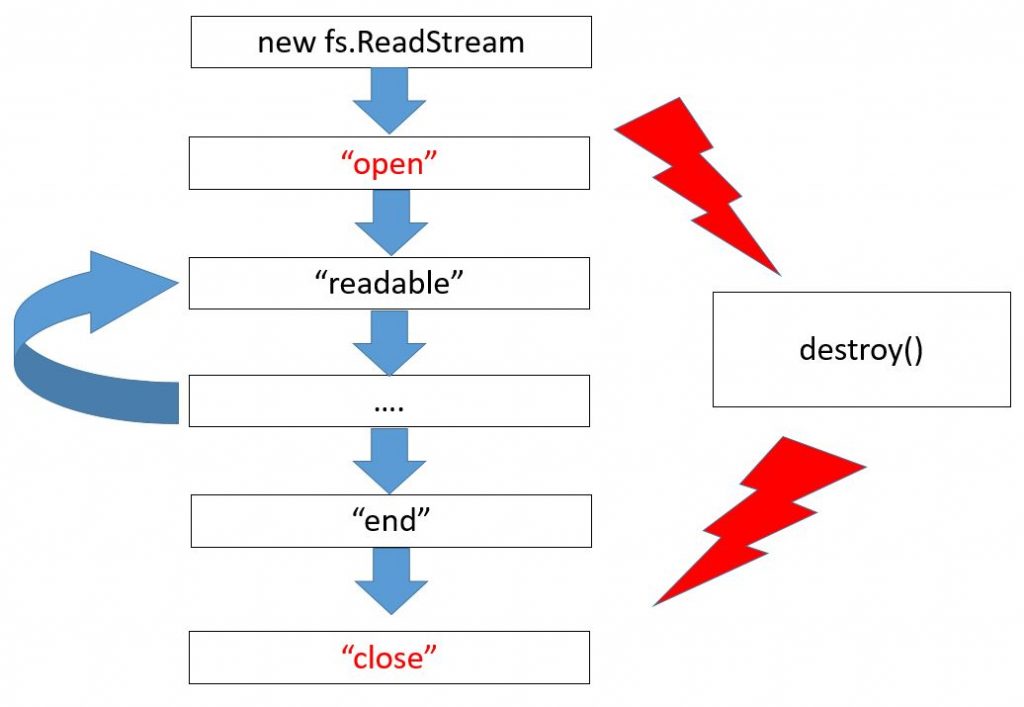
var stream = new OurStream("our resource");It won’t need any change of the left code because streams are, first of all, our interface. So, it means, if theoretically our stream performs all needed events and methods – in particular, it inherits from stream.Readable – everything should be ok. Of course, it will happen only if we do not use any special abilities that only file streams have got. To be more specific, the stream fs.ReadStream has extra events
Here we can see a draft exactly for fs.ReadStream, new events are colored in red. First, it is a file opening, while the last event is its closure. Focus your attention on the fact that if a file is read till its end, the end event occurs followed by close. And if a file is not entirely read – for instance, because of an error or upon calling the destroy method – there will be no end because the file hasn’t been ended. But the event close is always ensured upon a file closure.
Finally, our last, but not least detail here is error handling. So, let us see what will happen, if there is no file.
var stream = new fs.ReadStream("noFile.html");So, I get it launched. Oops! It crashed! Pay your attention to the fact the streams inherit from EventEmitter. If an error occurs, the whole Node.js process fails. It happens if an error of this kind does not have any handler. That’s why if we do not want our Node.js to fail because of an exception, we should install a handler:
var fs = require('fs');
// fs.ReadStream nherits from stream.Readable
var stream = new fs.ReadStream("noFile.html");
stream.on('readable', function() {
var data = stream.read();
if (data){
console.log(data.length);
}
else {
console.log('data is null')
}
});
stream.on('error', function(err) {
if (err.code == 'ENOENT') {
console.log("File not Found");
} else {
console.error(err);
}
});
So, we use streams to work with data sources in Node.js. Here we’ve analyzed a basic scheme, according to which they work, and a particular example – fs.ReadStream – that can read from a file.
This lesson’s coding can be found in our repository.
The article materials were borrowed from the following screencast.
We are looking forward to meeting you on our website blog.soshace.com